Abstract
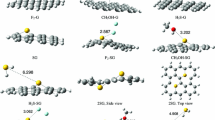
The adsorption behavior and hydrolysis mechanism of COS and CS2 on a graphene surface were studied by using density functional theory. It could be concluded that the most stable adsorption configuration for COS was in the form of straight line at the B site, and the adsorption energy was − 0.830 eV. However, the most stable adsorption structure for CS2 with an adsorption energy of − 0.867 eV was the three atoms in CS2 interacting with the C atoms on the graphene surface. By contrasting the two values, the conclusion that the CS2 would adsorb on the graphene surface firstly when the COS and CS2 exist simultaneously was easy to draw. Meanwhile, for the H2O, the maximal adsorption energy was − 0.244 eV and the corresponding configurations were in the form of a downward and upward “V”. So the COS and CS2 will adsorb on the graphene surface first when they react with H2O. Then, the gaseous H2O and adsorptive COS/CS2 create a low-energy system. The energy barrier values of COS and CS2 were 122.648 and 314.108 kcal/mol, respectively, during the hydrolysis process on the graphene surface. And the reaction energies were − 6.335 and 167.561 kcal/mol, respectively. Namely, when the two molecules resulted in the same final products, the COS initiated the reaction more easily.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Wang, D. Wu, S. Wang, Q. Yuan, J. Environ. Sci. China 20, 436 (2008)
A.L. Rich, J.T. Patel, Environ. Health Insights 10, 51 (2016)
B. Delley, J. Chem. Phys. 113, 7756 (2000)
B.C. Wood, S.Y. Bhide, D. Dutta, V.S. Kandagal, A.D. Pathak, S.N. Punnathanam, K.G. Ayappa, S. Narasimhan, J. Chem. Phys. 137, 8260 (2012)
X. Sun, P. Ning, X.L. Tang, H.H. Yi, K. Li, D. He, X.M. Xu, B. Huang, R.Y. Lai, J. Energy Chem. 23, 221 (2014)
H.H. Yi, K. Li, X.L. Tang, P. Ning, J.H. Peng, C. Wang, D. He, Chem. Eng. J. 230, 220 (2013)
P. Ning, K. Li, H.H. Yi, X.L. Tang, J.H. Peng, D. He, H.Y. Wang, S.Z. Zhao, J. Phys. Chem. C 116, 17055 (2012)
K. Li, X. Song, P. Ning, H.H. Yi, X.L. Tang, C. Wang, Energy Technol. Ger. 3, 136 (2015)
L. Yu, H. Gao, J. Zhao, J. Qiu, C. Yu, J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 8, 2492 (2011)
W.J. Liu, H. Jiang, H.Q. Yu, Chem. Rev. 115, 12251 (2015)
H.J. Zhang, W.L. Cen, J. Liu, J.X. Guo, H.Q. Yin, P. Ning, Appl. Surf. Sci. 324, 61 (2014)
H.H. Yi, S.Z. Zhao, X.L. Tang, C.Y. Song, F.Y. Gao, B.W. Zhang, Z.X. Wang, Y.R. Zuo, Fuel 128, 268 (2014)
W.J. Liu, F.X. Zeng, H. Jiang, X.S. Zhang, Bioresour. Technol. 102, 8247 (2011)
J. Li, D.H.L. Ng, P. Song, C. Kong, Y. Song, P. Yang, Biomass Bioenerg. 75, 189 (2015)
K. Sakanishi, Z. Wu, A. Matsumura, I. Saito, T. Hanaoka, T. Minowa, M. Tada, T. Iwasaki, Catal. Today 104, 94 (2005)
C. Deng, Q.G. Li, Y. Ren, N.B. Wong, S.Y. Chu, H.J. Zhu, J. Comput. Chem. 29, 466 (2008)
C. Deng, X.P. Wu, X.M. Sun, Y. Ren, Y.H. Sheng, J. Comput. Chem. 30, 285 (2010)
C. Wilson, D.M. Hirst, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 91, 793 (1995)
M.L. Mckee, Chem. Phys. Lett. 201, 41 (1993)
H. Ghiassi, H. Raissi, RSC Adv. 5, 84022 (2015)
W.J. Wang, L. Fan, G. Wang, Appl. Surf. Sci. 414, 92 (2017)
X.Q. Niu, L.X. Ling, J.J. Song, B.J. Wang, China. Sci. Paper 8, 1261 (2013)
O. Faye, A. Raj, V. Mittal, A.C. Beye, Comp. Mater. Sci. 117, 110 (2016)
G. Feng, C.F. Huo, C.M. Deng, L. Huang, Y.W. Li, J.G. Wang, H.J. Jiao, J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 304, 58 (2009)
W.J. Liu, H. Jiang, H.Q. Yu, Chem. Rev. 115, 12251 (2015)
B. Huang, B. Chen, R. Chen, Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 28, 143 (2015)
E.N.C. Paura, W.F.D. Cunha, L.F. Roncaratti, J.B.L. Martins, G.M.E. Silva, R. Gargano, RSC Adv. 5, 27412 (2015)
X.P. Chen, N. Yang, J.M. Ni, M. Cai, H.Y. Ye, C.K.Y. Wong, S.Y.Y. Leung, T.L. Ren, IEEE Electr. Device Lett. 36, 1366 (2015)
S. Seenithurai, R.K. Pandyan, S.V. Kumar, P. Munieswaran, C. Saranya, AIP Conf. Proc. 1665, 377 (2015)
W.B. Liu, Y. Liu, R.G. Wang, L. Hao, D.J. Song, Z. Li, Phys. Status Solidi B 251, 229 (2014)
L. Ling, R. Zhang, P. Han, B. Wang, J. Mol. Model. 18, 1625 (2012)
X.H. Li, S.J. Ren, X.G. Wei, Y. Zeng, G.W. Gao, Y. Ren, J. Zhu, K.C. Lau, W.K. Li, J. Phys. Chem. A 118, 3503 (2014)
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, M. Ernzerhof, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 3865 (1997)
S. Grimme, J. Comput. Chem. 27, 1787 (2006)
G.S. Rao, T. Hussain, M.S. Islam, M. Sagynbaeva, D. Gupta, P. Panigrahi, R. Ahuja, Nanotechnology 27(1), 015502 (2015)
B. Delley, J. Chem. Phys. 92, 508 (1990)
T.A. Halgren, W.N. Lipscomb, Chem. Phys. Lett. 49, 225 (1977)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21667015, 51408282 and 51708266), China Scholarship Council (201508530017, 201608530169 and 201608740011) and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Kunming University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, S., Yang, H., Ning, P. et al. Density functional theory study on the hydrolysis process of COS and CS2 on a graphene surface. Res Chem Intermed 44, 2637–2651 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3251-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-018-3251-1