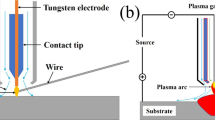
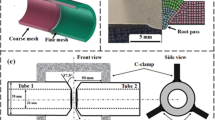
Recently, the welding of dissimilar metals has attracted great interest due to its widespread use in engineering building applications. In this article, welding methods of dissimilar metal joints containing different metal types with different chemical compositions are examined and their fatigue behavior is evaluated. In dissimilar metal welds, the difference in chemical composition affects the weldability and mechanical properties of the joints. In this study, the factors affecting the fatigue strength of dissimilar welded joints are described. Since welded structures can be used in sensitive and risky places, welding quality and mechanical properties of the weld are extremely important. In the research, a detailed literature review was presented by evaluating the latest studies on the mechanical properties of dissimilar welded joints such as fatigue strength, tensile strength, hardness, and the latest developments in the welding of different metals were reviewed. This study, which deals with the latest developments in the joining of different metal alloy combinations, is expected to increase the interest of the researchers in the future.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. F. Guo, H. C. Chen, C. N. Sun, et al., “Friction stir welding of dissimilar materials between AA6061 and AA7075 Al alloys effects of process parameters,” Mater Design, 56, 185–192 (2014).
K. Martinsen, S. J. Hu, and B. E. Carlson, “Joining of dissimilar materials,” CIRP Annals, 64, No. 2, 679–699 (2015).
G. Rogalski, A. Świerczyńska, M. Landowski, and D. Fydrych, “Mechanical and microstructural characterization of TIG welded dissimilar joints between 304L austenitic stainless steel and Incoloy 800HT nickel alloy,” Metals, 10, No. 5, 559 (2020).
K. D. Ramkumar, P. Mithilesh, D. Varun, et al., “Characterization of microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 and AISI 304 dissimilar weldments,” ISIJ Int, 54, No. 4, 900–908 (2014).
G. Li, J. Huang, and Y. Wu, “An investigation on microstructure and properties of dissimilar welded Inconel 625 and SUS 304 using high-power CO2 laser,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 76, No. 5, 1203–1214 (2015).
H. Ming, J. Wang, and E. H. Han, “Comparative study of microstructure and properties of low-alloysteel/nickel-based-alloy interfaces in dissimilar metal weld joints prepared by different GTAW methods,” Mater Charact, 139, 186–196 (2018).
M. Tumer, T. Karahan, and T. Mert, “Evaluation of microstructural and mechanical properties of dissimilar Inconel 625 nickel alloy–UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel weldment using MIG welding,” Weld World, 64, 21–35 (2020).
F. Hejripour and D. K. Aidun, “Consumable selection for arc welding between stainless steel 410 and Inconel 718,” J Mater Process Tech, 245, 287–299 (2017).
J. D. C. Payão Filho, E. K. D. Passos, R. S. Gonzaga, et al., “Ultrasonic inspection of a 9% Ni steel joint welded with Ni-based superalloy 625: simulation and experimentation,” Metals, 8, No. 10, 787 (2018).
H. W. Ahmad, U. M. Chaudry, M. R. Tariq, and D. H. Bae, “Assessment of fatigue and electrochemical corrosion characteristics of dissimilar materials weld between alloy 617 and 12 Cr steel,” J Manuf Process, 53, 275–282 (2020).
T. Soysal, S. Kou, D. Tat, and T. Pasang, “Macrosegregation in dissimilar-metal fusion welding,” Acta Mater, 110, 149–160 (2016).
S. Chen, J. Huang, J. Xia, et al., “Microstructural characteristics of a stainless steel/copper dissimilar joint made by laser welding,” Metall Mater Trans A, 44, 3690–3696 (2013).
A. A. Omar, “Effects of welding parameters on hard zone formation at dissimilar metal welds,” Weld J, 77, No. 6, 86–93 (1998).
H. S. Hosseini, M. Shamanian, and A. Kermanpur, “Microstructural and weldability analysis of Inconel617/AISI 310 stainless steel dissimilar welds,” Int J Pres Ves Pip, 144, 18–24 (2016).
M. A. Karim and Y. D. Park, “A review on welding of dissimilar metals in car body manufacturing,” J Weld Join, 38, 8–23 (2020).
A. D. Bharti and U. H. Babu, “Structural and thermal analysis of dissimilar metal welding of 1020 mild steel and 304 stainless steel,” Int J Sci Eng Technol Res, 4, No. 9, 1761–1771 (2015).
G. Çam, Ç. Yeni, S. Erim, et al., “Investigation into properties of laser welded similar and dissimilar steel joints,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 3, No. 4, 177–189 (1998).
B. Mvola, P. Kah, and J. Martikainen, “Welding of dissimilar non-ferrous metals by GMAW processes,” Int J Mech Mater Eng, 9, 1–11 (2014).
C. Yao, B. Xu, X. Zhang, J. Huang, et al., “Interface microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welding copper–steel dissimilar joint,” Opt Laser Eng, 47, Nos. 7–8, 807–814 (2009).
T. A. Mai and A. C. Spowage, “Characterisation of dissimilar joints in laser welding of steel–kovar, copper–steel and copper–aluminium,” Mater Sci Eng A, 374, Nos. 1–2, 224–233 (2004).
M. Schimek, A. Springer, S. Kaierle, et al., “Laser-welded dissimilar steel-aluminum seams for automotive lightweight construction,” Phys Procedia, 39, 43–50 (2012).
J. R. Berretta, W. de Rossi, M. D. M. das Neves, et al., “Pulsed Nd: YAG laser welding of AISI 304 to AISI 420 stainless steels,” Opt Laser Eng, 45, No. 9, 960–966 (2007).
S. Yu, D. Fan, and B. Dong, “Laser beam welding of dissimilar metals of aluminum alloy and galvanized steel sheet,” in: Second Int. Conf. on Mechanic Automation and Control Engineering, IEEE (2011), pp. 5030–5032.
A. P. Costa, L. Quintino, and M. Greitmann, “Laser beam welding hard metals to steel,” J Mater Process Tech, 141, No. 2, 163–173 (2003).
V. Balasubramanian, V. Ravisankar, and G. Madhusudhan Reddy, “Effect of pulsed current welding on mechanical properties of high strength aluminum alloy,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 36, No. 3, 254–262 (2008).
M. Singla, D. Singh, and D. Deepak, “Parametric optimization of gas metal arc welding processes by using factorial design approach,” J Miner Mater Charact Eng, 9, 353–363 (2010).
M. Sireesha, S. K. Albert, V. Shankar, and S. Sundaresan, “A comparative evaluation of welding consumables for dissimilar welds between 316LN austenitic stainless steel and Alloy 800,” J Nucl Mater, 279, No. 1, 65–76 (2000).
H. T. Wang, G. Z. Wang, F. Z. Xuan, et al., “Local mechanical properties and microstructures of Alloy52M dissimilar metal welded joint between A508 ferritic steel and 316L stainless steel,” Adv Mater Res, 509, 103–110 (2012).
Q. M. Nguyen and S. C. Huang, “An investigation of the microstructure of an intermetallic layer in welding aluminum alloys to steel by MIG process,” Materials, 8, No. 12, 8246–8254 (2015).
L. H. Shah, Z. Akhtar, and M. Ishak, “Investigation of aluminum-stainless steel dissimilar weld quality using different filler metals,” Int J Automot Mech Eng (IJAME), 8, 1121–1131 (2013).
H. T. Zhang and J. Q. Song, “Microstructural evolution of aluminum/magnesium lap joints welded using MIG process with zinc foil as an interlayer,” Mater Lett, 65, Nos. 21–22, 3292–3294 (2011).
X. Y. Wang, X. Y. Gu, D. Q. Sun, and C. Y. Xi, “Interface characteristics and mechanical behavior of metal inert-gas arc welded Mg-steel joints,” J Mater Res, 31, No. 5, 589–598 (2016).
S. Liu, D. Sun, X. Gu, and H. Li, “Microstructures and mechanical properties of metal inert-gas arc welded joints of Mg alloy and ultra-high strength steel,” J Mater Res, 32, No. 4, 843–851 (2017).
S. Baskutis, J. Baskutiene, R. Bendikiene, et al., “Comparative research of microstructure and mechanical properties of stainless and structural steel dissimilar welds,” Materials, 14, No. 20, 6180 (2021).
R. Borrisutthekul, P. Mitsomwang, S. Rattanachan, and Y. Mutoh, “Feasibility of using TIG welding in dissimilar metals between steel/aluminum alloy,” Energy Res J, 1, No. 2, 82–86 (2010).
J. L. Song, S. B. Lin, C. L. Yang, et al., “Analysis of intermetallic layer in dissimilar TIG welding–brazing butt joint of aluminium alloy to stainless steel,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 15, No. 3, 213–218 (2010).
L. Liu, X. Liu, and S. Liu, “Microstructure of laser-TIG hybrid welds of dissimilar Mg alloy and Al alloy with Ce as interlayer,” Scripta Mater, 55, No. 4, 383–386 (2006).
H. Wang and G. Song, “Influence of adhesive and Ni on the interface between Mg and Fe in the laser-TIGadhesive hybrid welding joint,” Int J Precis Eng Manuf, 17, No. 6, 823–827 (2016).
C. Mani, B., Sozharajan, R. Karthikeyan, and J. P. Davim, “Fatigue analysis of dissimilar metal welded joints of 316L stainless steel/Monel 400 alloy using GTAW,” in: J. P. Davim (Ed.), Welding Technology. Materials Forming, Machining and Tribology, Springer (2021), pp. 369–386.
G. Dak and C. Pandey, “Experimental investigation on microstructure, mechanical properties, and residual stresses of dissimilar welded joint of martensitic P92 and AISI 304L austenitic stainless steel,” Int J Pres Ves Pip, 194, 104536 (2021).
A. Sauraw, A. K. Sharma, D. Fydrych, et al., “Study on microstructural characterization, mechanical properties and residual stress of GTAW dissimilar joints of P91 and P22 steels,” Materials, 14, No. 21, 6591 (2021).
M. J. Torkamany, S. Tahamtan, and J. Sabbaghzadeh, “Dissimilar welding of carbon steel to 5754 aluminum alloy by Nd: YAG pulsed laser,” Mater Design, 31, No. 1, 458–465 (2010).
C. Dharmendra, K. P. Rao, J. Wilden, and S. Reich, “Study on laser welding–brazing of zinc coated steel to aluminum alloy with a zinc based filler,” Mater Sci Eng A, 528, No. 3, 1497–1503 (2011).
W. S. Chang, S. R. Rajesh, C. K. Chun, and H. J. Kim, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of hybrid laser-friction stir welding between AA6061-T6 Al alloy and AZ31 Mg alloy,” J Mater Sci Technol, 27, No. 3, 199–204 (2011).
L. Li, C. Tan, Y. Chen, et al., “Comparative study on microstructure and mechanical properties of laser welded–brazed Mg/mild steel and Mg/stainless steel joints,” Mater Design, 43, 59–65 (2013).
Z. Zeng, J. P. Oliveira, M. Yang, et al., “Functional fatigue behavior of NiTi-Cu dissimilar laser welds,” Mater Design, 114, 282–287 (2017).
J. P. Oliveira, Z. Zeng, C. Andrei, et al., “Dissimilar laser welding of superelastic NiTi and CuAlMn shape memory alloys,” Mater Design, 128, 166–175 (2017).
G. R. Mirshekari, A. Saatchi, A. Kermanpur, and S. K. Sadrnezhaad, “Laser welding of NiTi shape memory alloy: Comparison of the similar and dissimilar joints to AISI 304 stainless steel,” Opt Laser Technol, 54, 151–158 (2013).
L. A. Jácome, S. Weber, A. Leitner, et al., “Influence of filler composition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of steel—Aluminum joints produced by metal arc joining,” Adv Eng Mater, 11, No. 5, 350–358 (2009).
M. Kang and C. Kim, “Joining Al 5052 alloy to aluminized steel sheet using cold metal transfer process,” Mater Design, 81, 95–103 (2015).
J. Shang, K. Wang, Q. Zhou, et al., “Microstructure characteristics and mechanical properties of cold metal transfer welding Mg/Al dissimilar metals,” Mater Design, 34, 559–565 (2012).
D. Ren and L. Liu, “Interface microstructure and mechanical properties of arc spot welding Mg–steel dissimilar joint with Cu interlayer,” Mater Design, 59, 369–376 (2014).
M. Watanabe, K. Feng, Y. Nakamura, and S. Kumai, “Growth manner of intermetallic compound layer produced at welding interface of friction stir spot welded aluminum/steel lap joint,” Mater Trans, 52, No. 5, 953–959 (2011).
T. Morishige, A. Kawaguchi, M. Tsujikawa, et al., “Dissimilar welding of Al and Mg alloys by FSW,” Mater Trans, 49, No. 5, 1129–1131 (2008).
F. Czerwinski, “Welding and joining of magnesium alloys,” in: F. Czerwinski (Ed.), Magnesium Alloys – Design, Processing and Properties, InTech (2011).
H. D. Duong, M. Okazaki, and T. H. Tran, “Fatigue behavior of dissimilar friction stir welded T-lap joints between AA5083 and AA7075,” Int J Fatigue, 145, 106090 (2021).
S. Mabuwa and V. Msomi, “Fatigue behaviour of the multi-pass friction stir processed AA8011-H14 and AA6082-T651 dissimilar joints,” Eng Fail Anal, 118, 104876 (2020).
M. Vigneshwar, S. T. Selvamani, P. Hariprasath, and K. Palanikumar, “Analysis of mechanical, metallurgical and fatigue behavior of friction welded AA6061-AA2024 dissimilar aluminum alloys in optimized condition,” Mater Today Proc, 5, No. 2, 7853–7863 (2018).
S. Kumar, A. K. Srivastava, R. K. Singh, and S. P. Dwivedi, “Experimental study on hardness and fatigue behavior in joining of AA5083 and AA6063 by friction stir welding,” Mater Today Proc, 25, 646–648 (2020).
M. Vetrivel Sezhian, K. Giridharan, D. P. Pushpanathan, et al., “Microstructural and mechanical behaviors of friction stir welded dissimilar AA6082-AA7075 joints,” Adv Mater Sci Eng, 2021, 4113895 (2021).
A. Yürük, B. Çevik, and N. Kahraman, “Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded dissimilar 5754-H111-6013-T6 aluminum alloy joints,” Mater Test, 61, No. 10, 941–946 (2019).
E. Taban and E. Kaluc, “Microstructural and mechanical properties of double-sided MIG, TIG and friction stir welded 5083-H321 aluminium alloy,” Kovove Mater, 44, No. 1, 25 (2006).
C. Caglioni, F. M. Rigon, M. A. Losekann, et al., “Similar and dissimilar welding effect on the mechanical properties of 5383 H34, 5754 H34 and 6005 T6 aluminum alloys,” Matéria (Rio de Janeiro), 25, No. 2 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-707620200002.1009
G. Cam and S. Mistikoglu, “Recent developments in friction stir welding of Al-alloys,” J Mater Eng Perform, 23, No. 6, 1936–1953 (2014).
B. Çevik, Y. Ozcatalbas, and B. Gülenç, “Effect of welding speed on the mechanical properties and weld defects of 7075 Al alloy joined by FSW,” Kovove Mater, 54, No. 4, 241–247 (2016).
T. V. B. Babu, M. Selvam, and C. Devanathan, “Performance evaluation of thermally reduced ex situ wheat husk biocarbon-assisted dissimilar AA7075 T651-magnesium AZ31B friction stir welded joints,” Biomass Conv Bioref (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03409-w
S. K. Ales, Fatigue Behaviour of Aluminium Alloy AA2024 to Titanium Alloy Ti6Al4V Friction Stir Lap Welded Joints, PhD Thesis, Auckland University of Technology (2021).
Y. Uematsu, Y. Tozaki, K. Tokaji, and M. Nakamura, “Fatigue behavior of dissimilar friction stir welds between cast and wrought aluminum alloys,” Strength Mater, 40, No. 1, 138–141 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-008-0036-6
M. Makeshkumar, S. R. Surender, S. Arunprakash, et al., “Microstructural and mechanical properties evaluation of dissimilar aluminum alloy and bronze joints using friction stir welding,” Mater Today Proc, 47, 5239–5244 (2021).
Z. Shen, Y. Ding, J. Chen, and A. P. Gerlich, “Comparison of fatigue behavior in Mg/Mg similar and Mg/steel dissimilar refill friction stir spot welds,” Int J Fatigue, 92, 78–86 (2016).
Y. Uematsu, T. Kakiuchi, Y. Tozaki, and H. Kojin, “Comparative study of fatigue behaviour in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and Mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds fabricated by scroll grooved tool without probe,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 17, No. 5, 348–356 (2012).
K. Kumamoto, T. Kosaka, T. Kobayashi, et al, “Microstructure and fatigue behaviors of dissimilar A6061/galvannealed steel joints fabricated by friction stir spot welding,” Materials, 14, No. 14, 3877 (2021).
S. Rajan, P. Wanjara, J. Gholipour, and A. S. Kabir, “Fatigue behavior of linear friction welded Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.1Si dissimilar welds,” Materials, 14, No. 11, 3136 (2021).
B. Wang, X. Chen, J. Yang, et al., “Microstructural response at the interface and its effect on the fatigue fracture behavior of rotary friction welded dissimilar titanium alloys: Ti–5Al–2Sn–2Zr–4Mo–4Cr (Ti17) and Ti–6Al–2Sn–4Zr–2Mo (Ti6242),” Mater Res Express, 8, No. 10, 106513 (2021).
H. A. Derazkola, A. Eyvazian, and A. Simchi, “Submerged friction stir welding of dissimilar joints between an Al-Mg alloy and low carbon steel: Thermo-mechanical modeling, microstructural features, and mechanical properties,” Mater Res Express, 50, 68–79 (2020).
S. L. Hernández-Trujillo, V. H. Lopez-Morelos, M. A. García-Rentería, et al., “Microstructure and fatigue behavior of 2205/316L stainless steel dissimilar welded joints,” Metals, 11, No. 1, 93 (2021).
M. Sun, S. B. Behravesh, L. Wu, et al., “Fatigue behaviour of dissimilar Al 5052 and Mg AZ31 resistance spot welds with Sn‐coated steel interlayer,” Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 40, No. 7, 1048–1058 (2017).
L. Shi, J. Xue, J. Kang, et al., “Effect of specimen configuration and notch root angle on fatigue behavior of novel dissimilar resistance spot welds of AA5754 to HSLA steel,” Procedia Struct Integr, 37, 351–358 (2022).
M. S. Khan, S. D. Bhole, D. L. Chen, et al., “Welding behaviour, microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar resistance spot welds between galvannealed HSLA350 and DP600 steels,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 14, No. 7, 616–625 (2009).
S. Q. Wang, W. Y. Li, Y. Zhou, et al., “Tensile and fatigue behavior of electron beam welded dissimilar joints of Ti–6Al–4V and IMI834 titanium alloys,” Mater Sci Eng A, 649, 146–152 (2016).
S. Q. Wang, J. H. Liu, and D. L. Chen, “Tensile and fatigue properties of electron beam welded dissimilar joints between Ti–6Al–4V and BT9 titanium alloys,” Mater Sci Eng A, 584, 47–56 (2013).
B. Šimeková, E. Hodúlová, P. Kovačócy, et al., “Influence of electron beam welding parameters on the microstructure formation and mechanical behaviors of the Ti and Ni dissimilar metals welded joints,” Metals, 12, No. 6, 894 (2022).
S. Kuryntsev, “A review: laser welding of dissimilar materials (Al/Fe, Al/Ti, Al/Cu) – methods and techniques, microstructure and properties,” Materials, 15, No. 1, 122 (2021).
T. E. Abioye, T. O. Olugbade, and T. I. Ogedengbe, “Welding of dissimilar metals using gas metal arc and laser welding techniques: A review,” J Emerg Trends Eng Appl Sci, 8, No. 6, 225–228 (2017).
L. Liu, D. Ren, and F. Liu, “A review of dissimilar welding techniques for magnesium alloys to aluminum alloys,” Materials, 7, No. 5, 3735–3757 (2014).
R. Zeng, W. Ke, and Y. B. Xu, “Recent development and application of magnesium alloys,” Acta Metall Sin, 37, No. 7, 673–685 (2001).
P. Liu, Y. Li, H. Geng, and J. Wang, “Microstructure characteristics in TIG welded joint of Mg/Al dissimilar materials,” Mater Lett, 61, No. 6, 1288–1291 (2007).
A. Dorbane, B. Mansoor, G. Ayoub, et al., “Mechanical, microstructural and fracture properties of dissimilar welds produced by friction stir welding of AZ31B and Al6061,” Mater Sci Eng A, 651, 720–733 (2016).
A. O’Brien, Welding Handbook, Vol. 4: Materials and Applications, Part 1, 9th Edition, American Welding Society (2011).
P. Sakthivel, V. Manobbala, T. Manikandan, et al., “Investigation on mechanical properties of dissimilar metals using MIG welding,” Mater Today Proc, 37, No. 2, 531–536 (2021).
J. Wang, J. C. Feng, and Y. X. Wang, “Microstructure of Al–Mg dissimilar weld made by cold metal transfer MIG welding,” Mater Sci Tech, 24, No. 7, 827–831 (2008).
F. Liu, Z. Zhang, and L. Liu, “Microstructure evolution of Al/Mg butt joints welded by gas tungsten arc with Zn filler metal,” Mater Charact, 69, 84–89 (2012).
R. L. Klueh and J. F. King, “Austenitic stainless steel-ferritic steel weld joint failures,” Weld J, 61, No. 9, 302–311 (1982).
T. E. Abioye, “The effect of heat input on the mechanical and corrosion properties of AISI 304 electric arc weldments,” Br J Appl Sci Technol, 20, No. 5, 1–10 (2017).
Y. Bozkurt and M. K. Bilici, “Application of Taguchi approach to optimize of FSSW parameters on joint properties of dissimilar AA2024-T3 and AA5754-H22 aluminum alloys,” Mater Design, 51, 513–521 (2013).
W. C. Chung, J. Y. Huang, L. W. Tsay, and C. Chen, “Microstructure and stress corrosion cracking behavior of the weld metal in alloy 52-A508 dissimilar welds,” Mater Trans, 52, No. 1, 12–19 (2011).
C. R. Corleto and G. R. Argade, “Failure analysis of dissimilar weld in heat exchanger,” Case Stud Eng Fail Anal, 9, 27–34 (2017).
T. E. Abioye, J. Folkes, A. T. Clare, and D. G. McCartney, “Concurrent Inconel 625 wire and WC powder laser cladding: process stability and microstructural characterisation,” Surf Eng, 29, No. 9, 647–653 (2013).
I. N. Fridlyander, “Current-technology aluminum alloys for aerospace applications,” Met Sci Heat Treat, 43, Nos. 7–8, 297 (2001).
H. Babel, J. Gibson, M. Tarkanian, et al., “2099 aluminum-lithium with key-locked inserts for aerospace applications,” J Mater Eng Perform, 16, No. 5, 584–591 (2007).
C. C. Menzemer, P. C. Lam, C. F. Wittel, and T. S. Srivatsan, “A study of fusion zone microstructures of arcwelded joints made from dissimilar aluminum alloys,” J Mater Eng Perform, 10, No. 2, 173–177 (2001).
A. K. Lakshminarayanan, V. Balasubramanian, and K. Elangovan, “Effect of welding processes on tensile properties of AA6061 aluminium alloy joints,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 40, No. 3, 286–296 (2009).
S. H. Lee, “A hot cracking on dissimilar metal weld between A106Gr. B and A312 TP316L with buttering ERNiCr-3,” Metals, 9, No. 5, 533 (2019).
C. D. Lundin, “Dissimilar metal welds-transition joints literature review,” Weld J, 61, No. 2, 58–63 (1982).
S. X. Lv, X. J. Jing, Y. X. Huang, et al., “Investigation on TIG arc welding–brazing of Ti/Al dissimilar alloys with Al based fillers,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 17, No. 7, 519–524 (2012).
E. Hajjari, M. Divandari, S. H. Razavi, et al., “Dissimilar joining of Al/Mg light metals by compound casting process,” J Mater Sci, 46, No. 20, 6491–6499 (2011).
Y. Miyashita, R. Borrisutthekul, J. Chen, and Y. Mutoh, “Application of twin laser beam on AZ31/A5052 dissimilar metals welding,” Key Eng Mater, 353–358, 1956–1959 (2007).
A. R. Murthy, P. Gandhi, S. Vishnuvardhan, and G. Sudharshan, “Crack growth analysis and remaining life prediction of dissimilar metal pipe weld joint with circumferential crack under cyclic loading,” Nucl Eng Technol, 52, No. 12, 2949–2957 (2020).
Y. M. Baqer, S. Ramesh, F. Yusof, and S. M. Manladan, “Challenges and advances in laser welding of dissimilar light alloys: Al/Mg, Al/Ti, and Mg/Ti alloys,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 95, No. 9, 4353–4369 (2018).
V. Infante, D. F. O. Braga, F. Duarte, et al., “Study of the fatigue behaviour of dissimilar aluminium joints produced by friction stir welding,” Int J Fatigue, 82, 310–316 (2016).
N. Eslami, A. Harms, B. Henke, et al., “Electrical and mechanical properties of friction stir welded Al-Cu butt joints,” Weld World, 63, No. 3, 903–911 (2019).
M. Sun, S. B. Behravesh, L. Wu, et al., “Fatigue behaviour of dissimilar Al 5052 and Mg AZ31 resistance spot welds with Sn‐coated steel interlayer,” Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 40, No. 7, 1048–1058 (2017).
R. Paventhan, P. R. Lakshminarayanan, and V. Balasubramanian, “Fatigue behaviour of friction welded medium carbon steel and austenitic stainless steel dissimilar joints,” Mater Design, 32, No. 4, 1888–1894 (2011).
S. Mohammadzadeh Polami, P. Häfele, M. Rethmeier, and A. Schmid, “Study on fatigue behavior of dissimilar materials and different methods of friction-welded joints for drive pinion in trucks,” Weld World, 59, No. 6, 917–926 (2015).
D. I. Roberts, R. H. Ryder, and R. Viswanathan, “Performance of dissimilar welds in service,” J Press Vess-T ASME, 107, No. 3, 247–254 (1985).
K. Bettahar, M. Bouabdallah, R. Badji, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical behavior in dissimilar 13Cr/2205 stainless steel welded pipes,” Mater Design, 85, 221–229 (2015).
Q. Zhang, J. Zhang, P. Zhao, et al., “Low-cycle fatigue behaviors of a new type of 10% Cr martensitic steel and welded joint with Ni-based weld metal,” Int J Fatigue, 88, 78–87 (2016).
S. Kumar, P. K. Singh, K. N. Karn, and V. Bhasin, “Experimental investigation of local tensile and fracture resistance behaviour of dissimilar metal weld joint: SA508 Gr. 3 Cl. 1 and SA312 Type 304LN,” Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 40, No. 2, 190–206 (2017).
W. C. Zhang, M. L. Zhu, K. Wang, and F. Z. Xuan, “Failure mechanisms and design of dissimilar welds of 9% Cr and CrMoV steels up to very high cycle fatigue regime,” Int J Fatigue, 113, 367–376 (2018).
W. Zhang, W. Jiang, X. Zhao, and S. T. Tu, “Fatigue life of a dissimilar welded joint considering the weld residual stress: Experimental and finite element simulation,” Int J Fatigue, 109, 182–190 (2018).
D. Parkes, W. Xu, D. Westerbaan, et al., “Microstructure and fatigue properties of fiber laser welded dissimilar joints between high strength low alloy and dual-phase steels,” Mater Design, 51, 665–675 (2013).
H. Okamura and K. Aota, “Joining of dissimilar materials with friction stir welding,” Weld Int, 18, No. 11, 852–860 (2004).
H. Uzun, C. Dalle Donne, A. Argagnotto, et al., “Friction stir welding of dissimilar Al 6013-T4 to X5CrNi18-10 stainless steel,” Mater Design, 26, No. 1, 41–46 (2005).
G. Figner, R. Vallant, T. Weinberger, et al. “Friction stir spot welds between aluminium and steel automotive sheets: influence of welding parameters on mechanical properties and microstructure,” Weld World, 53, No. 1, R13–R23 (2009).
E. Taban, J. E. Gould, and J. C. Lippold, “Dissimilar friction welding of 6061-T6 aluminum and AISI 1018 steel: Properties and microstructural characterization,” Mater Design, 31, No. 5, 2305–2311 (2010).
G. Meneghetti, A. Campagnolo, D. Berto, et al., “Fatigue strength of austempered ductile iron-to-steel dissimilar arc-welded joints,” Weld World, 65, No. 4, 667–689 (2021).
A. Gullino, P. Matteis, and F. D’Aiuto, “Review of aluminum-to-steel welding technologies for car-body applications,” Metals, 9, No. 3, 315 (2019).
EN 1999-1-3:2007/A1:2011 – Eurocode 9, Design of Aluminium Structures – Part 1-3: Structures Susceptible to Fatigue, CEN (2011).
A. F. Hobbacher, Recommendations for Fatigue Design of Welded Joints and Components, IIW Collection, Springer (2016).
Y. Liu, Z. Zhu, X. Che, et al., “Fatigue properties and fracture behavior of Al/steel butt joints fabricated by laser‐MIG welding‐brazing,” Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 45, No. 8, 2187–2199 (2022).
I. Ibrahim, R. Ito, T. Kakiuchi, et al., “Fatigue behaviour of Al/steel dissimilar resistance spot welds fabricated using Al–Mg interlayer,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 21, No. 3, 223–233 (2016).
X. Sun, E. V. Stephens, and M. A. Khaleel, “Fatigue behaviors of self-piercing rivets joining similar and dissimilar sheet metals,” Int J Fatigue, 29, No. 2, 370–386 (2007).
J. Kang, H. M. Rao, D. R. Sigler, and B. E. Carlson, “Tensile and fatigue behaviour of AA6022-T4 to IF steel resistance spot welds,” Procedia Struct Integr, 5, 1425–1432 (2017).
S. Ales, S. Yazdanian, T. Pasang, and Z. W. Chen, “Fatigue strength of friction stir lap welded AA2024 to Ti6Al4V dissimilar joints,” Eng Fail Anal, 138, 106309 (2022).
Z. Ling, Y. Li, Z. Luo, et al., “Microstructure and fatigue behavior of resistance element welded dissimilar joints of DP780 dual-phase steel to 6061-T6 aluminum alloy,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 92, No. 5, 1923–1931 (2017).
H. Li, J. Gao, and Q. Li, “Fatigue of friction stir welded aluminum alloy joints: a review,” Appl Sci, 8, No. 12, 2626 (2018).
Z. H. Zhang, W. Y. Li, Y. Feng, et al., “Global anisotropic response of friction stir welded 2024 aluminum sheets,” Acta Mater, 92, 117–125 (2015).
Y. Fang, X. Jiang, D. Mo, et al., “A review on dissimilar metals’ welding methods and mechanisms with interlayer,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 102, No. 9, 2845–2863 (2019).
M. Balasubramanian, “Application of Box–Behnken design for fabrication of titanium alloy and 304 stainless steel joints with silver interlayer by diffusion bonding,” Mater Design, 77, 161–169 (2015).
A. Yıldız, Y. Kaya, and N. Kahraman, “Joint properties and microstructure of diffusion-bonded grade 2 titanium to AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel using pure Ni interlayer,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 86, Nos. 5–8, 1287–1298 (2016).
M. Sun, S. T. Niknejad, G. Zhang, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of resistance spot welded AZ31/AA5754 using a nickel interlayer,” Mater Design, 87, 905–913 (2015).
M. Sun, S. T. Niknejad, H. Gao, et al., “Mechanical properties of dissimilar resistance spot welds of aluminum to magnesium with Sn-coated steel interlayer,” Mater Design, 91, 331–339 (2016).
X. Y. Wang, D. Q. Sun, and Y. Sun, “Influence of Cu-interlayer thickness on microstructures and mechanical properties of MIG-welded Mg-steel joints,” J Mater Eng Perform, 25, No. 3, 910–920 (2016).
J. Ning, L. J. Zhang, G. C. Jiang, et al., “Narrow gap multi-pass laser butt welding of explosion welded CPTi/Q235B bimetallic sheet by using a copper interlayer,” J Alloy Compd, 701, 587–602 (2017).
N. Özdemir and B. Bilgin, “Interfacial properties of diffusion bonded Ti-6Al-4V to AISI 304 stainless steel by inserting a Cu interlayer,” Int J Adv Manuf Tech, 41, No. 5, 519–526 (2009).
D. Aboudi, S. Lebaili, M. Taouinet, and J. Zollinger, “Microstructure evolution of diffusion welded 304L/Zircaloy4 with copper interlayer,” Mater Design, 116, 386–394 (2017).
W. Zhang, D. Sun, L. Han, and D. Liu, “Interfacial microstructure and mechanical property of resistance spot welded joint of high strength steel and aluminium alloy with 4047 AlSi12 interlayer,” Mater Design, 57, 186–194 (2014).
R. Gan and Y. Jin, “Friction stir-induced brazing of Al/Mg lap joints with and without Zn interlayer,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 23, No. 2, 164–171 (2018).
R. Hashemi, H. Pashazadeh, and M. Hamedi, “An incrementally coupled thermo-electro-mechanical model for resistance spot welding,” Mater Manuf Process, 27, No. 12, 1442–1449 (2012).
M. R. Arghavani, M. Movahedi, and A. H. Kokabi, “Role of zinc layer in resistance spot welding of aluminium to steel,” Mater Design, 102, 106–114 (2016).
X. Y. Dai, H. T. Zhang, H. C. Zhang, et al., “Joining of magnesium and aluminum via arc-assisted ultrasonic seam welding with Sn/Zn composite interlayer,” Mater Lett, 178, 235–238 (2016).
T. Das, B. Sahoo, P. Kumar, and J. Paul, “Effect of graphene interlayer on resistance spot welded AISI-1008 steel joints,” Mater Res Express, 6, No. 8, 0865c3 (2019).
T. Das and J. Paul, “Resistance spot welding of similar and dissimilar metals: the effect of graphene interlayer,” JOM, 72, No. 8, 2863–2874 (2020).
J. P. Oliveira, B. Panton, Z., Zeng, et al., “Laser joining of NiTi to Ti6Al4V using a Niobium interlayer,” Acta Mater, 105, 9–15 (2016).
M. Winnicki, A. Małachowska, M. Korzeniowski, et al., “Aluminium to steel resistance spot welding with cold sprayed interlayer,” Surf Eng, 34, No. 3, 235–242 (2018).
D. Wang, H. Wang, H. Cui, and G. He, “Enhancement of the laser welded AA6061-carbon steel joints by using Al5Si intermediate layer,” J Mater Process Technol, 237, No. 1, 277–285 (2016).
Q. Chu, M. Zhang, J. Li, et al., “Influence of vanadium filler on the properties of titanium and steel TIG welded joints,” J Mater Process Technol, 240, 293–304 (2017).
J. H. Ordoñez, R. R. Ambriz, C. García, et al., “Overloading effect on the fatigue strength in resistance spot welding joints of a DP980 steel,” Int J Fatigue, 121, 163–171 (2019).
H. T. Kang, I. Accorsi, B. Patel, and E. Pakalnins, “Fatigue performance of resistance spot welds in three sheet stack-ups,” Procedia Eng, 2, No. 1, 129–138 (2010).
P. Penner, L. Liu, A. Gerlich, and Y. Zhou, “Feasibility study of resistance spot welding of dissimilar Al/Mg combinations with Ni based interlayers,” Sci Technol Weld Join, 18, No. 7, 541–550 (2013).
G. Janardhan, K. Kishore, G. Mukhopadhyay, and K. Dutta, “Fatigue properties of resistance spot welded dissimilar interstitial-free and high strength micro-alloyed steel sheets,” Met Mater Int, 27, No. 9, 3432–3448 (2021).
T. Das and J. Paul, “Interlayers in resistance spot-welded lap joints: a critical review,” Metallogr Microstruct Anal, 10, No. 1, 3–24 (2021).
E. Akca and A. Gürsel, “The importance of interlayers in diffusion welding – a review,” Period Eng Nat Sci, 3, No. 2, 12–16 (2015).
Technical Knowledge, What Are the Residual Stresses in a Dissimilar Metal Weld? TWI, Available online: https://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/faqs/faq-what-are-the-residual-stresses-in-a-dissimilarmetal-weld
Q. Wu, F. Lu, H. Cui, et al., “Role of butter layer in low-cycle fatigue behavior of modified 9Cr and CrMoV dissimilar rotor welded joint,” Mater Design, 59, 165–175 (2014).
L. Zhao, J. Liang, Q. Zhong, et al., “Numerical simulation on the effect of welding parameters on welding residual stresses in T92/S30432 dissimilar welded pipe,” Adv Eng Softw, 68, 70–79 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Problemy Mitsnosti, No. 1, p. 136, January – February, 2023.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Karakaş, O., Kardeş, F.B., Foti, P. et al. Dissimilar Welding Applications and Evaluation of Fatigue Behaviour of Welded Jo ints: An Overview. Strength Mater 55, 111–127 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-023-00507-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-023-00507-6