Abstract
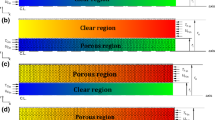
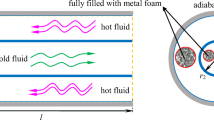
Turbulent flow and heat transfer in a counterflow double-tube heat exchanger partially filled with metal foam have been investigated numerically in the present study. The flow regime is considered to be turbulent in both the porous media and clear flow regions. Forchheimer-extended Darcy and local thermal equilibrium equations are utilized to simulate fluid flow and heat transfer inside porous layer. Also, a modified \(k-\varepsilon \) model is used to consider intra-pore level of turbulence within metal foam. Two different configurations of porous insert are considered in order to investigate the heat transfer enhancement and pressure drop, resulting from inserting porous media in double-tube heat exchangers. The effects of porous layer diameter, Darcy number and porous material thermal conductivity on the overall heat transfer coefficient of heat exchanger are investigated. The results exhibit the high amount of turbulent kinetic energy inside porous layer that supports the use of turbulence equations inside the porous region. Finally, a performance evaluation criterion is defined which enables one to establish the optimum porous media characteristics in double-tube heat exchangers in terms of thermal performance and pumping power.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alhusseny, A., Turan, A., Nasser, A.: Rotating metal foam structures for performance enhancement of double-pipe heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 105, 124–139 (2017)
Alkam, M., Al-Nimr, M.: Improving the performance of double-pipe heat exchangers by using porous substrates. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 42(19), 3609–3618 (1999)
Anderson, T.B., Jackson, R.: Fluid mechanical description of fluidized beds. Equations of motion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 6(4), 527–539 (1967)
Breugem, W., Boersma, B.: Direct numerical simulations of turbulent flow over a permeable wall using a direct and a continuum approach. Phys. Fluids 17(2), 025103 (2005)
Calmidi, V., Mahajan, R.: The effective thermal conductivity of high porosity fibrous metal foams. J. Heat Transf. 121(2), 466–471 (1999)
Cekmer, O., Mobedi, M., Ozerdem, B., Pop, I.: Fully developed forced convection in a parallel plate channel with a centered porous layer. Transp. Porous Media 93(1), 179–201 (2012)
Chan, H.-C., Huang, W., Leu, J.-M., Lai, C.-J.: Macroscopic modeling of turbulent flow over a porous medium. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 28(5), 1157–1166 (2007)
Chen, X., Tavakkoli, F., Vafai, K.: Analysis and characterization of metal foam-filled double-pipe heat exchangers. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 68(10), 1031–1049 (2015)
Dehghan, M.: Effects of heat generations on the thermal response of channels partially filled with non-Darcian porous materials. Transp. Porous Media 110(3), 461–482 (2015)
De Lemos, M.J.: Turbulence in Porous Media: Modeling and Applications. Elsevier, New York (2012)
Du, Y., Qu, Z., Zhao, C.-Y., Tao, W.: Numerical study of conjugated heat transfer in metal foam filled double-pipe. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53(21), 4899–4907 (2010)
Dybbs, A., Edwards, R.: A new look at porous media fluid mechanics—Darcy to turbulent. In: Bear, J., Corapcioglu M. Y., (eds.) Fundamentals of Transport Phenomena in Porous Media. NATO ASI Series. pp. 199–256. Martinus Nijhoff Publ, Dordrecht (1984)
Ferziger, J.H., Peric, M.: Computational Methods for Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Jouybari, N.F., Maerefat, M., Nimvari, M.E.: A macroscopic turbulence model for reacting flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 106(2), 355–381 (2015)
Kuznetsov, A.: Numerical modeling of turbulent flow in a composite porous/fluid duct utilizing a two-layer k-\(\varepsilon \) model to account for interface roughness. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 43(11), 1047–1056 (2004)
Lu, W., Zhao, C., Tassou, S.: Thermal analysis on metal-foam filled heat exchangers. Part I: metal-foam filled pipes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49(15), 2751–2761 (2006)
Mahdavi, M., Saffar-Avval, M., Tiari, S.: Entropy generation and heat transfer numerical analysis in pipes partially filled with porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 79, 496–506 (2014)
Mahmoudi, Y., Karimi, N.: Numerical investigation of heat transfer enhancement in a pipe partially filled with a porous material under local thermal non-equilibrium condition. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 68, 161–173 (2014)
Nakayama, A., Kuwahara, F.: A macroscopic turbulence model for flow in a porous medium. J. Fluids Eng. 121(2), 427–433 (1999)
Nimvari, M., Maerefat, M., El-Hossaini, M.: Numerical simulation of turbulent flow and heat transfer in a channel partially filled with a porous media. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 60, 131–141 (2012)
Nimvari, M.E., Jouybari, N.F.: Investigation of turbulence effects within porous layer on the thermal performance of a partially filled pipe. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 118, 374–385 (2017)
Patankar, S.: Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1980)
Qu, Z., Xu, H., Tao, W.: Fully developed forced convective heat transfer in an annulus partially filled with metallic foams: an analytical solution. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55(25), 7508–7519 (2012)
Russo, F., Basse, N.Y.: Scaling of turbulence intensity for low-speed flow in smooth pipes. Flow Meas. Instrum. 52, 101–114 (2016)
Saito, M.B., de Lemos, M.J.: A macroscopic two-energy equation model for turbulent flow and heat transfer in highly porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53(11), 2424–2433 (2010)
Shirvan, K.M., Ellahi, R., Mirzakhanlari, S., Mamourian, M.: Enhancement of heat transfer and heat exchanger effectiveness in a double pipe heat exchanger filled with porous media: numerical simulation and sensitivity analysis of turbulent fluid flow. Appl. Therm. Eng. 109, 761–774 (2016)
Shirvan, K.M., Mirzakhanlari, S., Kalogirou, S.A., Öztop, H.F., Mamourian, M.: Heat transfer and sensitivity analysis in a double pipe heat exchanger filled with porous medium. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 121, 124–137 (2017)
Silva, R.A., De Lemos, M.J.: Turbulent flow in a composite channel. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 38(8), 1019–1023 (2011)
Slattery, J.C.: Flow of viscoelastic fluids through porous media. AIChE J. 13(6), 1066–1071 (1967)
Targui, N., Kahalerras, H.: Analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer in a double pipe heat exchanger with porous structures. Energy Convers. Manag. 49(11), 3217–3229 (2008)
Targui, N., Kahalerras, H.: Analysis of a double pipe heat exchanger performance by use of porous baffles and pulsating flow. Energy Convers. Manag. 76, 43–54 (2013)
Teamah, M.A., El-Maghlany, W.M., Khairat Dawood, M.M.: Numerical simulation of laminar forced convection in horizontal pipe partially or completely filled with porous material. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 50(8), 1512–22 (2011)
Ucar, E., Mobedi, M., Pop, I.: Effect of an inserted porous layer located at a wall of a parallel plate channel on forced convection heat transfer. Transp. Porous Media 98(1), 35–57 (2013)
Vafai, K., Kim, S.-J.: Analysis of surface enhancement by a porous substrate. J. Heat Transf. 112(3), 700–706 (1990)
Wang, B., Hong, Y., Hou, X., Xu, Z., Wan, P., Fang, X., Ruan, X.: Numerical configuration design and investigation of heat transfer enhancement in pipes filled with gradient porous materials. Energy Convers. Manag. 105, 206–215 (2015)
Webb, R., Eckert, E.: Application of rough surfaces to heat exchanger design. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 15(9), 1647–1658 (1972)
Whitaker, S.: The equations of motion in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 21(3), 291–300 (1966)
Xu, H., Qu, Z., Tao, W.: Numerical investigation on self-coupling heat transfer in a counter-flow double-pipe heat exchanger filled with metallic foams. Appl. Therm. Eng. 66(1), 43–54 (2014)
Yucel, N., Guven, R.T.: Forced-convection cooling enhancement of heated elements in a parallel-plate channels using porous inserts. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 51(3), 293–312 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamarani, A., Maerefat, M., Jouybari, N.F. et al. Thermal Performance Evaluation of a Double-Tube Heat Exchanger Partially Filled with Porous Media Under Turbulent Flow Regime. Transp Porous Med 120, 449–471 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0933-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0933-x