Abstract
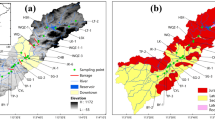
Bharathapuzha River is the second longest river in southwest India, where three physiographic regions show a distinctive spatial variation and their bed sediments can be considered environmental hosts for end-products generated by human activities and natural radionuclide components. Thus, the study of this river sediments in SW India is important not only because they are recorders of adverse human impacts (e.g., intense agricultural activities and urban pollution), but also because of their potential health hazards due to their common use as construction materials. Magnetic (e.g., magnetic susceptibility, anhysteretic remanent magnetisation and isothermal remanent magnetisation), radionuclide (226Ra, 232Th and 40K) and chemical (trace and major elements) measurements were carried out in bed sediment samples along 33 sites from the uppermost catchment downstream. Magnetic measurements show the dominance of ferrimagnetic minerals; their concentration ranges widely along the river and between regions, showing up to 7-fold higher values for concentration-dependent magnetic parameters, e.g., mean values of saturation of isothermal remanent magnetisation acquisition are 67.9 and 9.4 × 10-3 Am2 kg-1 for highland and lowland regions, respectively. Multivariate statistical analyses show the existence of relationships between magnetic, radioactivity and chemical variables. In particular, magnetic concentrationdependent parameters are significantly correlated with radioactivity variables 40K and 226Ra (with concentrations about 20% higher than the worldwide mean values), as well as with some elements: Fe, Ca and P. Such analyses also show differences between physiographic regions where samples from the highland (and lowland) region are well grouped showing higher (lower) magnetic concentrations and lower (higher) coercivity minerals. The spatial variation of magnetic parameters along the river can be related to the influence of both natural sources and human activities, i.e. urbanisation and intense agricultural activities. In this sense, environmental magnetism data provide very useful tools to investigate adverse human activities occurring in the riverine environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agustine E., Fitriani D., Safiuddin L.O, Tamuntuan G. and Bijaksana S., 2013. Magnetic susceptibility properties of pesticide contaminated volcanic soil AIP Conference Proceedings, 1554, 230–233.
Akhtar N., Tufail M., Ashraf M. and Mohsin Iqbal M., 2005. Measurement of environmental radioactivity for estimation of radiation exposure from saline soil of Lahore, Pakistan. Radiat. Meas., 39, 11–14.
Alharbi W.R., 2013. Natural radioactivity and dose assessment for brands of chemical and organic fertilizers used in Saudi Arabia. J. Modern Phys., 4, 344–348.
Basak P., James E.J. and Nandeshwar M.D., 1995. Water Atlas of Kerala. CWRDM/ STEC, Calicut, India.
Beckwith P., Ellis J., Revitt D. and Oldfield F., 1986 Heavy metal and magnetic relationships for urban source sediments. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter., 42, 67–75.
Bulman R.A., Johnson T.E. and Reed A.L., 1984. An examination of new procedures for fractionation of plutonium- and americium-bearing sediments. Sci. Tot. Environ., 35, 239–250.
Chandrajith R., Seneviratna S., Wickramaarachchi K., Attanayake T., Aturaliya T.N.C. and Dissanayake C.B., 2010. Natural radionuclides and trace elements in rice field soils in relation to fertilizer application: study of a chronic kidney disease area in Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci., 60, 193–201.
Chaparro M.A.E, Bidegain J.C., Sinito A.M., Jurado S. and Gogorza C.S., 2004. Relevant magnetic parameters and heavy metals from relatively polluted stream-sediments- spatial distribution along a cross-city stream in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Stud. Geophys. Geod., 48, 615–636.
Chaparro M.A.E, Gogorza C.S.G., Chaparro M.A.E., Irurzun M.A. and Sinito A.M., 2006. Review of magnetism and pollution studies of various environments in Argentina. Earth Planets Space, 58, 1411–1422.
Chaparro M.A.E., Sinito A.M., Ramasamy V., Marinelli C., Chaparro M.A.E., Mullainathan S. and Murugesan S., 2008. Magnetic measurements and pollutants of sediments from Cauvery and Palaru River, India. Environ. Geol., 56, 425–437.
Chaparro M.A.E., Chaparro M.A.E., Rajkumar P., Ramasamy V. and Sinito A.M., 2011. Magnetic parameters, trace elements and multivariate statistical studies of river sediments from south eastern India: A case study from Vellar River. Environ. Earth Sci., 63, 297–310.
Chaparro M.A.E., Chaparro M.A.E. and Sinito A.M., 2012. An interval fuzzy model for magnetic monitoring: estimation of a pollution index. Environ. Earth Sci., 66, 1477–1485.
Chaparro M.A.E., Suresh G., Chaparro M.A.E., Ramasamy V. and Sinito A.M., 2013. Magnetic studies and elemental analysis of river sediments: A case study from the Ponnaiyar River (southeastern India). Environ. Earth Sci., 70, 201–213.
Chauhan P., Chauhan R.P. and Gupta M., 2013. Estimation of naturally occurring radionuclides in fertilizers using gamma spectrometry and elemental analysis by XRF and XRD techniques. Microchem. J., 106, 73–78.
Chen W., Chang A.C. and Wu L., 2007. Assessing long-term environmental risks of trace elements in phosphate fertilizers. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe., 67, 48–58.
De Meijer R.J., Put L.W., Bergman R., Landeweer G., Riezebos H.J., Schuiling R.D., Scholten M.J. and Veldhuizen A., 1985.. Local variation of outdoor radon concentrations in the Netherlands and physics properties of sand with enhanced natural radioactivity. Sci. Tot. Environ., 45, 101–109.
De Meijer R.J., Lesscher H.M.E., Schuiling R.D. and Eldburg M.E., 1990. Estimate of the heavy mineral content in sand and its provenance by radiometric methods. Nucl. Geophys., 4, 450–460.
Dearing J., 1999. Magnetic susceptibility. In: Walden J., Oldfield F. and Smith J. (Eds), Environmental Magnetism: a Practical Guide. Technical Guide No. 6. Quaternary Research Association, London U.K., 35–62.
Dearing J., Dann R., Hay K., Lees J., Loveland P., Maher B. and O’Grady K., 1996. Frequencydependent susceptibility measurements of environmental materials. Geophys. J. Int., 124, 228–240.
Desenfant F., Petrovský E. and Rochette P., 2004. Magnetic signature of industrial pollution of stream sediments and correlation with heavy metals: case study from South France. Water Air Soil Pollut., 152, 297–312.
Dunlop D.J. and Özdemir Ö., 1997. Rock Magnetism. Fundamentals and Frontiers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K., 573 pp.
El-Bahi S.M., 2004. Assessment of radioactivity and radon exhalation rate in Egyptian cement. Health Phys., 86, 517–522.
El-Gamal A., Nasr S. and El-Taher A., 2007. Study of the spatial distribution of natural radioactivity in the upper Egypt Nile River sediments. Radiat. Meas., 42, 457–465.
Elejalde C., Herranz M., Romero F. and Legarda F., 1996. Correlations between soil parameters and radionuclide contents in samples from Biscay (Spain). Water Air Soil Pollut., 89, 23–31.
Evans M.E. and Heller F., 2003. Environmental Magnetism, Principles and Applications of Enviromagnetics. Academic Press, New York, 299 pp.
Franke C., Kissel C., Robin E., Bonté P. and Lagroix F., 2009. Magnetic particle characterization in the Seine river system: Implications for the determination of natural versus anthropogenic input. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 10, Q08Z0.
Guereschi A. and Baldo E., 1993. Petrología y geoquímica de las rocas metamórficas del sector centro-oriental de la Sierra de Comechingones, Córdoba. XII Congreso Geológico Argentino y II Congreso de Exploración de Hidrocarburos. Actas I: 1–5 (in Spanish).
Hunt A., Jones J. and Oldfield F., 1984. Magnetic measurements and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates of anthropogenic origin Sci. Tot. Environ., 33, 129–139.
Jibiri N.N. and Fasae K.P., 2012. Activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th and 40K in brands of fertilizer used in Nigeria. Radiat. Prot. Dosim., 148, 132–137.
Jordanova D.V., Hoffmann V. and Fehr T.K., 2004. Mineral magnetic characterization of anthropogenic magnetic phases in the Danube river sediments (Bulgarian part). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 221, 71–89.
Kannan N. and Joseph S., 2009. Quality of groundwater in the shallow aquifers of a paddy dominated agricultural river basin, Kerala, India. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol., 3, 1137–1155.
King J., Banerjee S.K., Marvin J. and Özdemir Ö., 1982. A comparison of different magnetic methods for determining the relative grain size of magnetite in natural materials: Some results from lake sediments. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 59, 404–419.
Knab M., Hoffmann V., Petrovský E., Kapicka A., Jordanova N. and Appel E., 2006. Surveying the anthropogenic impact of the Moldau river sediments and nearby soils using magnetic susceptibility. Environ. Geol., 49, 527–535.
Krishnamoorthy N., Mullainathan S., Mehra R., Chaparro M.A.E. and Chaparro M.A.E., 2014. Radiation impact assessment of naturally occurring radionuclides and magnetic mineral studies of Bharathapuzha river sediments, South India. Environ. Earth. Sci., 71, 3593–3604.
Lecomte K.L., 2006. Control geomorfológico en la geoquímica de los ríos de Montaña, Sierras Pampeanas, Provincia de Córdoba, Argentina. PhD Thesis, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas, Físicas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Córdoba, Córdoba, Argentina, 279 pp. (in Spanish).
Ligero R.A., Ramos-Lerate I., Barrera M. and Casas-Ruiz M., 2001. Relationships between sea-bed radionuclide activities and some sedimentological variables J. Environ. Radioact., 57, 7–19.
Magesh N.S., Jitheshlal K.V., Chandrasekar N. and Jini K.V., 2013. Geographical information system-based morphometric analysis of Bharathapuzha river basin, Kerala, India. Appl. Water. Sci., 3, 467–477.
Magiera T., Strzyszcz Z. and Kostecki M., 2002. Seasonal changes of magnetic susceptibility in sediments from Lake Zywiec (South Poland). Water Air Soil Pollut., 141, 55–71.
Maher B.A., Thompson R. and Hounslow M.W., 1999. Introduction. In: Maher B.A. and Thompson R. (Eds), Quaternary Climate, Environments and Magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K., 1–48.
McCubbin D., Leonard K.S., Young A.K., Maher B.A. and Bennett S., 2004. Application of magnetic extraction technique to assess radionuclide-mineral association in Cumbrian shoreline sediments. J. Environ. Radioact., 77, 11–131.
McLennan S.M., 2001. Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2, 2000GC000109.
Milliman J.D. and Farnsworth K.L., 2011. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean. A Global Synthesis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K.
Montes M.L., Mercader R.C., Taylor M.A., Runco J. and Desimoni J., 2012. Assessment of natural radioactivity levels and their relationship with soil characteristics in undisturbed soils of the northeast of Buenos Aires province, Argentina J. Environ. Radioact., 105, 30–39.
Mustonen R., 1985. Radioactivity of fertilizers in Finland. Sci. Tot. Environ., 45, 127–134.
Nikhil Raj P.P. and Azeez P.A., 2012. Morphometric analysis of a tropical medium river system: A case from Bharathapuzha River, Southern India. Open J. Modern Hydrol., 2, 91–98.
Parizanganeh A.H., Bijnavand V., Zamani A.A. and Hajabolfath A., 2012. Concentration, distribution and comparison of total and bioavailable heavy metals in top soils of Bonab District in Zanjan Province. Open J. Soil Sci., 2, 123–132.
Peters C. and Dekkers M.J., 2003. Selected room temperature magnetic parameters as a function of mineralogy, concentration and grain size. Phys. Chem. Earth, 28, 659–667.
Petrovský E. and Elwood B.B., 1999. Magnetic monitoring of air, land and water pollution. In: Maher B.A. and Thompson R. (Eds), Quaternary Climate, Environments and Magnetism. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge U.K., 279–322.
Raj N. and Azeez P.A., 2009. Spatial and temporal variation in Surface water chemistry of a tropical river, the river Bharathapuzha, India. Current Sci., 96, 245–251.
Ramasamy V., Paramasivam K., Suresh G. and Jose M.T., 2014. Role of sediments characteristcs on natural radiation level of the Vaigai river sediment, Tamilnadu, India. J. Environ. Radioact., 127, 64–74.
Rapela C.W., 1982. Aspectos geoquímicos y petrológicos del Batolito de Achala, provincia de Córdoba. Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina, 37, 314–330 (in Spanish).
Righi S., Lucialli P. and Bruzzi L., 2005. Health and environmental impacts of a fertilizer plant — Part I: assessment of radioactive pollution J. Environ. Radioact., 82, 167–182.
Roselli C., Desideri D., Assunta Meli M. and Feduzi L., 2010. Sequential extraction for the leachability evaluation of phosphate fertilizers. Microchem. J., 95, 373–376.
Sakthimurugan S., 2007. Groundwater Information Booklet of Thrissur District, Kerala State. Central Ground Water Board, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India (http://cgwb.gov.in/District_Profile/Kerala/Thrissur.pdf).
Sandeep K., Shankar R. and Krishnaswamy J., 2011. Assessment of suspended particulate pollution in the Bhadra River catchment, Southern India: an environmental magnetic approach. Environ. Earth Sci., 62, 625–637.
Savci S., 2012. An agricultural pollutant: chemical fertilizer. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Develop., 3, 77–80.
Scholger R., 1998. Heavy metal pollution monitoring by magnetic susceptibility measurements applied to sediments of the river Mur (Styria, Austria). Eur. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys., 3, 25–37.
Scholten L.C. and Timmermans C.W.M., 1996. Natural radioactivity in phosphate fertilizers. Fertil. Res., 43, 103–107.
Sreela S.R., 2009. An Integrated Study on the Hydrogeology of Bharathapuzha River Basin, South West Coast of India. Ph.D Thesis, Cochin University of Science and Technolology, Cochin, Kerala, India.
Sreela R., Rej S., Girish G., Rajesh R. and Kurian S., 2012. A numerical weighted parameter rating (WPR) for artificial groundwater recharging in Bharathapuzha river basin: Southern India Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng., 5, 268–275.
Suresh G., Ramasamy V., Meenakshisundaram V., Venkatachalapathy R. and Ponnusamy V., 2011. A relationship between the natural radioactivity and mineralogical composition of the Ponnaiyar river sediments, India. J. Environ. Radioact., 102, 370–377.
Thompson R. and Oldfield F., 1986. Environmental Magnetism. Allen & Unwin Publishers Ltd., London U.K., 225 pp.
Tume P., Bech J., Longan L., Tume L., Reverter F. and Sepúlveda B., 2006. Trace elements in natural surface soils in Sant Climent (Catalonia, Spain). Ecol. Eng., 27, 145–152.
UNSCEAR, 2000. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effect of Atomic Radiation. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation. Report to General Assembly. United Nations Organization, New York.
Veiga R., Sancher N., Anjos R.M., Macario K., Bastos J., Iguatemya M., Aguiar J.G., Santos A.M.A., Mosquera B., Carvalho C., Baptista F.M. and Umisedo N.K., 2006. Measurement of natural radioactivity in Brazilian beach sands. Radiat. Meas., 4, 189–196.
Yafa C. and Farmer J.G., 2006. A comparative study of acid-extractable and total digestion methods for the determination of inorganic elements in peat material by inductively coupled plasmaoptical emission spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 557, 296–303.
Yang T., Liu Q., Chan L. and Liu Z., 2007. Magnetic signature of heavy metals pollution of sediments: Case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environ. Geol., 52, 1639–1650.
Zhang C.X., Qiao Q., Piper J.D.A. and Huang B., 2011. Assessment of heavy metal pollution from a Fe-smelting plant in urban river sediments using environmental magnetic and geochemical methods. Environ. Pollut., 159, 3057–3070.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaparro, M.A.E., Krishnamoorthy, N., Chaparro, M.A.E. et al. Magnetic, chemical and radionuclide studies of river sediments and their variation with different physiographic regions of Bharathapuzha river, southwestern India. Stud Geophys Geod 59, 438–460 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-014-0145-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11200-014-0145-6