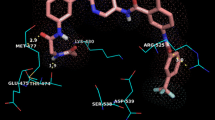
Abstract
B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) can inhibit apoptosis via heterodimerization with pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, and is over-expressed in many different types of human tumors and has been regarded as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. Due to the fact that current Bcl-xl inhibitors lack sustained effectiveness and the occurrence of some unpredictable side effects, the development of new inhibitors is necessary. In this study, computational study was applied to a series of Bcl-xL inhibitors to reveal the relationship between structure and activities through applying molecular docking, three-dimensional qualitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR), and molecular dynamic (MD) simulations. A molecular docking study was performed to explore possible modes of action between inhibitors and Bcl-xL protein. Subsequently, 3D-QSAR models were generated with comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA). For the best CoMFA model, the Q2 and R2 values were computed as 0.927 and 0.999, while those were computed as 0.943 and 0.998 for the best CoMSIA model. Twenty new Bcl-xL inhibitors were designed, and all their predictive activities were improved than molecules in the dataset based on the contour maps. In addition, MD simulations were conducted to evaluate the stability of the complexes conformed by two inhibitors and Bcl-xL, and the results were consistent with those of the molecular docking and 3D-QSAR studies. Finally, binding free energy was computed through molecular mechanics performed by surface area approach (MM-GBSA), and the result congruent with the activities which indicated van der Waals as well as lipophilic energy contributing the most during the molecular with Bcl-xL protein binding. In brief, our research provided valuable information for further development of Bcl-xL inhibitors.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bcl-xL:
-
B-cell lymphoma-extra large
- CoMFA:
-
Comparative molecular field analysis
- CoMSIA:
-
Comparative molecular similarity indices analysis
- LOO:
-
Leave-one-out
- MD:
-
Molecular dynamics
- MM-GBSA:
-
Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area
- ONC:
-
The optimum number of component
- PDB:
-
Protein data bank
- PH:
-
Pleckstrin nomology
- PLS:
-
Partial Least Squares
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- Q2 :
-
Cross-validated coefficient
- R2 :
-
The correlation coefficient
- RMSD:
-
Root mean square deviation
- RMSF:
-
Root mean square fluctuation
- SASA:
-
Solvent accessible surface area
- SEE:
-
The standard error of estimate
- SPC:
-
Simple point charge
- XED:
-
Extended election distribution
- 3D-QSAR:
-
Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationships
References
Park H-A, Broman K, Jonas EA (2021) Oxidative stress battles neuronal Bcl-xL in a fight to the death. Neural Regen Res 16:12–15
Xu XY, Iwasa H, Hossain S, Sarkar A, Maruyama J, Arimoto-Matsuzaki K, Hata Y (2017) BCL-XL binds and antagonizes RASSF6 tumor suppressor to suppress p53 expression. Genes Cells 22:993–1003
Singh R, Letai A, Sarosiek K (2019) Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:175–193
de Jong Y, Monderer D, Brandinelli E, Monchanin M, van den Akker BE, van Oosterwijk JG, Blay JY, Dutour A, Bovee J (2018) Bcl-xl as the most promising Bcl-2 family member in targeted treatment of chondrosarcoma. Oncogenesis 7:9
Wight JC, Chong G, Grigg AP, Hawkes EA (2018) Prognostication of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the molecular era: moving beyond the IPI. Blood Rev 32:400–415
Vardaki I, Sanchez C, Fonseca P, Olsson M, Chioureas D, Rassidakis G, Ullen A, Zhivotovsky B, Bjorkholm M, Panaretakis T (2016) Caspase-3-dependent cleavage of Bcl-xL in the stroma exosomes is required for their uptake by hematological malignant cells. Blood 128:2655–2665
Kamath PR, Sunil D, Ajees AA, Pai KSR, Biswas S (2016) N '-((2-(6-bromo-2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene) benzohydra zide as a probable Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor with apoptotic and anti-metastatic potential. Eur J Med Chem 120:134–147
Setoguchi K, Cui L, Hachisuka N, Obchoei S, Shinkai K, Hyodo F, Kato K, Wada F, Yamamoto T, Harada-Shiba M, Obika S, Nakano K (2017) Antisense oligonucleotides targeting Y-box binding protein-1 inhibit tumor angiogenesis by downregulating Bcl-xL-VEGFR2/-tie axes. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 9:170–181
Wang L, Doherty GA, Judd AS, Tao Z-F, Hansen TM, Frey RR, Song X, Bruncko M, Kunzer AR, Wang X, Wendt MD, Flygare JA, Catron ND, Judge RA, Park CH, Shekhar S, Phillips DC, Nimmer P, Smith ML, Tahir SK, Xiao Y, Xue J, Zhang H, Le PN, Mitten MJ, Boghaert ER, Gao W, Kovar P, Choo EF, Diaz D, Fairbrother WJ, Elmore SW, Sampath D, Leverson JD, Souers AJ (2020) Discovery of A-1331852, a first-in-class, potent, and orally-bioavailable BCL-XL inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 11:1829-1836
Gloaguen C, Voisin-Chiret AS, Santos J S-d O, Fogha J, Gautier F, De Giorgi M, Burzicki G, Perato S, Pétigny-Lechartier C, Jeune KS-L, Brotin E, Goux D, N’Diaye M, Lambert B, Louis M-H, Ligat L, Lopez F, Juin P, Bureau R, Rault S, Poulain L (2015) First evidence that oligopyridines, α-helix foldamers, inhibit Mcl-1 and sensitize ovarian carcinoma cells to Bcl-xL-targeting strategies. J Med Chem 58:1644–1668
Wang Z, Song T, Feng Y, Guo Z, Fan Y, Xu W, Liu L, Wang A, Zhang Z (2016) Bcl-2/MDM2 dual inhibitors based on universal pyramid-like α-helical mimetics. J Med Chem 59:3152–3162
Kamath PR, Sunil D, Ajees AA, Pai KS, Biswas S (2016) N'-((2-(6-bromo-2-oxo-2H-chromen-3-yl)-1H-indol-3-yl)methylene) benzohydrazide as a probable Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor with apoptotic and anti-metastatic potential. Eur J Med Chem 120:134–147
Chung C -w, Dai H, Fernandez E, Tinworth CP, Churcher I, Cryan J, Denyer J, Harling JD, Konopacka A, Queisser MA, Tame CJ, Watt G, Jiang F, Qian D, Benowitz AB (2020) Structural insights into PROTAC-mediated degradation of Bcl-xL. ACS Chem Biol 15:2316-2323
Henz K, Al-Zebeeby A, Basoglu M, Fulda S, Cohen GM, Varadarajan S, Vogler M (2019) Selective BH3-mimetics targeting BCL-2, BCL-XL or MCL-1 induce severe mitochondrial perturbations. Biol Chem 400:181–185
Huang K, O’Neill KL, Li J, Zhou W, Han N, Pang X, Wu W, Struble L, Borgstahl G, Liu Z, Zhang L, Luo X (2019) BH3-only proteins target BCL-xL/MCL-1, not BAX/BAK, to initiate apoptosis. Cell Res 29:942–952
Saleh T, Carpenter VJ, Tyutyunyk-Massey L, Murray G, Leverson JD, Souers AJ, Alotaibi MR, Faber AC, Reed J, Harada H, Gewirtz DA (2020) Clearance of therapy-induced senescent tumor cells by the senolytic ABT-263 via interference with BCL-XL–BAX interaction. Mol Oncol 14:2504-2519
Montoya JJ, Turnidge MA, Wai DH, Patel AR, Lee DW, Gokhale V, Hurley LH, Arceci RJ, Wetmore C, Azorsa DO (2019) In vitro activity of a G-quadruplex-stabilizing small molecule that synergizes with Navitoclax to induce cytotoxicity in acute myeloid leukemia cells. BMC Cancer 19:1251
Seymour JF, Davids MS, Pagel JM, Kahl BS, Wierda WG, Puvvada S, Gerecitano JF, Kipps TJ, Anderson MA, Huang DCS (2014) ABT-199 (GDC-0199) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL): high complete- response rate and durable disease control. Asco Meeting Abstracts 32
Ashkenazi A, Fairbrother WJ, Leverson JD, Souers AJ (2017) From basic apoptosis discoveries to advanced selective BCL-2 family inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16:273–284
Chen J, Zhou H, Aguilar A, Liu L, Bai L, McEachern D, Yang C-Y, Meagher JL, Stuckey JA, Wang S (2012) Structure-based discovery of BM-957 as a potent small-molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL capable of achieving complete tumor regression. J Med Chem 55:8502–8514
Zhou H, Aguilar A, Chen J, Bai L, Liu L, Meagher JL, Yang C-Y, McEachern D, Cong X, Stuckey JA, Wang S (2012) Structure-based design of potent Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitors with strong in vivo antitumor activity. J Med Chem 55(13):6149–6161
Aguilar A, Zhou H, Chen J, Liu L, Bai L, McEachern D, Yang C-Y, Meagher J, Stuckey J, Wang S (2013) A potent and highly efficacious Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor. J Med Chem 56:3048–3067
Purohit D, Saini V, Kumar S, Kumar A, Narasimhan B (2020) Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) and molecular docking study of 2-((pyridin-3-yloxy)methyl) piperazines as alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. Mini-Rev Med Chem 20:1031–1041
Ding L, Wang ZZ, Sun XD, Yang J, Ma CY, Li W, Liu HM (2017) 3D-QSAR (CoMFA, CoMSIA), molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations study of 6-aryl-5-cyano-pyrimidine derivatives to explore the structure requirements of LSD1 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:3521-3528
Wang T, Yuan XS, Wu MB, Lin JP, Yang LR (2017) The advancement of multidimensional QSAR for novel drug discovery - where are we headed? Expert Opin Drug Discovery 12:769–784
Chohan TA, Chen JJ, Qian HY, Pan YL, Chen JZ (2016) Molecular modeling studies to characterize N-phenylpyrimidin-2-amine selectivity for CDK2 and CDK4 through 3D-QSAR and molecular dynamics simulations. Mol BioSyst 12:1250–1268
Cheng P, Li JJ, Wang J, Zhang XY, Zhai HL (2018) Investigations of FAK inhibitors: a combination of 3D-QSAR, docking, and molecular dynamics simulations studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 36:1529–1549
Gu X, Wang Y, Wang M, Wang J, Li N (2019) Computational investigation of imidazopyridine analogs as protein kinase B (Akt1) allosteric inhibitors by using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn 26:1–16
Wang Y, Feng S, Gao H, Wang J (2020) Computational investigations of gram-negative bacteria phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase inhibitors using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations. J Biomol Struct Dyn 38:1435–1447
Wang M, Wang Y, Kong D, Jiang H, Wang J, Cheng M (2018) In silico exploration of aryl sulfonamide analogs as voltage-gated sodium channel 1.7 inhibitors by using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking study, and molecular dynamics simulations. Comput Biol Chem 77:214–225
Gajjar KA, Gajjar AK (2020) CoMFA, CoMSIA and HQSAR analysis of 3-aryl-3-ethoxypropanoic acid derivatives as GPR40 modulators. Current drug discovery technologies 17:100–118
Abdizadeh R, Hadizadeh F, Abdizadeh T (2019) Molecular modeling studies of anti-Alzheimer agents by QSAR, molecular docking and molecular dynamic simulations. Techniques, Medinical Chemistry
Jujjavarapu SE, Dhagat S (2018) In silico discovery of novel ligands for antimicrobial lipopeptides for computer-aided drug design. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 10:129–141
Seth A, Ojha PK, Roy K (2020) QSAR modeling with ETA indices for cytotoxicity and enzymatic activity of diverse chemicals. J Hazard Mater 394:122498
Abbasi M, Sadeghi-Aliabadi H, Amanlou M (2018) 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamic simulations for prediction of new Hsp90 inhibitors based on isoxazole scaffold. J Biomol Struct Dyn 36:1463–1478
Ul-Haq Z, Ashraf S, Bkhaitan MM (2019) Molecular dynamics simulations reveal structural insights into inhibitor binding modes and mechanism of casein kinase II inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37:1120–1135
Shah BM, Modi P, Trivedi P (2020) Pharmacophore- based virtual screening, 3D- QSAR, molecular docking approach for identification of potential dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 7:1–23
Li M, Wei D, Zhao H, Du Y (2014) Genotoxicity of quinolones: substituents contribution and transformation products QSAR evaluation using 2D and 3D models. Chemosphere 95:220–226
Dare JK, Silva DR, Ramalho TC, Freitas MP Conformational fingerprints in the modelling performance of MIA-QSAR: a case for SARS-CoV protease inhibitors. Molecular Simulation:7
Rajagopal K, Varakumar P, Aparna B, Byran G, Jupudi S (2020) Identification of some novel oxazine substituted 9-anilinoacridines as SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors for COVID-19 by molecular docking, free energy calculation and molecular dynamics studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 12:1–12
Mehta CC, Patel A, Bhatt HG (2020) New molecular insights into dual inhibitors of tankyrase as Wnt signaling antagonists: 3D-QSAR studies on 4H-1,2,4-triazole derivatives for the design of novel anticancer agents. Structural Chemistry:19
Zhang J, Liu X, Wang SQ, Liu GY, Xu WR, Cheng XC, Wang RL (2017) Identification of dual ligands targeting angiotensin II type 1 receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ by core hopping of telmisartan. J Biomol Struct Dyn 35:2665–2680
De Vivo M, Masetti M, Bottegoni G, Cavalli A (2016) Role of molecular dynamics and related methods in drug discovery. J Med Chem 59:4035–4061
Shekhar MS, Venkatachalam T, Sharma CS, Pratap Singh H, Kalra S, Kumar N (2019) Computational investigation of binding mechanism of substituted pyrazinones targeting corticotropin releasing factor-1 receptor deliberated for anti-depressant drug design. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37:3226–3244
Balasubramanian PK, Balupuri A, Bhujbal SP, Cho SJ (2019) 3D-QSAR-aided design of potent c-met inhibitors using molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy calculation. J Biomol Struct Dyn 37:2165–2178
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC1807118), Shenyang Young Scientific and Technological Innovators Programme (RC200408), and Liaoning BaiQianWan Talents Program (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3138 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Gu, X., Meng, C. et al. Computational investigation of 4,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid derivatives as B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL) inhibitors by using 3D-QSAR, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulations. Struct Chem 32, 1005–1018 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-020-01631-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11224-020-01631-8