Abstract
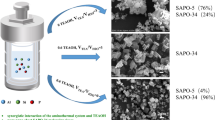
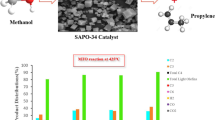
In this study, different templates (DIEA: N,N-diisopropylethylamine; TEAOH: tetraethylammonium hydroxide; DEA: diethylamine) were selected to conduct the grinding synthesis of SAPO-18 molecular sieves. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized SAPO-18 samples were thoroughly analyzed by XRD, CHN elemental measurements, TG, 13C NMR, SEM, EDS, N2 adsorption/desorption, and NH3-TPD experiments. The results show that SAPO-18 molecular sieves with better phase purity are synthesized only at the molar ratios of DIEA/TEAOH = 0.5/0.5 and DIEA/DEA = 0.9/0.1 for the dual template systems. The 13C NMR measurement indicates that the actual template is TEAOH for the sample SP18-DIEA0.5TEAOH0.5 instead of the mixture of TEAOH and DIEA. SEM, N2 adsorption/desorption, and NH3-TPD results suggest that the crystal size, textural parameters, and acidic properties of these SAPO-18 samples vary with the types of template molecules. The catalytic performances of three representative SAPO-18 catalysts were evaluated in the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction. Owing to its unique sheet-like morphology and suitable acidity, the sample SP18-DIEA0.5TEAOH0.5 exhibits the best catalytic performances in the MTO reaction, giving the longest catalytic lifetime of 430 min and ethylene plus propylene selectivity of 86%.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corma A, Mengual J, Miguel PJ (2012) Steam catalytic cracking of naphtha over ZSM-5 zeolite for production of propene and ethene: Micro and macroscopic implications of the presence of steam. Appl Catal A-Gen 417:220–235
Tian P, Wei YX, Ye M, Liu ZM (2015) Methanol to olefins (MTO): from fundamentals to commercialization. ACS Catal 5(3):1922–1938
Wang W, Buchholz A, Seiler M, Hunger M (2003) Evidence for an initiation of the methanol-to-olefin process by reactive surface methoxy groups on acidic zeolite catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 125(49):15260–15267
Bleken F, Bjorgen M, Palumbo L, Bordiga S, Svelle S, Lillerud K-P, Olsbye U (2009) The effect of acid strength on the conversion of methanol to olefins over acidic microporous catalysts with the cha topology. Top Catal 52(3):218–228
Zhao X, Niu L, Hao Z, Long X, Wang D, Li G (2021) Sodium persulfate promoted interzeolite transformation of USY into SSZ-13 via a solid-state grinding route and its enhanced catalytic lifetime in the methanol-to-olefins reaction. React Kinet Mech Catal 134(2):837–849
Wen MT, Ren L, Zhang JY, Jiang JA, Xu H, Guan YJ, Wu P (2021) Designing SAPO-18 with energetically favorable tetrahedral Si ions for an MTO reaction. Chem Commun 57(46):5682–5685
Xie JX, Firth DS, Cordero-Lanzac T, Airi A, Negri C, Oien-Odegaard S, Lillerud KP, Bordiga S, Olsbye U (2022) MAPO-18 catalysts for the methanol to olefins process: influence of catalyst acidity in a high-pressure syngas (CO and H-2) environment. ACS Catal 12(2):1520–1531
Chen J, Wright PA, Thomas JM, Natarajan S, Marchese L, Bradley SM, Sankar G, Catlow CRA, Gai-Boyes PL (1994) SAPO-18 catalysts and their broensted acid sites. J Phys Chem 98(40):10216–10224
Alvaro-Munoz T, Marquez-Alvarez C, Sastre E (2016) Mesopore-modified SAPO-18 with potential use as catalyst for the MTO reaction. Top Catal 59(2–4):278–291
Zhong JW, Han JF, Wei YX, Xu ST, Sun TT, Zeng S, Guo XW, Song CS, Liu ZM (2019) Tuning the product selectivity of SAPO-18 catalysts in MTO reaction via cavity modification. Chin J Catal 40(4):477–485
Wragg DS, Akporiaye D, Fjellvag H (2011) Direct observation of catalyst behaviour under real working conditions with X-ray diffraction: comparing SAPO-18 and SAPO-34 methanol to olefin catalysts. J Catal 279(2):397–402
Wendelbo R, Akporiaye D, Andersen A, Dahl IM, Mostad HB (1996) Synthesis, characterization and catalytic testing of SAPO-18, MgAPO-18, and ZnAPO-18 in the MTO reaction. Appl Catal A 142(2):L197–L207
Chen J, Thomas JM, Wright PA, Townsend RP (1994) Silicoaluminophosphate number eighteen (SAPO-18): a new microporous solid acid catalyst. Catal Lett 28(2):241–248
Hirota Y, Yamada M, Uchida Y, Sakamoto Y, Yokoi T, Nishiyama N (2016) Synthesis of SAPO-18 with low acidic strength and its application in conversion of dimethylether to olefins. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 232:65–69
Wu Q, Meng X, Gao X, Xiao F-S (2018) Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites: mechanism and utility. Acc Chem Res 51(6):1396–1403
Ren L, Wu Q, Yang C, Zhu L, Li C, Zhang P, Zhang H, Meng X, Xiao F-S (2012) Solvent-free synthesis of zeolites from solid raw materials. J Am Chem Soc 134(37):15173–15176
Jin Y, Sun Q, Qi G, Yang C, Xu J, Chen F, Meng X, Deng F, Xiao F-S (2013) Solvent-free synthesis of silicoaluminophosphate zeolites. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(35):9172–9175
Liu Y, Lyu Y, Zhao X, Xu L, Mintova S, Yan Z, Liu X (2018) Silicoaluminophosphate-11 (SAPO-11) molecular sieves synthesized via a grinding synthesis method. Chem Commun 54(78):10950–10953
Martinez-Franco R, Li ZB, Martinez-Triguero J, Moliner M, Corma A (2016) Improving the catalytic performance of SAPO-18 for the methanol-to-olefins (MTO) reaction by controlling the Si distribution and crystal size. Catal Sci Technol 6(8):2796–2806
Konnov SV, Pavlov VS, Ivanova II (2020) Effect of coating with silica on acidic and catalytic properties of SAPO-18 in MTO conversion. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 300:110158
Nazari M, Behbahani RM, Moradi G, Lemraski AS (2016) A facile synthesis route for modifying the catalytic performance of SAPO-18 in MTO process. J Porous Mater 23(4):1037–1046
Ono K, Miyake K, Nakai M, Al Jabri H, Hirota Y, Uchida Y, Tanaka S, Miyamoto M, Nishiyama N (2017) Development of AEI type germanoaluminophosphate (GeAPO-18) with ultra-weak acid sites and its catalytic properties for the methanol to olefin (MTO) reaction. Catal Sci Technol 7(20):4622–4628
Yao J, Tian H, Zha F, Ma S, Tang X, Chang Y, Guo X (2021) Regulating the size and acidity of SAPO-34 zeolites using dual templates to enhance the selectivity of light olefins in MTO. New J Chem 45(26):11812–11822
Chae H-J, Park I-J, Song Y-H, Jeong K-E, Kim C-U, Shin C-H, Jeong S-Y (2010) Physicochemical characteristics of SAPO-34 molecular sieves synthesized with mixed templates as MTO catalysts. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 10(1):195–202
Zhao D, Zhang Y, Li Z, Wang Y, Yu J (2017) Synthesis of AEI/CHA intergrowth zeolites by dual templates and their catalytic performance for dimethyl ether to olefins. Chem Eng J 323:295–303
Zhao X, Chen J, Sun Z, Li A, Li G, Wang X (2013) Formation mechanism and catalytic application of hierarchical structured FeAlPO-5 molecular sieve by microwave-assisted ionothermal synthesis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 182:8–15
Alvaro-Munoz T, Marquez-Alvarez C, Sastre E (2014) Aluminium chloride: a new aluminium source to prepare SAPO-34 catalysts with enhanced stability in the MTO process. Appl Catal A-Gen 472:72–79
Chen J, Li J, Yuan C, Xu S, Wei Y, Wang Q, Zhou Y, Wang J, Zhang M, He Y, Xu S, Liu Z (2014) Elucidating the olefin formation mechanism in the methanol to olefin reaction over AlPO-18 and SAPO-18. Catal Sci Technol 4(9):3268–3277
Li Z, Martinez-Triguero J, Yu J, Corma A (2015) Conversion of methanol to olefins: stabilization of nanosized SAPO-34 by hydrothermal treatment. J Catal 329:379–388
Groen JC, Peffer LAA, Pérez-Ramı́rez J (2003) Pore size determination in modified micro and mesoporous materials Pitfalls and limitations in gas adsorption data analysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 60(1):1–17
Nazari M, Moradi G, Behbahani RM, Ghavipour M, Abdollahi S (2015) Preparation and evaluation of the modified nanoparticle SAPO-18 for catalytic conversion of methanol to light olefins. Catal Lett 145(10):1893–1903
Ye L, Cao F, Ying W, Fang D, Sun Q (2011) Effect of different TEAOH/DEA combinations on SAPO-34’s synthesis and catalytic performance. J Porous Mater 18(2):225–232
Tan J, Liu Z, Bao X, Liu X, Han X, He C, Zhai R (2002) Crystallization and Si incorporation mechanisms of SAPO-34. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 53(1):97–108
Sun C, Wang Y, Chen H, Wang X, Wang C, Zhang X (2020) Seed-assisted synthesis of hierarchical SAPO-18/34 intergrowth and SAPO-34 zeolites and their catalytic performance for the methanol-to-olefin reaction. Catal Today 355:188–198
Bleken F, Bjørgen M, Palumbo L, Bordiga S, Svelle S, Lillerud K-P, Olsbye U (2009) The effect of acid strength on the conversion of methanol to olefins over acidic microporous catalysts with the CHA topology. Top Catal 52(3):218–228
Chen D, Moljord K, Fuglerud T, Holmen A (1999) The effect of crystal size of SAPO-34 on the selectivity and deactivation of the MTO reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 29(1):191–203
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21666019, 22168022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, L., Li, Y., Long, X. et al. Grinding synthesis of SAPO-18 zeolite by a single/dual-template route: which is the best catalyst of methanol-to-olefins reaction?. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 135, 3085–3098 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02295-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02295-7