Abstract
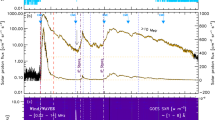
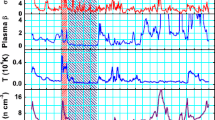
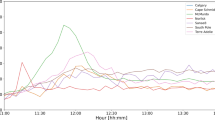
A ground level enhancement (GLE) event of solar cosmic rays refers to the sudden, sharp, and short-lived enhancement of energetic particles at ground level generated from a solar flare accompanied by a coronal mass ejection (CME). The study of GLE events not only provides the basis for the research of the origin, propagation, and acceleration of cosmic rays but also has important significance for space-weather research. In this article, we analyzed the temporal profile and flux variation of the electrons, X rays, and protons of 18 GLE events during Solar Cycles 23 and 24 using GOES series spacecraft data. The results suggested that the release time, onset time, peak time, and end time of the GLEs depend upon the energy and species of particles. The release time of protons with higher energies is later than for those with lower energies; the opposite is true for the onset time, peak time, and end time. The rise time decreases with the energy, and the recovery time increases first and then decreases with increasing energy. The energy spectrum of particles at onset time is harder than the peak spectrum. The energy spectrum at onset time is most affected by the CME speed, and the correlation of the peak energy spectrum and the flare longitude is strongest. The acceleration ability of CME-driven shock to low-energy particles is stronger than that of high-energy particles.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The GOES data are freely available through the NOAA network at www.ngdc.noaa.gov/stp/satellite/goes/index.html. The NM data are freely available through the Neutron Monitor Database at www.nmdb.eu/nest/index.php.
References
Cliver, E.W., Mekhaldi, F., Muscheler, R.: 2020, Solar longitude distribution of high-energy proton flares: fluences and spectra. Astrophys. J. Lett. 900, L11. DOI. ADS.
Firoz, K.A., Gan, W.Q., Li, Y.P., Rodríguez-Pacheco, J., Kudela, K.: 2019, On the possible mechanism of GLE initiation. Astrophys. J. 872, 178. DOI. ADS.
Forbush, S.E.: 1946, Three unusual cosmic-ray increases possibly due to charged particles from the Sun. Phys. Rev. 70, 771. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Usoskin, I.: 2005, Coronal mass ejections and ground level enhancements. In: Acharya, B.S., Gupta, S., Jagadeesan, P., Jain, A., Karthikeyan, S., Morris, S., Tonwar, S. (eds.) 29th Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC29: Pune) 1, TIFR, Mumbai, 169. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Yashiro, S., Akiyama, S., Mäkelä, P., Usoskin, I.G.: 2012, Properties of ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 23. DOI. ADS.
Gopalswamy, N., Xie, H., Akiyama, S., Yashiro, S., Usoskin, I.G., Davila, J.M.: 2013, The first ground level enhancement event of solar cycle 24: direct observation of shock formation and particle release heights. Astrophys. J. Lett. 765, L30. DOI. ADS.
Kahler, S.: 1994, Injection profiles of solar energetic particles as functions of coronal mass ejection heights. Astrophys. J. 428, 837. DOI. ADS.
Kahler, S.W., Vourlidas, A.: 2005, Fast coronal mass ejection environments and the production of solar energetic particle events. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12S01. DOI. ADS.
Karpov, S.N., Miroshnichenko, L.I., Vashenyuk, E.V.: 1998, Muon bursts at the Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope during energetic solar phenomena. Nuovo Cimento, C Geophys. Space Phys. 21C, 551. ADS.
Le, G.-M., Li, C., Zhang, X.-F.: 2017, Dependence of \(E \geq 100\) MeV protons on the associated flares and CMEs. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 17, 073. DOI. ADS.
Le, G.-M., Tang, Y.-H., Han, Y.-B.: 2006, Solar energetic particle event of 2005 January 20: release times and possible sources. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 6, 751. ADS.
Le, G.-M., Zhang, X.-F.: 2017, Dependence of large SEP events with different energies on the associated flares and CMEs. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 17, 123. DOI. ADS.
Li, C., Firoz, K.A., Sun, L.P., Miroshnichenko, L.I.: 2013, Electron and proton acceleration during the first ground level enhancement event of solar cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 770, 34. DOI. ADS.
Mewaldt, R.A., Cohen, C.M.S., Haggerty, D.K., Gold, R.E., Krimigis, S.M., Leske, R.A., Ogliore, R.C., Roelof, E.C., Stone, E.C., von Rosenvinge, T.T., Wiedenbeck, M.E.: 2003, Heavy ion and electron release times in solar particle events. In: Kajita, T., Asaoka, Y., Kawachi, A., Matsubara, Y., Sasaki, M. (eds.) Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC28: Tsukuba) 6, Universal Academy Press, Tokyo, 3313. ADS.
Mewaldt, R.A., Looper, M.D., Cohen, C.M.S., Haggerty, D.K., Labrador, A.W., Leske, R.A., Mason, G.M., Mazur, J.E., von Rosenvinge, T.T.: 2012, Energy spectra, composition, and other properties of ground-level events during solar cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. 171, 97. DOI. ADS.
Miroshnichenko, L.I., Klein, K.-L., Trottet, G., Lantos, P., Vashenyuk, E.V., Balabin, Y.V.: 2005, Electron acceleration and relativistic nucleon production in the 2003 October 28 solar event. Adv. Space Res. 35, 1864. DOI. ADS.
Mishev, A.L., Kocharov, L.G., Usoskin, I.G.: 2014, Analysis of the ground level enhancement on 17 May 2012 using data from the global neutron monitor network. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 670. DOI. ADS.
Mishev, A., Usoskin, I., Raukunen, O., Paassilta, M., Valtonen, E., Kocharov, L., Vainio, R.: 2018, First analysis of ground-level enhancement (GLE) 72 on 10 September 2017: spectral and anisotropy characteristics. Solar Phys. 293, 136. DOI. ADS.
Perez-Peraza, J.A., Márquez-Adame, J.C., Caballero-Lopez, R.A., Manzano Islas, R.R.: 2020, Spectra of the two official GLEs of solar cycle 24. Adv. Space Res. 65, 663. DOI. ADS.
Petrosian, V.: 2016, Particle acceleration in solar flares and associated CME shocks. Astrophys. J. 830, 28. DOI. ADS.
Poluianov, S.V., Usoskin, I.G., Mishev, A.L., Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 2017, GLE and sub-GLE redefinition in the light of high-altitude polar neutron monitors. Solar Phys. 292, 176. DOI. ADS.
Reames, D.V.: 1995, Solar energetic particles: a paradigm shift. Rev. Geophys. 33, 585. DOI. ADS.
Reames, D.V.: 2009a, Solar energetic-particle release times in historic ground-level events. Astrophys. J. 706, 844. DOI. ADS.
Reames, D.V.: 2009b, Solar release times of energetic particles in ground-level events. Astrophys. J. 693, 812. DOI. ADS.
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 1990, A summary of major solar proton events. Solar Phys. 127, 297. DOI. ADS.
Shea, M.A., Smart, D.F.: 2002, Solar proton event patterns: the rising portion of five solar cycles. Adv. Space Res. 29, 325. DOI. ADS.
Simnett, G.M.: 2006, The timing of relativistic proton acceleration in the 20 January 2005 flare. Astron. Astrophys. 445, 715. DOI. ADS.
Simpson, J.A.: 1990, Astrophysical phenomena discovered by cosmic ray and solar flare ground level events: the early years. In: Protheroe, R.J. (ed.) Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC21: Adelaide) 12, 187. ADS.
Tylka, A.J., Cohen, C.M.S., Dietrich, W.F., Krucker, S., McGuire, R.E., Mewaldt, R.A., Ng, C.K., Reames, D.V., Share, G.H.: 2003, Onsets and release times in solar particle events. In: Kajita, T., Asaoka, Y., Kawachi, A., Matsubara, Y., Sasaki, M. (eds.) Internat. Cosmic Ray Conf. (ICRC28: Tsukuba) 6, Universal Academy Press, Tokyo, 3305. ADS.
Vashenyuk, E.V., Balabin, Y.V., Perez-Peraza, J., Gallegos-Cruz, A., Miroshnichenko, L.I.: 2006, Some features of the sources of relativistic particles at the Sun in the solar cycles 21 – 23. Adv. Space Res. 38, 411. DOI. ADS.
Xu, Z.G., Li, C., Ding, M.D.: 2017, Observations of a coronal shock wave and the production of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 840, 38. DOI. ADS.
Zhao, M.-X., Le, G.-M.: 2020, A study on the dynamic spectral indices for SEP events on 2000 July 14 and 2005 January 20. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 20, 037. DOI. ADS.
Zhao, M.-X., Le, G.-M., Chi, Y.-T.: 2018, Investigation of the possible source for the solar energetic particle event on 2017 September 10. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 18, 074. DOI. ADS.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to GOES and NMDB for making their data available online. This work is jointly funded by the National Key R&D Program of China National (Grant No. 2018YFA0404202) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant No. 12147208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Jia, H., Feng, Y. et al. Study of Temporal Profile and Flux Variation of GLE Events During Solar Cycles 23 and 24 Using GOES Data. Sol Phys 297, 75 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02010-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-022-02010-8