Abstract
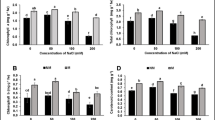
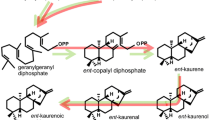
Gibberellins (GAs) play a pivotal role in the induction of somatic embryogenesis from in vitro root apices of spinach plants. With the aim to understand the role of GAs in this process and to improve somatic embryo (SE) regeneration efficiency, the impact of light and GAs on SE initiation from the in vitro root apices was studied. The root sections were isolated from in vitro-grown SE-derived plants and placed on medium containing 20 µM α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) and 0–10 µM GA3 or GA1, and cultivated under light conditions or in darkness. The most efficient SE regeneration response (100% regenerating SEs and 40.73 SEs per root apices) was achieved only in the presence of both light and GAs, with GA3 always exhibiting much stronger effect than GA1. Considering that light enhances GAs biosynthesis and the necessity of GAs for SE initiation, the expression levels of genes encoding the key enzymes involved in the final steps of GAs synthesis (SoGA20-ox1 and SoGA3-ox1) and deactivation (SoGA2-ox1, SoGA2-ox2 and SoGA2-ox3) were analyzed. Light enhanced the expression of all five GA-ox genes, while exogenously supplied NAA + GA3 provoked downregulation of SoGA20-ox1 and SoGA3-ox1 and upregulation of SoGA2ox-2 and SoGA2ox-3 expression. The expression of SoGA2ox-1 only slightly decreased. The results indicated the capability of isolated spinach roots to perceive the light and autonomously produce GAs. The expression levels of genes encoding key enzymes involved in GA biosynthesis suggest that lower levels of GAs favor SE initiation.
Key message
Light and gibberellins (GA) synergistically promote somatic embryogenesis in spinach. Expression levels of genes encoding key enzymes for GA metabolism suggest that lower levels of GAs may favor somatic embryogenesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ait-Ali T, Frances S, Weller JL, Reid JB, Kendrick RE, Kamiya Y (1999) Regulation of gibberellin 20-oxidase and gibberellin 3β-hydroxylase transcript accumulation during de-etiolation of pea seedlings. Plant Physiol 121:783–791
Al-Khayri JM, Huang FH, Morelock TE, Busharar TA, Gbur EE (1991) Genotype-dependent response of spinach cultivars to in vitro callus induction and plant regeneration. Plant Sci 78:121–126
Atta R, Laurens L, Boucheron-Dubuisson E, Guivarc’h A, Carnero E, Giraudat-Pautot V, Rech P, Chriqui D (2009) Pluripotency of Arabidopsis xylem pericycle underlies shoot regeneration from root and hypocotyl explants grown in vitro. Plant J 57:626–644
Binenbaum J, Weinstain R, Shani E (2018) Gibberellin localization and transport in plants. Trends Plant Sci 23:410–421
Blazquez S, Olmos E, Hernández JA, Fernández-García N, Fernández JA, Piqueras A (2009) Somatic embryogenesis in saffron (Crocus sativus L.). Histological differentiation and implication of some components of the antioxidant enzymatic system. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 97:49–57
Cabrera-Ponce JL, López L, León-Ramírez CG, Jofre-Garfias AE, Verver-y-Vargas A (2015) Stress induced acquisition of somatic embryogenesis in common bean Phaseolus vulgaris L. Protoplasma 252:559–570
Chen JT, Chang WC (2003) Effects of GA, ancymidol, cycocel and paclobutrazol on direct somatic embryogenesis of Oncidium in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 72:105–108
Chiappetta A, Fambrini M, Petrarulo M, Rapparini F, Michelotti V, Bruno L, Greco M, Baraldi R, Salvini M, Pugliesi C, Bitonti MB (2009) Ectopic expression of LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LIKE gene and localized auxin accumulation mark embryogenic competence in epiphyllous plants of Helianthus annuus × H. tuberosus.. Ann Bot 103:735–747
Ćulafić LJ, Budimir S, Vujičić R, Nešković M (1987) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and embryo development in Rumex acetosella L. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 11:133–139
Economou AS, Read PE (1987) Light treatments to improve efficiency of in vitro propagation systems. Hortic Sci 22:751–754
Fehér A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 74:201–228
Frigerio M, Alabadí D, Pérez-Gómez J, García-Cárcel L, Phillips AL, Hedden P, Blázquez MA (2006) Transcriptional regulation of gibberellin metabolism genes by auxin signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 142:553–563
Galen C, Rabenold JJ, Liscum E (2007) Light-sensing in roots. Plant Signal Behav 2:106–108
Gašić K, Hernandez A, Korban S (2004) RNA extraction from different apple tissues rich in polyphenols and polysaccharides for cDNA library construction. Plant Mol Biol Rep 22:437–438
Geekiyanage S, Takase T, Watanabe S, Fukai S, Kiyouse T (2006) The combined effect of photoperiod, light intensity and GA3 on adventitious shoot regeneration from cotyledons of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Biotechnol 23:431–435
Graebe JE (1987) Gibberellin biosynthesis and control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 38:419–465
Hedden P, Phillips AL (2000) Gibberellin metabolism: new insights revealed by the genes. Trends Plant Sci 5:523–530
Hisamatsu T, King RW, Helliwell CA, Koshioka M (2005) The involvement of gibberellin 20-oxidase genes in phytochrome regulated petiole elongation of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138:1106–1116
Hunault G, Maatar A (1995) Enhancement of somatic embryogenesis frequency by gibberellic acid in fennel. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 41:171–176
Igielski R, Kępczyńska E (2017) Gene expression and matabolite profiling of gibberellin biosynthesis during induction of somatic embryogenesis in Medicago truncatula Gaertn. PLoS ONE 12:e0182055. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0182055
Ishizaki T, Komai F, Masuda K (2001) Screening for strongly regenerative genotypes of spinach in tissue culture using subcultured root explants. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 67:251–255
Israelsson M, Mellerowcz E, Chon M, Gullberg J, Moritz T (2004) Cloning and overproduction of gibberellin 3-oxidase in hybrid aspen trees. Effect on gibberellin homeostasis and development. Plant Physiol 135:221–230
Jackson SD, James PE, Carrera E, Prat S, Thomas B (2000) Regulation of transcript levels of a potato gibberellin 20-oxidase gene by light and phytochrome B. Plant Physiol 124:423–430
Jani JN, Jha SK, Nagar DS (2015) Root explant produces multiple shoot from pericycle in Psoralea corylifolia—a leprosy destroyer medicinal plant. Ind Crops Prod 67:324–329
Joseph JA, Shukitt-Hale B, Denisova NA, Bielinski D, Martin A, McEwen JJ, Bickford PC (1999) Reversals of age-related declines in neuronal signal transduction, cognitive, and motor behavioral deficits with blueberry, spinach, or strawberry dietary supplementation. J Neurosci 19:8114–8121
Kanwar K, Joseph J, Deepika R (2010) Comparison of in vitro regeneration pathways in Punica granatum L. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 100:199–207
Kawade K, Masuda K (2009) Transcriptional control of two ribosome – inactivating protein genes expressed in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) embryos. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:327–334
Kim DH, Lee B, Kim MJ, Park MH, An HJ, Lee EK, Chung KW, Park JW, Yu BP, Choi JS, Chung HY (2016) Molecular mechanism of betaine on hepatic lipid metabolism: inhibition of forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) binding to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). J Agric Food Chem 64:6819–6825
Knoll KA, Short KC, Curtis IS, Power JB, Davey JB (1997) Shoot regeneration from cultured root explants of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.): a system for Agrobacterium transformation. Plant Cell Rep 17:96–101
Komai F, Okwe I, Harada T (1996a) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in culture of root segments of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Sci 113:203–208
Komai F, Okuse I, Harada T (1996b) Effective combinations of plant growth regulators for somatic embryogenesis from spinach root segments. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 65:559–564
Kononowicz H, Janick J (1984) Response of embryogenic callus of Theobroma cacao L. to gibberellic acid and inhibitors of gibberellic acid synthesis. Z Pflanzenphysiol 113:359–366
Kurczyńska EU, Gaj MD, Ujczak A, Mazur E (2007) Histological analysis of direct somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 226:619–628
Lee DJ, Zeevaart JAD (2002) Differential regulation of RNA levels of gibberellin dioxygenases by photoperiod in spinach. Plant Physiol 130:2085–2094
Lee DJ, Zeevaart JAD (2005) Molecular cloning of GA 2-oxidase3 from spinach and its ectopic expression in Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Physiol 138:243–254
Lee DJ, Zeevaart JAD (2007) Regulation of gibberellin 20-oxidase1 expression in spinach by photoperiod. Planta 226:35–44
Li G, Zhu C, Gan L, Ng D, Xia K (2015) GA3 enhances root responsiveness to exogenous IAA by modulating auxin transport and signalling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 34:483–494
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the ∆∆Ct method. Methods 25:402–408
Lomnitski L, Bergman M, Nyska A, Ben-Shaul V, Grossman S (2003) Composition, efficacy, and safety of spinach extracts. Nutr Cancer 46:222–231
MacMillan J (2001) Occurence of gibberellins in vascular plants, fungi and bacteria. J Plant Growth Regul 20:387–442
Maheswaran G, Williams EG (1985) Origin and development of somatic embryoids formed directly on immature embryos of Trifoliumrepens in vitro. Ann Bot 56:619–630
Mc Manus JFA, Mowry RW (1960) Staining methods. In: Hoeber PB (ed) Histology and histochemistry. Harper and Row, New York, pp 275–276
Méndez-Hernández HA, Ledezma-Rodríguez M, Avilez-Montalvo RN, Juárez-Gómez YL, Skeete A, Avilez-Montalvo J, De-la-Peña C, Loyola-Vargas VM (2019) Signaling overview of plant somatic embryogenesis. Front Plant Sci 10:77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00077
Milić M, Savić J, Tubić LJ, Devrnja N, Ćalić D, Zdravković-Korać S, Milojević J (2017) Expression of the gene for ribosome-inactivating protein, SoRIP2, as a tool for the evaluation of somatic embryogenesis in spinach. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 129:483–491
Milojević J, Tubić Lj, Zdravković-Korać S, Dragićević I, Ćalić-Dragosavac D, Vinterhalter B (2011) Increased regeneration capacity in spinach lines obtained by in vitro self-fertilisation. Sci Hortic 130:681–690
Milojević J, Tubić L, Pavlović S, Mitić N, Ćalić D, Vinterhalter B, Zdravković-Korać S (2012) Long days promote somatic embryogenesis in spinach. Sci Hortic 142:32–37
Mitsuhashi W, Toyomasu T, Masui H, Katho T, Nakaminami K, Kashiwagi Y, Akutsu M, Kenmoku H, Sassa T, Yamaguchi S, Kamiya Y, Kamada H (2003) Gibberellin is essentially required for carrot (Daucus carota L.) somatic embryogenesis: dynamic regulation of gibberellin 3-oxidase gene expressions. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:2438–2447
Mo M, Yokawa K, Wan Y, Baluška F (2015) How and why do root apices sense light under the soil surface? Front Plant Sci 6:775. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00775
Muktadir MA, Habib MA, Milan MAK, Akhond MAY (2016) Regeneration efficiency based on genotype, culture condition and growth regulators of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Agric Nat Resour 50:38–42
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nameth B, Dinka SJ, Chatfield SP, Morris A, English J, Lewis D, Oro R, Raizada MN (2013) The shoot regeneration capacity of excised Arabidopsis cotyledons is established during the initial hours after injury and is modulated by a complex genetic network of light signalling. Plant Cell Environ 36:68–86
Nguyen QV, Sun HJ, Boo KH, Lee D, Lee JH, Lim PO, Lee HY, Riu KZ, Lee DS (2013) Effect of plant growth regulator combination and culture period on in vitro regeneration of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Biotechnol Rep 7:99–108
Paparelli E, Parlanti S, Gonzali S, Novi G, Mariotti L, Ceccarelli N, van Dongen JT, Kölling K, Zeeman SC, Perata P (2013) Nighttime sugar starvation orchestrates gibberellin biosynthesis and plant growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:3760–3769
Polito VS, McGranahan G, Pinney K, Leslie C (1989) Origin of somatic embryos from repetitively embryogenic cultures of walnut (Juglans regia L.): implications for Agrobacterium mediated transformation. Plant Cell Rep 8:219–221
Radi A, Lange T, Niki T, Koshioka M, Pimenta Lange MJ (2006) Ectopic expression of pumpkin gibberellin oxidases alters gibberellin biosynthesis and development of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant Physiol 140:528–536
Reuveni M, Evenor D (2007) On the effect of light on shoot regeneration in petunia. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 89:49–54
Rieu I, Ruiz-Rivero O, Fernandez-Garcia N, Griffiths J, Powers SJ, Gong F, Linhartova T, Eriksson S, Nilsson O, Thomas SG, Phillips AL, Hedden P (2008) The gibberellin biosynthetic genes AtGA20ox1 and AtGA20ox2 act, partially redundantly, to promote growth and development throughout the Arabidopsis life cycle. Plant J 53:488–504
Roberts JL, Moreau R (2016) Functional properties of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) phytochemicals and bioactives. Food Funct 7:3337–3353
Rocha DI, Vieira LM, Tanaka FAO, da Silva LC, Oton WC (2012) Anatomical and ultrastructural analyses of in vitro organogenesis from root explants of commercial passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims). Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 111:69–78
Rudus I, Kępczyńska E, Kępczyński J (2002) Regulation of Medicago sativa L. somatic embryogenesis by gibberellins. Plant Growth Regul 36:91–95
Sakai WS (1973) Simple method for differential staining of paraffin embedded plant material using toluidine blue. Stain Technol 48:247–249
Salisbury FJ, Hall A, Grierson CS, Halliday KJ (2007) Phytochrome coordinates Arabidopsis shoot and root development. Plant J 50:429–438
Silva ALL, Rodriguez C, Costa JL, Machado MP, Penha RO, Buasi LA, Vanderberghe LPS, Soccol CR (2013) Gibberellic acid fermented extract obtained by solid-state fermentation using citric pulp by Fusarium moniliforme: influence on Lavandula anguistifolia Mill. cultivated in vitro. Pak J Bot 45:2057–2064
Shohag MJI, Wei YY, Yu N, Zhang J, Wang K, Patring J, He Z, Yang X (2011) Natural variation of folate content and composition in spinach (Spinacia oleracea) germplasm. J Agric Food Chem 59:12520–12526
Subotić A, Jevremović S, Trifunović M, Petrić M, Milošević S, Grubišić D (2009) The influence of gibberellic acid and paclobutrazol on induction of somatic embryogenesis in wild type and hairy root cultures of Centaurium erythraea Gillib. Afr J Biotechnol 8:3223–3228
Tal I, Zhang Y, Jørgensen ME, Pisanty O, Barbosa ICR, Zourelidou M, Regnault T, Crocoll C, Olsen CE, Weinstain R, Schwechheimer C, Halkier BA, Nour-Eldin HH, Estelle M, Shani E (2016) The Arabidopsis NPF3 is a GA transporter. Nat Commun 7:11486. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11486
Talla ST, Madam E, Manga S, Aileni M, Mamidala P (2018) Efficient TDZ-induced regeneration from capitulum explants of Gerbera jamesonii Bolus ex Hooker F.—an ornamental plant with high aesthetic value. Plant Biosyst 153:679–685
Talon M, Zeevaart JAD, Gage DA (1991) Identification of gibberellins in spinach and effects of light and darkness on their levels. Plant Physiol 97:1521–1526
Thomas TD (2006) Effect of sugars, gibberellic acid and abscisic acid on somatic embryogenesis in Tylophora indica (Burm. f.) Merrill. Chin J Biotechnol 22:465–471
Verdeil JL, Alemanno L, Niemenak N, Trambarger TJ (2007) Pluripotent versus totipotent plant stem cells: dependence versus autonomy? Trends Plant Sci 12:245–252
Wang H, Caruso LV, Downie AB, Perry SE (2004) The embryo MADS domain protein AGAMOUS-Like 15 directly regulates expression of a gene encoding an enzyme involved in gibberellin metabolism. Plant Cell 16:1206–1219
Weston DE, Reid JB, Ross JJ (2009) Auxin regulation of gibberellin biosynthesis in the roots of pea (Pisum sativum). Funct Plant Biol 36:362–369
Wu K, Li L, Gage DA, Zeevaart JAD (1996) Molecular cloning and photoperiod-regulated expression of gibberellin 20-oxidase from the long-day plant spinach. Plant Physiol 110:547–554
Yamaguchi S, Kamiya Y (2000) Gibberellin biosynthesis: its regulation by endogenous and environmental signals. Plant Cell Physiol 3:251–257
Yang JL, Seong ES, Kim MJ, Ghimire BK, Kang WH, Yu CY, Li CH (2010) Direct somatic embryogenesis from pericycle cells of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) root explants. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 100:49–58
Ye J, Coulouris G, Zaretskaya I, Cutcutache I, Rozen S, Madden T (2012) Primer–BLAST: a tool to design target-specific primers for polymerase chain reaction. BMC Bioinform 13:134–145
Yumbla-Orbes M, Ferreira da Cruz AC, Marques Pinheiro MV, Rocha DI, Batista DS, Koehler AD, Barbosa JG, Otoni WC (2017) Somatic embryogenesis and de novo shoot organogenesis can be altenatively induced by reactivating pericycle cells in Lisianthus (Eustoma grandifolium (Raf.) Shinners) root explants. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 53:209–218
Zeevaart JAD, Gage DA, Talon M (1993) Gibberellin A1 is required for stem elongation in spinach. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7401–7405
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia through contract No. 173015 and a grant given to Maja Belić (former Milić, Grant No. 451-03-1629/2017/2138). The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr R.P. Pharis for kind gift of GA1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JM and SZK designed the research. MB, ST, NB and JM conducted tissue culture experiments. MB and DJ conducted histological study, and MB, JS and JM performed RTqPCR analysis. MB and JM analyzed data. JM, SZK, DJ and MB wrote the manuscript and JS, ST and NB contributed to editing. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Sergey V. Dolgov.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belić, M., Zdravković-Korać, S., Janošević, D. et al. Gibberellins and light synergistically promote somatic embryogenesis from the in vitro apical root sections of spinach. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 142, 537–548 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01878-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01878-3