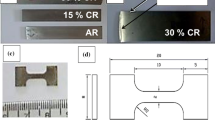
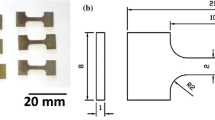
The paper studies the evolution of the structure, phase composition, and impact toughness of the Ti-6Al-3Mo titanium alloy after two types of processing. Mode I consists of heating and hot helical rolling, followed by quenching into water. In mode II, an additional air quenching is used between the rolling and quenching processes. This approach, combining two alloy cooling stages (in air and in water), makes it possible to control the recrystallization time and form a gradient structure over the cross-section of the bar stock. The processing of titanium alloy according to mode I leads to a decrease of the impact strength. An addition of an air-cooling stage (in mode II) leads to an insignificant decrease in the hardness and an increase of the alloy toughness. The treatment of the titanium alloy by modes I and II results in the formation of a structure containing large grains of the primary α-phase in a thin-plate structure of the secondary α-phase in the β-phase. It is shown that these structural states of the alloy affect the crack propagation under impact loading and change the amount of the energy spent on the complete failure of the samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. C. Ren, Y. J. Liu, H. B. Zhang, et al., Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 49, No. 3 (2020).
Z. Y. Li, G. Q. Wu, and Z. Huang, Mater. Res. Express., 5, No. 3 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab39e.
F. Li, B. Qi, Y. Zhang, et al., Metals, 11, No. 2, 346 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020346.
R. Julien, V. Velay, V. Vidal, et al., Mater. Lett., 208, 7 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.05.050.
L. Wanying, L. Yuanhua, C. Yuhai, et al., Rare Metal Mater. Eng., 46, No. 3, 634 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30109-1.
S. P. Belov, M. Ya. Brun, and S. G. Glazunov, Metallography of Titanium and its Alloys [in Russian] (Exec. Eds. S. G. Glazunov and B. A. Kolachev), Metallurgiya, Moscow (1992).
X. Yang, Z. Zhao, Y. Ning, and H. Guo, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 745, 240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.12.046.
L. E. Popova and A. A. Popov, Austenite Transformation Diagrams in Steels and Beta-solutions in Titanium Alloys: A heat-treater reference book [in Russian], Metallurgiya, Moscow (1991).
H. Shao, Y. Zhao, P. Ge, and W. Zeng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 586, 215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2013.08.012.
S. L. Semiatin, S. L. Knisley, P. N. Fagin, et al., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 34, No. 10, 2377 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0300-0.
S. L. Semiatin, T. M. Lehner, J. D. Miller, et al., Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 38, 910 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-007-9088-7.
N. Pushilina, E. Stepanova, A. Stepanov, and M. Syrtanov, Metals, 11, No. 3, 512 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11030512.
A. Bahador, J. Umeda, and H. Ghandvar, Mater. Charact., 172, 110855 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110855.
A. Ebuzer, S. Yalcinkaya, and Y. Sahin, Mater. Res. Express., 7, No. 3, 035402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab7c88.
D. Wojtas and K. Wierzbanowski, J. Alloys Compd. 837, 155576 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155576.
Yu. R. Kolobov, Russ. Phys. J., 61, No. 4, 611 (2018). URL: https://www. elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=32836577.
S. V. Razorenov, G. V. Garkushin, A. S. Savinykh, et al., Fizich. Mezomekh., 24, No. 3, 17 (2021).
J. Xu, W. Zeng, X. Sun, and Z. Jia, J. Alloys Compd., 637, 449 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.03.042.
G. Chi, H. Liu, and D. Yi, Mater. Lett., 284, 128925 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128925.
Y. Chong, T. Bhattacharjee, Y. Tian, et al., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 71, 138 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2020.08.057.
E. V. Naydenkin, I. P. Mishin, I. V. Ratochka, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 810, 140968 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.140968.
M. Motyka, J. Sieniawski, and W. Ziaja, Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 60, 2033 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/amm-2015-0345.
X. Zhu, Q. Fan, X. Liu, et al., Prog. Natural Sci.: Mater. Int., 31, No. 1, 105 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2020.11.007.
R. Dong, J. Li, H. Kou, et al., Mater. Charact., 129, 135 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2017.04.031.
J. Xu, W. Zeng, Y. Zhao, and Z. Jia, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 676, 434 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.017.
B. A. Kolachev, Yu. B. Egorova, and S. B. Belova, Metal Science and Heat Treatment, 50, No. 7, 367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11041-008-9061-0.
Z. Zhao, J. Chen, H. Tan, et al., Scripta Mater., 146, 187 (2018). – https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2017.11.021.
M. Motyka, K. Kubiak, J. Sieniawski, and W. Ziaja, Comprehensive Materials Processing, 2, 7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-096532-1.00202-8.
G. Chi, D. Yi, B. Jiang, et al., J. Alloys Compd., 852, No. 25, 156581 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156581.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Fizika, No. 5, pp. 22–28, May, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vlasov, I.V., Gomorova, J.F., Yakovlev, A.V. et al. The Influence of Helical Rolling and Controlled Cooling on Impact Toughness of Ti-6Al-3Mo Titanium Alloy. Russ Phys J 65, 786–793 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02698-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11182-022-02698-y