Abstract
Objective
To investigate the relationship between immune parameters and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in obese children.
Design
Cross-sectional study
Setting
Hospital-based study in Zhejiang Province, China between July to September 2015.
Participants
A total of 117 obese children and 209 healthy nonobese children were studied as the obese and control groups. Depending on the severity of NAFLD, the obese group was divided into subgroups 1 (without NAFLD), 2 (with simple fatty liver) and 3 (with steatohepatitis).
Outcome Measures
Glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism and immune parameters.
Results
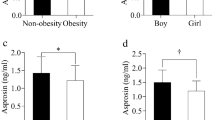
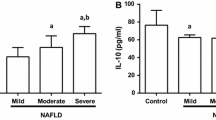
In the obese group, body mass index (BMI), waist-and hip-circumferences, fasting insulin, Homeostasis model of assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), triglyceride, total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein (Apo)B/ApoA1, alanine aminotransferase, uric acid, white blood cells, neutrophils percentage, platelet and interleukin (IL)-6 were significantly higher than those in the controls (P<0.05), while lower high density lipoprotein cholesterol and lymphocyte percentage were noted (P<0.05). IL-10 in the subgroup 3 was higher than those in the control group, subgroup 1 and 2 (P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that BMI, LDL-C, HOMA-IR and IL-10 were independent factors of NAFLD (P<0.05).
Conclusions
These results support a low-grade chronic inflammation in obese children. Moreover, obesity, dyslipidaemia and IR are risk factors while IL-10 may be a protective factor for NAFLD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yki-Jarvinen H. Diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Diabetologia. 2016;59:1104–11.
Takaki A, Kawai D, Yamamoto K. Multiple hits, including oxidative stress, as pathogenesis and treatment target in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14:20704–28.
Than NN, Newsome PN. A concise review of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Atherosclerosis. 2015;239:192–202.
Boga S, Alkim H, Koksal AR, Bayram M, Ozguven MB, Ergun M, et al. Increased plasma levels of asymmetric simethylarginine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Relation with insulin resistance, inflammation, and liver histology. J Investig Med. 2015;63:871–7.
Rodriguez-Ramos C, Galan F, Diaz F, Elvira J, Martin-Herrera L, Giron-Gonzalez JA. Expression of proinflammatory cytokines and their inhibitors during the course of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46:1668–76.
Jia G, Di F, Wang Q, Shao J, Gao L, Wang L, et al. Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease is a risk factor for the development of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE. 2015; 10: e0142808.
Das SK, Balakrishnan V. Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2011;26:202–9.
Li H, JI CY. Height and weight standardized growth charts for chinese children and adolescents aged 0 to 18 years. Chin J Pediatr. 2009;47:487–92.
The Chinese National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease for the Chinese Liver Disease Association. Guidelines for Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease:An Updated and Revised Edition. Chin J Hepatol. 2010;18:163–6.
Mencin AA, Lavine JE. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011;14:151–7.
Xanthakos S, Miles L, Bucuvalas J, Daniels S, Garcia V, Inge T. Histologic spectrum of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in morbidly obese adolescents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:226–32.
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993; 259: 87–91.
Yang W, Chi LY, Xie XY. Relationship of body mass index and white blood cell count in hypertensive patients. Chin Heart J. 2008;20:216–8.
Cinti S, Mitchell G, Barbatelli G, Murano I, Ceresi E, Faloia E, et al. Adipocyte death defines macrophage localization and function in adipose tissue of obese mice and humans. J Lipid Res. 2005;46:2347–55.
Perticone F, Ceravolo R, Candigliota M, Ventura G, Iacopino S, Sinopoli F, et al. Obesity and body fat distribution induce endothelial dysfunction by oxidative stress: Protective effect of vitamin C. Diabetes. 2001;50:159–65.
Braunersreuther V, Viviani GL, Mach F, Montecucco F. Role of cytokines and chemokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:727–35.
Paredes-Turrubiarte G, Gonzalez-Chavez A, Perez-Tamayo R, Salazar-Vazquez BY, Hernandez VS, Garibay-Nieto N, et al. Severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with high systemic levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and low serum interleukin 10 in morbidly obese patients. Clin Exp Med. 2016;16:193–202.
Li D, Zhang LJ, Chen ZX. Effects of TNFá, IL-6 and IL-10 on the development of experimental rat liver fibrosis. World Chin J Digestol. 2001;9:1242–5.
Cintra DE, Pauli JR, Araujo EP, Moraes JC, Souza CT, Milanski M, et al. Interleukin-10 is a protective factor against diet-induced insulin resistance in liver. J Hepatol. 2008;48:628–37.
Bertola A, Bonnafous S, Anty R, Patouraux S, Saint-Paul MC, Iannelli A, et al. Hepatic expression patterns of inflammatory and immune response genes associated with obesity and NASH in morbidly obese patients. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13577.
Miller AM, Wang H, Bertola A, Park O, Horiguchi N, Ki SH, et al. Inflammation-associated interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation ameliorates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Hepatology. 2011;54:846–56.
Stojsavljevic S, Gomercic Palcic M, Virovic Jukic L, Smircic Duvnjak L, Duvnjak M. Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:18070–91.
Kumar R, Prakash S, Chhabra S, Singla V, Madan K, Gupta, SD, et al. Association of pro-inflammatory cytokines, adipokines & oxidative stress with insulin resistance & non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Indian J Med Res. 2012;136:229–36.
Jin X, Zimmers TA, Perez EA, Pierce RH, Zhang Z, Koniaris LG. Paradoxical effects of short-and long-term interleukin-6 exposure on liver injury and repair. Hepatology. 2006;43:474–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, JQ., Shen, WX., Wang, XZ. et al. Relationship between immune parameters and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. Indian Pediatr 54, 825–829 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1143-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-017-1143-x