Abstract
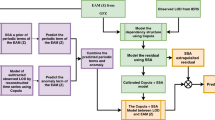
Real-time estimates of the Earth orientation parameters (EOP) are currently unavailable for users owing to the delay caused by complex data processing and heavy computation procedures. Accurate short-term predictions of the EOP are therefore essential for several real-time applications such as navigation and tracking of interplanetary spacecrafts and precise orbit determination of Earth satellites, whilst medium- and long-term predictions are required for Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) autonomous satellite navigation, climate forecasting as well as for astrogeodynamic studies. Universal time (UT1 – UTC) or its first time derivative, length of day (ΔLOD), representing the changes of the Earth’s rotation rate, are the most challenging to predict among the EOP. Various methods and techniques have been used to improve ΔLOD predictions since the present prediction accuracy is yet unsatisfactory even up a few days into the future. This study employs a popular time-series analysis method, called singular spectrum analysis (SSA), in combination with the neural network (NN) technique for medium- and long-term prediction of ΔLOD up to 2 years in the future. The SSA is first applied to extracting the predominant periodic components including annual and semiannual oscillations and irregular short-period signals in ΔLOD data. These extracted predominant periodic components are then extrapolated by the proposed SSA-based data filling strategy. Next, the residuals (the difference between these predominant components and the data themselves) are modeled and predicted by the NN technique. The predicted ΔLOD value is sum of the extrapolation of the predominant periodic components and the prediction of the residuals. The results show that the accuracy of the 180-day ahead predictions is worse than that by the combination of least squares (LS) extrapolation and a stochastic method including autoregressive and NN technology in terms of the mean absolute prediction error. However, the proposed SSA extrapolation in combination with NN modeling can achieve a noticeably better accuracy for the medium- and long-term predictions out 180 days than the combined LS + stochastic technology. The improvement in the prediction accuracy for lead time of 1 year and 2 years can reach up to 53% and 56%, respectively. The combined SSA extrapolation and NN modeling is thus very promising for medium- and long-term prediction of ΔLOD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyilmaz O. and Kutterer H., 2004. Prediction of Earth rotation parameters by fuzzy inference systems. J. Geodesy, 78, 82–93
Bizouard C., Lambert S., Gattano C., Becker O. and Richard J.V., 2019. The IERS EOP 14C04 solution for Earth orientation parameters consistent with ITRF 2014. J. Geodesy, 93, 621–633
Dick W. and Thaller D., 2020. IERS Annual Report 2018. Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, ISBN: 978-3-86482-136-3
Dill R., Dobslaw H. and Thomas M., 2019. Improved 90-day Earth orientation predictions from angular momentum forecasts of atmosphere, ocean, and terrestrial hydrosphere. J. Geodesy, 93, 287–295
Ding H., An Y. and Shen W., 2021. New evidence for the fluctuation characteristics of intradecadal periodic signals in length-of-day variation. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth, 126, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JB020990
Duan P.S., Liu G.Y., Liu L.T., Hu X.G., Hao X.G., Huang Y., Zhang Z.M. and Wang B.B., 2015. Recovery of the 6-year signal in length of day and its long-term decreasing trend. Earth Planets Space, 67, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0328-6
Gambis D. and Luzum B., 2011. Earth rotation monitoring, UT1 determination and prediction. Metrologia, 48, https://doi.org/10.1088/0026-1394/48/4/S06.
Ghil M., Allen M.R., Dettinger M.D., Ide K., Kondrashov D., Mann M.E., Robertson A.W., Saunders A., Tian Y., Varadi F. and Yiou P., 2002. Advanced spectral methods for climatic time series. Rev. Geophys., 40, 31–41
Gross R.S, Marcus S.L., Eubanks T.M., Dickey J.O. and Keppenne C.L., 1996. Detection of an ENSO signal in seasonal length-of-day variations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 3373–3376
Guessoum S., Belda S., Ferrandiz J.M., Modiri S., Raut S., Dhar S., Heinkelmann R. and Schuh H., 2022. The short-term prediction of length of day using 1D convolutional neural networks (1D CNN). Sensors, 22, https://doi.org/10.3390/s22239517
Guo J.Y., Li Y.B., Dai C.L. and Shum C.K., 2013. A technique to improve the accuracy of Earth orientation prediction algorithms based on least squares extrapolation. J. Geodyn., 70, 36–18
Golyandina N.E., Nekrutkin V.V. and Zhigljavsky A.A., 2001. Analysis of Time Series Structure: SSA and Related Techniques. Chapman&Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL
Huang G.B., Zhu Q.Y. and Siew C.K., 2006. Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70, 489–501
Jin X., Guo J.Y, Shen Y. and Liu X., 2021. Application of singular spectrum analysis and multilayer perceptron in the mid-long-term polar motion prediction. Adv. Space Res., 68, 3562–3573
Johnson T.J., Luzum B.J. and Ray J.R., 2005. Improved near-term Earth rotation predictions using atmospheric angular momentum analysis and forecasts. J. Geodyn.,39, 209–221
Kalarus M., Schuh H., Kosek W., Akyilmaz O., Bizouard C., Gambis D., Gross R., Jovanovic B., Kumakshev S., Kutterer H., Cerveira P.J.M., Pasynok S. and Zotov L., 2010. Achievements of the Earth orientation parameters prediction comparison campaign. J. Geodesy, 84, 587–596
Kosek W., McCarthy D. and Luzum B., 1998. Possible improvement of Earth orientation forecast using autocovariance prediction procedures. J. Geodesy, 72, 189–199
Kur T., Dobslaw H., Śliwińska J., Nastula J., Wińska M. and Partyka A., 2022. Evaluation of selected short-term predictions of UT1-UTC and LOD collected in the second earth orientation parameters prediction comparison campaign. Earth Planets Space, 74, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-022-01753-9
Lei Y., Guo M., Cai H.B., Hu D.D. and Zhao D.N., 2015a. Prediction of length-of-day using Gaussian process regression. J. Navig., 68, 563–575
Lei Y., Zhao D.N. and Cai H.B., 2015b. Prediction of length-of-day using extreme learning machine. J. Geod. Geodyn., 6, 151–159
Liao D.C., Wang Q.J., Zhou Y.H, Liao X.H. and Huang C.L., 2012. Long-term prediction of the Earth orientation parameters by the artificial neural network technique. J. Geodyn., 62, 87–92
Michalczak M. and Ligas M., 2021. Kriging-based prediction of the Earth’s pole coordinates. J. Appl. Geodesy, 15, 233–241
Modiri S., Belda, S., Heinkelmann R., Ferrándiz J.M. and Schuh H., 2018. Polar motion prediction using the combination of SSA and copula-based analysis. Earth, planets and space, 70, 1–18.
Nastula J., Chin T.M., Gross, R., Śliwińska J. and Wińska M., 2020. Smoothing and predicting celestial pole offsets using a Kalman filter and smoother. J. Geodesy, 94, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-020-01349-9
Niedzielski T and Kosek W., 2008. Prediction of UT1-UTC, LOD and AAM χ3 by combination of least-squares and multivariate stochastic methods. J. Geodesy, 82, 83–92
Petit G. and Luzum B. (Eds), 2010. IERS Conventions (2010). Verlag des Bundesamts für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, ISBN: 1019-456
Refaeilzadeh P., Tang L. and Liu H., 2009. Cross-validation. In: Liu L. and Tamer Özsu M. (Eds), Encyclopedia of Database Systems, 5, 532–538. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-39940-9_565
Schuh H., Ulrich M., Egger, D., Müller J. and Schwegmann W., 2002. Prediction of Earth orientation parameters by artificial neural networks. J. Geodesy, 76, 247–258
Shen Y., Guo J.Y., Liu X., Kong Q.L., Guo L.X. and Li W., 2018. Long-term prediction of polar motion using a combined SSA and ARMA model. J. Geodesy, 92, 333–343
Shen Y., Guo J.Y., Liu X., Wei X.B. and Li W.D., 2017. One hybrid model combining singular spectrum analysis and LS+ARMA for polar motion prediction. Adv. Space Res., 59, 513–523
Vautard R., Yiou P. and Ghil M., 1992. Singular-spectrum analy sis: A toolkit for short, noisy chaotic signals. Physica D, 58, 95–126.
Wang Q.J., Du Y.N. and Liu J., 2014. Introducing atmospheric angular momentum into prediction of length of day change by generalized regression neural network model. J. Cent. South Univ., 21, 1396–1401
Xu X.Q. and Zhou Y.H., 2015. EOP prediction using least square fitting and autoregressive filter over optimized data intervals. Adv. Space Research, 56, 2248–2253
Yang Y.G., Nie W.F., Xu T.H., Fang Z.L., Xue H.J. and Sun Z.Z., 2022. Earth orientation parameters prediction based on the hybrid SSA+LS+SVM model. Meas. Sci. Technol., 33, https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/ac8ec6
Zhao D.N. and Lei Y., 2020. A technique to reduce the edge effect in least squares extrapolation for enhanced Earth orientation prediction. Stud. Geophys. Geod., 64, 293–305
Zhigljavsky A., 2010. Singular spectrum analysis for time series: introduction to this special issue. Stat. Interface, 3, 255–258
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the IERS and M. Kalarus for providing ΔLOD observations from the C04 series and predictions from the 1st EOP PCC, respectively. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11503031) and the Shaanxi Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 2023-JC-YB-057 and 2022-JM031).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, Y., Zhao, D. & Guo, M. Medium- and long-term prediction of length-of-day changes with the combined singular spectrum analysis and neural networks. Stud Geophys Geod 67, 107–123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-022-0558-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-022-0558-6