Abstract
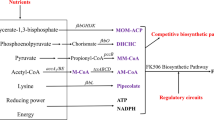
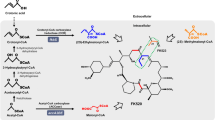
FK506, a widely used immunosuppressant, is produced by industrial fermentation using Streptomyces tsukubaensis. In this study, a novel precursor, salicyl alcohol, was added and provided significant improvement in FK506 production. Furthermore, differences of the expression of the structural genes between the two media were also investigated. The results showed that the expression of key genes in enriched medium was much higher than that in the control. Compared with the non-enriched medium, the enriched medium caused 52.25-% enhancement of FK506 production. Salicyl alcohol could play a crucial role in the transcription of FK506 structural genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Kino, H. Hatanaka, M. Hashimoto, M. Nishiyama, T. Goto, M. Okuhara et al., FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 40(9), 1249–1255 (1987)
J. Turło, W. Gajzlerska, M. Klimaszewska, M. Król, M. Dawidowski et al., Enhancement of tacrolimus productivity in Streptomyces tsukubaensis by the use of novel precursors for biosynthesis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 51(6), 388–395 (2012)
A.W. Thomson, P.B. Carroll, J. McCauley, J. Woo, K. Abu-Elmagd, T.E. Starzl et al., FK 506: a novel immunosuppressant for treatment of autoimmune disease. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 14(4), 323–344 (1993)
B.G. Gold, Neuroimmunophilin ligands: evaluation of their therapeutic potential for the treatment of neurological disorders. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 9(10), 2331–2342 (2000)
J. Liu, J.D. Farmer Jr, W.S. Lane, J. Friedman, I. Weissman, S.L. Schreiber, Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin a and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell 66(4), 807–815 (1991)
J.D. Pirsch, J. Miller, M.H. Deierhoi, F. Vincenti, R.S. Filo, A comparison of tacrolimus (FK-506) and cyclosporine for immunosuppression after cadaveric renal transplantation. FK506 kidney transplant study group. Transplant. 63(7), 977–983 (1997)
H. Jiang, M. Kobayashi, Differences between cyclosporin A and tacrolimus in organ transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 31(5), 1978–1980 (1999)
D. Kelly, P. Jara, B. Rodeck, R. Reding, O. Bernard, M. Burdelski et al., Tacrolimus dual therapy versus cyclosporin-microemulsion triple therapy in pediatric liver transplantation: results from a multicentre randomized trial. Am. J. Transplant. 2(Suppl 3), 351 (2002)
T. Kino, H. Hatanaka, S. Miyata, N. Inamura, M. Nishiyama, T. Yajima et al., FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. II. Immunosuppressive effect of FK-506 in vitro. J Antibiot. 40(9), 1256–1265 (1987)
J.N. Andexer, S.G. Kendrew, M. Nur-e-Alam, O. Lazos, T.A. Foster, A. Zimmermann et al., Biosynthesis of the immunosuppressants FK506, FK520, and rapamycin involves a previously undescribed family of enzymes acting on chorismate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 108(12), 4776–4781 (2011)
D. Goranovič, G. Kosec, P. Mrak, S. Fujs, J. Horvat, E. Kuščer et al., Origin of the allyl group in FK506 biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 285(19), 14292–14300 (2010)
M.A. Gregory, H. Hong, R.E. Lill, S. Gaisser, H. Petkovic, L. Low et al., Rapamycin biosynthesis: elucidation of gene product function. Org. Biomol. Chem. 4(19), 3565–3568 (2006)
R. McDaniel, M. Welch, C.R. Hutchinson, Genetic approaches to polyketide antibiotics. 1. Chem. Rev. 105(2), 543–558 (2005)
K. Wu, L. Chung, W.P. Revill, L. Katz, C.D. Reeves, The FK520 gene cluster of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. ascomyceticus (ATCC 14891) contains genes for biosynthesis of unusual polyketide extender units. Gene 251(1), 81–90 (2000)
H. Motamedi, S. Cai, A. Shafiee, K.O. Elliston, Structural organization of a multifunctional polyketide synthase involved in the biosynthesis of the macrolide immunosuppressant FK506. Eur. J. Biochem. 244(1), 74–80 (1997)
B.P. Singh, B.K. Behera, Regulation of tacrolimus production by altering primary source of carbons and amino acids. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 49(2), 254–259 (2009)
D. Abbanat, W. Maiese, M. Greenstein, Biosynthesis of the pyrroindomycins by Streptomyces rugosporus LL-42D005; characterization of nutrient requirements. J. Antibiot. 52(2), 117–126 (1999)
B. Gust, G.L. Challis, K. Fowler, T. Kieser, K.F. Chater, PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 100(4), 1541–1546 (2003)
B. Gust, G. Chandra, D. Jakimowicz, T. Yuqing, C.J. Bruton, K.F. Chater, λ Red-mediated genetic manipulation of antibiotic-producing Streptomyces. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 54, 107–128 (2004)
S.J. Mo, S.K. Lee, Y.Y. Jin et al., Application of a combined approach involving classical random mutagenesis and metabolic engineering to enhance FK506 production in Streptomyces sp. RM7011. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 97, 3053–3062 (2013)
R. Ye, Q. Wang, X. Zhou, Lincomycin, rational selection of high producing strain and improved fermentation by amino acids supplementation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 32(4), 521–529 (2009)
Y. Zhao, R. Ye, L. Zheng, Studies on quantitative determination methods of tacrolimus in the fermentation broth. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 26(10), 1417–1420 (2006)
K. Tasun, P. Chose, K. Ghen, Sugar determination of DNS method. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 12, 921 (1970)
H.A. El-Enshasy, N.A. Mohamed, M.A. Farid, A.I. El-Diwany, Improvement of erythromycin production by Saccharopolyspora erythraea in molasses based medium through cultivation medium optimization. Bioresour. Technol. 99(10), 4263–4268 (2008)
Z. Wei, L. Bai, Z. Deng, J. Zhong, Impact of nitrogen concentration on validamycin A production and related gene transcription in fermentation of Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 35(7), 1201–1208 (2012)
W. Du, D. Huang, M. Xia, J. Wen, M. Huang, Improved FK506 production by the precursors and product-tolerant mutant of Streptomyces tsukubaensis based on genome shuffling and dynamic fed-batch strategies. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 41(7), 1131–1143 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Ye, R. Impact of a novel precursor on FK506 production and key gene transcription in Streptomyces tsukubaensis No. 9993. Res Chem Intermed 42, 3351–3358 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2215-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-015-2215-y