Abstract
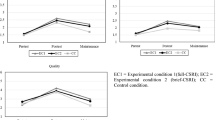
The current two studies examined the effects of an instructional unit on synthesis writing for 9th grade students on holistic text quality. Because students' writing routines have been shown to affect the effectiveness of writing instruction, we designed a unit that aimed to be equally effective for all writers, regardless of their routines. On two occasions in the unit, we provided students with options to choose between a Preplanning or Drafting strategy. They could create an individual learning path within the unit. We tested the effects of the unit in two consecutive studies with independent samples, using a quasi-experimental pretest–posttest design with switching panels. Study 1 included three teachers and 152 9th grade students from five classes in one school. We found a significant effect of the unit on text quality in both panels. However, analyses showed that this effect was moderated by writing routine. To generalize the effect across writing routines, we provided students in Study 2 with an extra session on metacognitive knowledge about (synthesis) writing processes, enabling them to make better-informed strategy choices. Study 2 included six teachers and 233 students from 10 classes in three schools, all different from Study 1. Analyses again showed a significant effect of the experimental condition in panel 1, which was replicated in panel 2. Moreover, the effect was no longer moderated by writing routine. This indicates that the redesigned intervention was equally effective for students with different routines.


Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
The datafiles will be published via figshare, the University of Amsterdam's repository.
Reference
Arias-Gundín, O., & Fidalgo, R. (2017). Writer profile as a modulating variable of processes involved in written composition in undergraduate students. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 7(1), 59–68. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe7010005
Arias-Gundín, O., Real, S., Rijlaarsdam, G., & López, P. (2021). Validation of the writing strategies questionnaire in the context of primary education: A multidimensional measurement model. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.700770
Baaijen, V. M., Galbraith, D., & de Glopper, K. (2014). Effects of writing beliefs and planning on writing performance. Learning and Instruction, 33, 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2014.04.001
Baaijen, V. M., & Galbraith, D. (2018). Discovery through writing: Relationships with writing processes and text quality. Cognition and Instruction, 36(3), 199–223. https://doi.org/10.1080/07370008.2018.1456431
Barzilai, S., & Ka’adan, I. (2017). Learning to integrate divergent information sources: The interplay of epistemic cognition and epistemic metacognition. Metacognition and Learning, 12(2), 193–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11409-016-9165-7
Bonset, H. (2010). Nederlands in het voortgezet en hoger onderwijs: Hoe sluit dat aan? Deel 1 [The subject of Dutch in secondary and higher education: How does that connect? Part 1.]. Levende Talen Magazine, 97(3), 16–20.
Boscolo, P., Arfé, B., & Quarisa, M. (2007). Improving the quality of students’ academic writing: An intervention study. Studies in Higher Education, 32(4), 419–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070701476092
Britt, M. A., & Aglinskas, C. (2002). Improving students’ ability to identify and use source information. Cognition and Instruction, 20(4), 485–522. https://doi.org/10.1207/S1532690XCI2004_2
Butler, D. (1998). The strategic content learning approach to promoting self-regulated learning: A report of three studies. Journal of Educational Psychology, 90(4), 682–697. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.4.682
Daher, T. A., & Kiewra, K. A. (2016). An investigation of SOAR study strategies for learning from multiple online resources. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 46, 10–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2015.12.004
Darowski, E. S., Helder, E., & Patson, N. D. (2020). Explicit writing instruction in synthesis: Combining in-class discussion and an online tutorial. Teaching of Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1177/0098628320979899
Darowski, E. S., Patson, N. D., & Helder, E. (2016). Implementing a synthesis tutorial to improve student literature reviews. Behavioral and Social Sciences Librarian, 35(3), 94–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/01639269.2016.1243437
De Smedt, F., Van Keer, H., & Merchie, E. (2016). Student, teacher and class-level correlates of Flemish late elementary school children’s writing performance. Reading and Writing, 29(5), 833–868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-015-9590-z
Galbraith, D. (1992). Conditions for discovery through writing. Instructional Science, 21(1–3), 45–71.
Galbraith D., & Torrance M. (2004). Revision in the context of different drafting strategies. In: L. Allal, L. Chanquoy, & P. Largy (Eds.), Revision Cognitive and Instructional Processes. Studies in Writing (Vol 13). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-1048-1_5
Gil, L., Vidal-Abarca, E., & Martínez, T. (2008). Eficacia de tomar notas para integrar información de varios textos. [Effectiveness of Notetaking for Integrating Information from Various Texts]. Infancia y Aprendizaje, 31(2), 259–272. https://doi.org/10.1174/021037008784132905
Hayes, J. R. (2012). Modeling and remodeling writing. Written Communication, 29(3), 369–388.
Karweit, N. (1984). Time-on-task reconsidered: Synthesis of research on time and learning. Educational Leadership, 41(8), 32–35.
Kellogg, R. T. (1996). A model of working memory in writing. In C. M. Levy & S. Ransdell (Eds.), The science of writing: Theories, methods, individual differences, and applications (pp. 57–72). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Kellogg, R. T. (1987). Writing performance: Effect of cognitive strategies. Written Communication, 4, 269–298. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088387004003003
Kellogg, R. T. (1988). Attentional overload and writing performance: Effects of rough draft and outline strategies. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 14, 355–365. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-7393.14.2.355
Kellogg, R. T. (2001). Competition for working memory among writing processes. American Journal of Psychology, 114, 175–191. https://doi.org/10.2307/1423513
Kellogg, R. T. (2008). Training writing skills: A cognitive developmental perspective. Journal of Writing Research, 1, 1–26. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2008.01.01.1
Kieft, M., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2005). Schrijftaken en schrijverstypen. [Writing tasks and writer types.]. Levende Talen Magazine, 92(2), 9–12.
Kieft, M., Rijlaarsdam, G., Galbraith, D., & van den Bergh, H. (2007). The effects of adapting a writing course to students’ writing strategies. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 77(3), 565–578. https://doi.org/10.1348/096317906x120231
Kieft, M., Rijlaarsdam, G., & Van den Bergh, H. (2008). An aptitude–treatment interaction approach to writing-to-learn. Learning and Instruction, 18(4), 379–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.07.004
Kirkpatrick, L. C., & Klein, P. D. (2009). Planning text structure as a way to improve students’ writing from sources in the compare-contrast genre. Learning and Instruction, 19(4), 309–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2008.06.001
Klein, P. D., & Boscolo, P. (2016). Trends in research on writing as a learning activity. Journal of Writing Research, 7(3), 311–350. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2016.07.03.01
Leijten, M., Van Waes, L., Schrijver, I., Bernolet, S., & Vangehuchten, L. (2017). Hoe schrijven masterstudenten syntheseteksten? Het brongebruik van gevorderde schrijvers in kaart gebracht. [How do master students write synthesis texts? Source use of advanced writers mapped.] Pedagogische Studiën, 94(4), 233–253. https://pedagogischestudien.nl/download?type=document&identifier=641006
Limpo, T., & Alves, R. A. (2018). Effects of planning strategies on writing dynamics and final texts. Acta Psychologica, 188, 97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2018.06.001
Lundstrom, K., Diekema, A. R., Leary, H., Haderlie, S., & Holliday, W. (2015). Teaching and learning information synthesis: An intervention and rubric based assessment. Communications in Information Literacy, 9(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.15760/comminfolit.2015.9.1.176
Luo, L., & Kiewra, K. A. (2019). Soaring to successful synthesis writing. Journal of Writing Research, 11(1), 163–209. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2019.11.01.06
Martínez, I., Mateos, M., Martín, E., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2015). Learning history by composing synthesis texts: Effects of an instructional programme on learning, reading and writing processes, and text quality. Journal of Writing Research, 7(2), 275–302. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2015.07.02.03
Mateos, M., Martín, E., Villalón, R., & Luna, M. (2008). Reading and writing to learn in secondary education: Online processing activity and written products in summarizing and synthesizing tasks. Reading and Writing, 21(7), 675–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-007-9086-6
Meestringa, T. (2011). Propedeutische schrijftaken. Analyse van 18 schrijftaken uit Nederlandse en Vlaamse opleidingen hoger onderwijs. [Propaedeutic writing tasks. Analysis of 18 writing tasks from Dutch and Flemish higher education courses.] SLO.
Meestringa, T., & Ravesloot, C. (2013). Schrijven in de Tweede Fase [Writing in Grades 10 to 12.]. Levende Talen Tijdschrift, 14(6), 6–10.
Ministerie O. C. W. (2009). Referentiekader Taal en Rekenen. [Frame of reference Language and Mathemetics.] SLO. https://www.slo.nl/publish/pages/5901/referentiekader_taal_en_rekenen_referentieniveaus.pdf
O’Donnell, C. L. (2008). Defining, conceptualizing, and measuring fidelity of implementation and its relationship to outcomes in K–12 curriculum intervention research. Review of Educational Research, 78(1), 33–84. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307313793
Oudakker, M., & Groenendijk, R. (2020). Kan schrijfvaardigheid in het voortgezet onderwijs (nog) beter aansluiten bij het hoger onderwijs? [Can writing skills in secondary education match higher education (even) better?]. Levende Talen Magazine, 107(8), 10–14.
Rijlaarsdam, G. & Van den Bergh, H. (2004). Effective learning and teaching of writing: Student involvement in the teaching of writing. In G. Rijlaarsdam, H. van den Bergh, & M. Couzijn, (Eds.). Studies in Writing. (Vol. 14, pp. 1–16). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-2739-0_1.pdf
Rijlaarsdam, G., Van den Bergh, H., Couzijn, M., Janssen, T., Braaksma, M., Tillema, M., Van Steendam, E., & Raedts, M. (2012). Writing. In: Harris K. R., Graham S., Urdan T., Bus A. G., Major S., & Swanson H. L. (Eds.), APA handbooks in psychology®. APA educational psychology handbook, Vol. 3. Application to learning and teaching (p. 189–227). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/13275-009
Robledo-Ramón, P. (2016) Eficacia de un programa de instrucción estratégica para la mejora de las síntesis escritas en alumnado universitario. [Efficacy of a strategic instruction program for the improvement of written syntheses in university students.] In Variables Psicológicas y Educativas para la intervención en el ámbito escolar: Volumen II (pp. 45–52). ASUNIVEP. https://doi.org/10.1787/ayuda_sintesis-2013-9-es
Segev-Miller, R. (2004). Writing from sources: The effect of explicit instruction on college students' processes and products. L1-Educational studies in language and literature, 4(1), 5–33. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:esll.0000033847.00732.af
Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference (2nd ed.). Houghton, Mifflin and Company. https://doi.org/10.1086/345281
Solé, I., Miras, M., Castells, N., Espino, S., & Minguela, M. (2013). Integrating information: An analysis of the processes involved and the products generated in a written synthesis task. Written Communication, 30(1), 63–90. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741088312466532
Spivey, N., & King, J. R. (1989). Readers as writers composing from sources. Reading Research Quarterly. https://doi.org/10.1598/rrq.24.1.1
Torrance, M., & Galbraith, D. (2006). The Processing demands of writing. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (pp. 67–80). The Guilford Press.
Van den Bergh, H., & Eiting, M. H. (1989). A method of estimating rater reliability. Journal of Educational Measurement, 26(1), 29–40.
Vandermeulen, N. (2020). Synthesis writing in upper-secondary education: From a baseline of texts and processes to process-oriented feedback. [Doctoral Thesis, University of Antwerp]. https://lirias.kuleuven.be/3070762
Vandermeulen, N., De Maeyer, S., Van Steendam, E., Lesterhuis, M., Van den Bergh, H., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2020). Syntheseschrijven in het hoger secundair onderwijs in Nederland in kaart gebracht. Een nationale peiling naar tekstkwaliteit, schrijfproces en schrijverskenmerken. [Mapping synthesis writing in various levels of Dutch upper-secondary education A national baseline study on text quality, writing process and students’ perspectives on writing]. Pedagogische Studiën, 97(3), 187–236. https://pedagogischestudien.nl/search?identifier=717755
Van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2018). Syntheseteksten leren schrijven in het voortgezet onderwijs; Het verband tussen schrijfaanpak en voorkeur voor leeractiviteiten. [Learning to write synthesis texts in secondary education; The association between writing routine and preference for learning activities.] Levende Talen Tijdschrift, 19(2), 3–14.
Van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2019). Learning to write synthesis texts: a review of intervention studies. Journal of Writing Research, 10(3), 401–428. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2019.10.03.01 .
Van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2021a). Learning how to synthesize: The design and evaluation of a reading-writing learning unit for high-school students. L1 Educational Studies in Language and Literature, 21(running issue). https://doi.org/10.17239/l1esll-2021.21.01.06.
Van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2021b). Een mini-interventie: het effect van een animatievideo van drie minuten op de integratie van broninformatie in syntheseteksten. [A brief intervention: does a three-minute animation video promote the integration of source information in synthesis texts?] Pedagogische Studiën, 98(1), 46–66. https://pedagogischestudien.nl/search?identifier=721616.
White, M. J., & Bruning, R. (2005). Implicit writing beliefs and their relation to writing quality. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 30, 166–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2004.07.002
Zhang, C. (2013). Effect of instruction on ESL students’ synthesis writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 22(1), 51–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2012.12.001
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Huub van den Bergh (Utrecht University) for helping us with the statistical analyses, and to the students and colleagues of the participating schools for their great efforts.
Funding
This work is part of the research program ‘Promotiebeurs voor leraren’ with project number 023.007.011, which is financed by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the studies' conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Liselore van Ockenburg, Daphne van Weijen and Gert Rijlaarsdam. The first draft of the manuscript was written by all three authors and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Study 1: ERB_Approval_9673; Study 2: ERB_Approval_10908.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Ockenburg, L., van Weijen, D. & Rijlaarsdam, G. Choosing how to plan informative synthesis texts: Effects of strategy-based interventions on overall text quality. Read Writ 36, 997–1023 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10226-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10226-6