Abstract
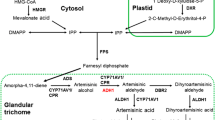
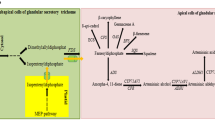
Artemisinin is a frequently used anti-malaria drug extracted from glandular trichomes (GSTs) in Artemisia annua L. In this study, we report on the characterization of the promoter of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) involved in the biosynthesis of artemisinin. A 1620-bp promoter fragment was cloned upstream of the ALDH1 start codon. Putative regulatory cis-acting elements are predicted by software, revealing that this gene is affected by complex factors. The activity of the ALDH1 promoter was analyzed using a reporter gene GUS. GUS expression showed a spatial difference in leaves at different ages. In young leaves, GUS staining was exclusively discovered in GSTs. In older leaves, both GSTs and T-shaped trichomes (TSTs) showed GUS signals. Only TSTs showed GUS staining in lower leaves. No GUS staining was detected in the bottom leaves. The result demonstrates that the ALDH1 promoter is trichome-specific. The RT-Q-PCR analysis revealed that both wild-type and recombinant promoters showed similar activity in A. annua. After application of exogenous 100 μM methyl jasmonate, 100 μM gibberellin and 100 μM salicylic acid separately, the transcript levels were increased significantly, indicating that ALDH1 may play an important role in the response to hormones in A. annua.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsenault PR, Vail D, Wobbe KK, Erickson K, Weathers PJ (2010) Reproductive development modulates gene expression and metabolite levels with possible feedback inhibition of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. Plant Physiol 154:958–968
Bakhsh A, Rao QA, Shamim Z, Husnain T (2011) Rubisco small subunit as a strong, green tissue-specific promoter. Arch Biol Sci 63:299–307
Banyai W, Mii M, Supaibulwatana K (2011) Enhancement of artemisinin content and biomass in Artemisia annua by exogenous GA3 treatment. Plant Growth Regul 63:45–54
Bouwmeester HJ, Wallaart TE, Janssen MH et al (1999) Amorpha-4,11-diene synthase catalyses the first probable step in artemisinin biosynthesis. Phytochem 52:843–854
Brown GD, Sy LK (2004) In vivo transformations of dihydroartemisinic acid in Artemisia annua plants. Tetrahedron 60:1139–1159
Brown GD, Sy LK (2007) In vivo transformations of artemisinic acid in Artemisia annua plants. Tetrahedron 63:9548–9566
Brown GD, Liang GY, Sy LK (2003) Terpenoids from the seeds of Artemisia annua. Phytochem 64:303–323
Caretto S, Quarta A, Durante M, Nisi R, De Paolis A, Blando F, Mita G (2011) Methyl jasmonate and miconazole differently affect arteminisin production and gene expression in Artemisia annua suspension cultures. Plant Biol 13:51–58
Ferreira JFS, Janick J (1996) Distribution of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. In: Janick J (ed) Progress in new crops. ASHS, Arlington, pp 579–584
Fütterer J, Gisel A, Iglesias V, Klöti A, Kost B, Mittelsten Scheid O, Neuhaus G, Neuhaus-Url G, Schrott M, Shillito R, Spangenberg G, Wang ZY (1995) Standard molecular techniques for the analysis of transgenic plants. In: Potrykus I, Spangenberg G (eds) Gene transfer to plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 215–263
Guo XX, Yang XQ, Yang RY, Zeng QP (2010) Salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate but not Rose Bengal enhance artemisinin production through invoking burst of endogenous singlet oxygen. Plant Sci 178:390–397
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusion: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plant. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Jiang WM, Lu X, Qiu B, Zhang FY, Shen QY, Lv ZY, Fu XQ, Yan TX, Gao ED, Zhu MM, Chen LX, Zhang L, Wang GF, Sun XF, Tang KX (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of a trichome-specific promoter of artemisinic aldehyde △11(13) reductase (DBR2) in Artemisia annua. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:82–91
Kapoor R, Chaudhary V, Bhatnagar AK (2007) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza and phosphorus application on artemisinin concentration in Artemisia annua L. Mycorrhiza 17:581–587
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-DDCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Lommen WJM, Schenk E, Bouwmeester HJ, Verstappen FWA (2006) Trichome dynamics and artemisinin accumulation during development and senescence of Artemisia annua leaves. Planta Med 72:336–345
Lu X, Shen Q, Zhang L, Zhang FY, Jiang WM, Lv ZY, Yan TX, Fu XQ, Wang GF, Tang KX (2013) Promotion of artemisinin biosynthesis in transgenic Artemisia annua by overexpressing ADS, CYP71AV1 and CPR genes. Ind Crop Prod 49:380–385
McCormick S, Niedermeyer J, Fry J, Barnason A, Horsch R, Fraley R (1986) Leaf disc transformation of cultivated tomato (L. esculentum) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Rep 5(2):81–84
Mercke P, Bengtsson M, Bouwmeester HJ, Posthumus MA, Brodelius PE (2000) Molecular cloning, expression, and characterization of amorpha-4,11-diene synthase a key enzyme of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Arch Biochem Biophys 381:173–180
Miller JN, Miller JC (2010) Statistics and chemometrics for analytical chemistry, 6th edn. Prentice Hall, England
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nguyen KT, Arsenault PR, Weathers PJ (2011) Trichomes plus roots plus ROS=artemisinin: regulating artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol-Plant 47:329–338
Olsson ME, Olofsson LM, Lindahl A-L, Lundgren A, Brodelius M, Brodelius PE (2009) Localization of enzymes of artemisinin biosynthesis to the apical cells of glandular secretory trichomes of Artemisia annua L. Phytochemistry 70:1123–1128
Pu GB, Ma DM, Chen JL, Ma LQ, Wang H, Li GF, Ye HC, Liu BY (2009) Salicylic acid activates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Rep 28(7):1127–1135
Ro DK, Paradise EM, Ouellet M, Fisher KJ, Newman KL, Ndungu JM, Ho KA, Eachus RA, Ham TS, Kirby J, Chang MC, Withers ST, Shiba Y, Sarpong R, Keasling JD (2006) Production of the antimalarial drug precursor artemisinic acid in engineered yeast. Nature 440:940–943
Soetaert SS, Van Neste CM, Vandewoestyne ML, Head SR, Goossens A, Van Nieuwerburgh FC, Deforce DL (2013) Differential transcriptome analysis of glandular and filamentous trichomes in Artemisia annua. BMC Plant Biol 13(1):220
Sy LK, Brown GD (2002) The mechanism of the spontaneous autoxidation of dihydroartemisinic acid. Tetrahedron 58:897–908
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Nowak G, Covello PS (2006) Artemisia annua L. (Asteraceae) trichome-specific cDNAs reveal CYP71AV1 a cytochrome P450 with a key role in the biosynthesis of the antimalarial sesquiterpene lactone artemisinin. FEBS Lett 580:1411–1416
Teoh KH, Polichuk DR, Reed DW, Covello PS (2009) Molecular cloning of an aldehyde dehydrogenase implicated in artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua. Botany 87:635–642
Waleerat B, Chalermpol K, Masahiro M, Kanyaratt S (2010) Overexpress of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPS) gene affected artemisinin content and growth of Artemisia annua L. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 103:255–265
Wang H, Olofsson F, Lundgren A, Brodelius PE (2011) Trichome-specific expression of amorpha-4,11-diene synthase, a key enzyme of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L., as reported by a promoter-GUS fusion. Am J Plant Sci 2:619–628
Wang H, Han J, Kanagarajan S, Lundgren A, Brodelius PE (2013) Trichome-specific expression of the amorpha-4,11-diene 12-hydroxylase (cyp71av1) gene, encoding a key enzyme of artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua, as reported by a promoter-GUS fusion. Plant Mol Biol 81(1–2):119–138
World Health Organization (2015) World malaria report 2014. WHO, Geneva
Zhang YS, Teoh KH, Reed DW, Maes L, Goossens A, Olson DJ, Ross AR, Covello PS (2008) The molecular cloning of artemisinic aldehyde 11(13) reductase and its role in glandular trichome-dependent biosynthesis of artemisinin in Artemisia annua. J Biol Chem 283:21501–21508
Zhu M, Zhang F, Lv Z, Shen Q, Zhang L, Lu X, Jiang WM, Fu XQ, Yang TX, Chen LX, Wang GF, Tang KX (2014) Characterization of the promoter of Artemisia annua amorpha-4,11-diene synthase (ADS) gene using homologous and heterologous expression as well as deletion analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:406–418
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the China National High-Tech “863” Program (Grant No. 2011AA100605), the Shanghai Key Discipline Cultivation and Construction Project (Horticulture), and the Shanghai Jiao Tong University Agri-Engineering Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, M., Shi, P., Fu, X. et al. Characterization of a trichome-specific promoter of the aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) gene in Artemisia annua . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 126, 469–480 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1015-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-016-1015-4