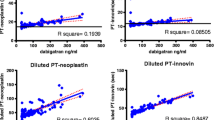
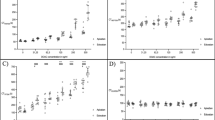
Abstract
Rapidly available tests might be useful to measure the anticoagulant effect of direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) in emergency situations as bleedings, surgery, or before thrombolysis. The aim of this study was to assess the effects of DOAs on global thromboelastometry (ROTEM). Coagulation parameters assessed at peak and trough in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation receiving apixaban, dabigatran or rivaroxaban at steady-state (patients) were compared to those of healthy volunteers (controls). Citrated blood samples were tested by ROTEM using diluted EXTEM assay, with and without the addition of an anti-FXa catcher, and using ECATEM-B, with and without the addition of an anti-FIIa catcher. Overall 30 patients (10 for each DOA) and 15 controls were included. The mean clotting time (CT) of patients at peak and trough were significantly higher compared to controls. The mean CT was significantly shortened after the addition of the anti-FXa catcher to apixaban (p = 0.005 for peak and p = 0.009 for trough) and to rivaroxaban samples (p = 0.005 for both peak and trough) and after the addition of anti-FIIa cather to dabigatran samples (p = 0.005 for both peak and trough). ROC curve analyses showed a good accuracy for CT and for CT/CT + catcher (CTc) in measuring dabigatran anticoagulant activity (AUC 1.000 and 0.993, respectively); for CT, CT/CTc and clot formation time (CFT)/CFT + catcher (CFTc) in measuring both apixaban activity (0.917, 0.880 and 0.880, respectively) and rivaroxaban activity (0.973, 0.987 and 0.860, respectively). In this study the use of ad-hoc designed reagents and catcher molecules was able to accurately identify DOAs activity at ROTEM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkman HJ (2015) Global assays and the management of oral anticoagulation. Thromb J 10(13):9
Brown KS, Zahir H, Grosso MA, Lanz HJ, Mercuri MF, Levy JH (2016) Nonvitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant activity: challenges in measurement and reversal. Crit Care 20:273
Steffel J, Verhamme P, Potpara TS, Albaladejo P, Antz M, Desteghe L, Haeusler KG, Oldgren J, Reinecke H, Roldan-Schilling V, Rowell N, Sinnaeve P, Collins R, Camm AJ, Heidbüchel H, ESC Scientific Document Group (2018) The 2018 European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 39:1330–1393
Barrett YC, Wang Z, Frost C, Shenker A (2010) Clinical laboratory measurement of direct factor Xa inhibitors: anti-Xa assay is preferable to prothrombin time assay. Thromb Haemost 104:1263–1271
Douxfils J, Mullier F, Loosen C, Chatelain C, Chatelain B, Dogne JM (2012) Assessment of the impact of rivaroxaban on coagulation assays: laboratory recommendations for the monitoring of rivaroxaban and review of the literature. Thromb Res 130:956–966
Morishima Y, Kamisato C (2015) Laboratory measurements of the oral direct factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban: comparison of prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, and thrombin generation assay. Am J Clin Pathol 143:241–247
Hillarp A, Baghaei F, Fagerberg Blixter I, Gustafsson KM, Stigendal L, Sten-Linder M et al (2011) Effects of the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban on commonly used coagulation assays. J Thromb Haemost 9:133–139
Douxfils J, Chatelain C, Chatelain B, Dogne JM, Mullier F (2013) Impact of apixaban on routine and specific coagulation assays: a practical laboratory guide. Thromb Haemost 110:283–294
Douxfils J, Chatelain B, Chatelain C, Dogne JM, Mullier F (2016) Edoxaban: impact on routine and specific coagulation assays. A practical laboratory guide. Thromb Haemost 115:368–381
Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Morrow DA, Murphy SA, Kuder JF et al (2015) Association between edoxaban dose, concentration, anti-Factor Xa activity, and outcomes: an analysis of data from the randomised, double-blind ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 trial. Lancet 385:2288–2295
Samama MM, Contant G, Spiro TE, Perzborn E, Guinet C, Gourmelin Y et al (2012) Rivaroxaban Anti-Factor Xa Chromogenic Assay Field Trial Laboratories: evaluation of the anti-factor Xa chromogenic assay for the measurement of rivaroxaban plasma concentrations using calibrators and controls. Thromb Haemost 107:379–387
Asmis LM, Alberio L, Angelillo-Scherrer A, Korte W, Mendez A, Reber G et al (2012) Rivaroxaban: quantification by anti-FXa assay and influence on coagulation tests: a study in 9 Swiss laboratories. Thromb Res 129(4):492–498
Gouin-Thibault I, Flaujac C, Delavenne X, Quenet S, Horellou MH, Laporte S et al (2014) Assessment of apixaban plasma levels by laboratory tests: suitability of three anti-Xa assays. A multicentre French GEHT study. Thromb Haemost 111:240–248
Lippi G, Ardissino D, Quintavalla R, Cervellin G (2014) Urgent monitoring of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation: a tentative approach based on routine laboratory tests. J Thromb Thrombolysis 38:269–274
Spalding GJ, Hartrumpf M, Sierig T, Oesberg N, Kirschke CG, Albes JM (2007) Cost reduction of perioperative coagulation management in cardiac surgery: value of “bedside” thrombelastography (ROTEM). Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 31:1052–1057
Schöchl H, Nienaber U, Hofer G, Voelckel W, Jambor C, Scharbert G et al (2010) Goal-directed coagulation management of major trauma patients using thromboelastometry (ROTEM)-guided administration of fibrinogen concentrate and prothrombin complex concentrate. Crit Care 14(2):R55
Sølbeck S, Meyer MA, Johansson PI, Meyer AS, Cotton BA, Stensballe J et al (2014) Monitoring of dabigatran anticoagulation and its reversal in vitro by thrombelastography. Int J Cardiol 176:794–799
Sølbeck S, Nilsson CU, Engström M, Ostrowski SR, Johansson PI (2014) Dabigatran and its reversal with recombinant factor VIIa and prothrombin complex concentrate: a Sonoclot in vitro study. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 74(7):591–598
Bowry R, Fraser S, Archeval-Lao JM, Parker SA, Cai C, Rahbar MH, Grotta JC (2014) Thrombelastography detects the anticoagulant effect of rivaroxaban in patients with stroke. Stroke 45:880–883
Casutt M, Konrad C, Schuepfer G (2012) Effect of rivaroxaban on blood coagulation using the viscoelastic coagulation test ROTEM™. Anaesthesist 61:948–953
Mahamad S, Chaudhry H, Nisenbaum R, McFarlan A, Rizoli S, Ackery A, Sholzberg M (2019) Exploring the effect of factor Xa inhibitors on rotational thromboelastometry: a case series of bleeding patients. J Thromb Thrombolysis 47:272–279
Kubitza D, Becka M, Wensing G, Voith B, Zuehlsdorf M (2005) Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—after multiple dosing in healthy male subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 61:873–880
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H, Gansser D, Roth W (2007) The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of dabigatran etexilate, a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, in healthy male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64:292–303
Frost C, Nepal S, Wang J, Schuster A, Byon W, Boyd RA et al (2013) Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of multiple oral doses of apixaban, a factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 76:776–786
Lippi G, Favaloro EJ (2015) Recent guidelines and recommendations for laboratory assessment of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): is there consensus? Clin Chem Lab Med 53:185–197
Favaloro EJ, Lippi G (2015) Laboratory testing in the era of direct or non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants: a practical guide to measuring their activity and avoiding diagnostic errors. Semin Thromb Hemost 41:208–227
Heidbuchel H, Verhamme P, Alings M, Antz M, Diener HC, Hacke W et al (2015) Updated European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of non-vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Europace 17:1467–1507
Pernod G, Albaladejo P, Godier A, Samama CM, Susen S, Gruel Y et al (2013) Working Group on Perioperative Haemostasis. Management of major bleeding complications and emergency surgery in patients on long-term treatment with direct oral anticoagulants, thrombin or factor-Xa inhibitors: proposals of the working group on perioperative haemostasis (GIHP)—March 2013. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 106:382–393
Iapichino GE, Bianchi P, Ranucci M, Baryshnikova E (2017) Point-of-care coagulation tests monitoring of direct oral anticoagulants and their reversal therapy: state of the art. Semin Thromb Hemost 43:423–432
Dias JD, Norem K, Doorneweerd DD, Thurer RL, Popovsky MA, Omert LA (2015) Use of thromboelastography (TEG) for detection of new oral anticoagulants. Arch Pathol Lab Med 139:665–673
Seyve L, Richarme C, Polack B, Marlu R (2018) Impact of four direct oral anticoagulants on rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM). Int J Lab Hematol 40:84–93
Honickel M, Maron B, van Ryn J, Braunschweig T, ten Cate H, Spronk HM et al (2016) Therapy with activated prothrombin complex concentrate is effective in reducing dabigatran-associated blood loss in a porcine polytrauma model. Thromb Haemost 115:271–284
Oswald E, Velik-Salchner C, Innerhofer P et al (2015) Results of rotational thromboelastometry, coagulation activation markers and thrombin generation assays in orthopedic patients during thromboprophylaxis with rivaroxaban and enoxaparin: a prospective cohort study. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 26:136–144
Crapelli GB, Bianchi P, Isgrò G, Biondi A, De Vincentiis C, Ranucci M (2016) A case of fatal bleeding following emergency surgery of an ascending aorta intramural hematoma in a patient under dabigatran treatment. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 4:1027–1031
Herrmann R, Thom J, Wood A, Phillips M, Muhammad S, Baker R (2014) Thrombin generation using the calibrated automated thrombinoscope to assess reversibility of dabigatran and rivaroxaban. Thromb Haemost 111:989–995
Henskens YMC, Gulpen AJW, van Oerle R, Wetzels R, Verhezen P, Spronk H et al (2018) Detecting clinically relevant rivaroxaban or dabigatran levels by routine coagulation tests or thromboelastography in a cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb J 16:3
Bliden KP, Chaudhary R, Mohammed N, Muresan AA, Lopez-Espina CG, Cohen E, Raviv G, Doubleday M, Zaman F, Mathew B, Tantry US, Gurbel PA (2017) Determination of non-Vitamin K oral anticoagulant (NOAC) effects using a new-generation thrombelastography TEG 6s system. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43:437–445
Samuelson BT, Cuker A, Siegal DM, Crowther M, Garcia DA (2017) Laboratory assessment of the anticoagulant activity of direct oral anticoagulants: a systematic review. Chest 151:127–138
Ruiz Ortiz M, Muñiz J, Raña Míguez P, Roldán I, Marín F, Asunción Esteve-Pastor M, Cequier A, Martínez-Sellés M, Bertomeu V, Anguita M, FANTASIIA Study Investigators (2018) Inappropriate doses of direct oral anticoagulants in real-world clinical practice: prevalence and associated factors. A subanalysis of the FANTASIIA Registry. Europace 20:1577–1583
Howard M, Lipshutz A, Roess B, Hawes E, Deyo Z, Burkhart JI, Moll S, Shilliday BB (2017) Identification of risk factors for inappropriate and suboptimal initiation of direct oral anticoagulants. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43:149–156
Acknowledgement
We thank Tem Innovations GmbH for providing reagents free of charge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
G.A. reports consulting fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi Sankyo, lecture fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Sanofi-Aventis. C.B. reports lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo and Bristol-Myers Squibb. M.C.V., M.G.M. and F.I. have no disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedovati, M.C., Mosconi, M.G., Isidori, F. et al. Global thromboelastometry in patients receiving direct oral anticoagulants: the RO-DOA study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 49, 251–258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-01956-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-01956-0