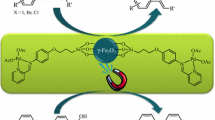
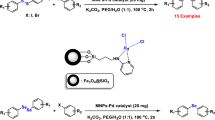
Abstract
A palladium organic–inorganic hybrid magnetic nanocatalyst for the Heck-cross coupling reactions was developed. This newly synthesized phosphine-free PdMNPs catalyzed Heck-cross coupling reactions in short reaction times (20–30 min) and high to excellent yields (75–93%). The catalyst was separated simply by an external magnet and reused in 10 successive runs without significant decrease in catalytic activity. The structure of the catalyst was established by Fourier transform infrared, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer and thermogravimetric analysis analyses.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karimi B, Enders D (2006) New N-heterocyclic carbene palladium complex/ionic liquid matrix immobilized on silica: application as recoverable catalyst for the Heck reaction. Org Lett 8:1237–1240
Prakash GKS, Krishnan HS, Jog PV, Iyer AP, Olah GA (2012) A domino approach of Heck coupling for the synthesis of β-trifluoromethylstyrenes. Org Lett 14:1146–1149
de Meijere A, Meyer Frank E (1995) Fine feathers make fine birds: the Heck reaction in modern garb. Angew Chem Int Ed 33:2379–2411
Heck RF (1991) In: Trost MB (ed) Comprehensive organic synthesis. Elsevier, New York
Beletskaya IP, Cheprakov AV (2000) The Heck reaction as a sharpening stone of palladium catalysis. Chem Rev 100:3009–3066
de Meijere A, Bräse S (2004) Metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. Wiley-VCH, New York
Pratihar JL, Pattanayak P, Patra D, Lin C-H, Chattopadhyay S (2012) Synthesis, characterization and structure of new diazoketiminato chelates of palladium(II): potential catalyst for C-C coupling reactions. Polyhedron 33:67–73
Aydemir M, Durap F, Baysal A, Akba O, Gümgüm B, Özkar S, Yıldırım LT (2009) Synthesis and characterization of new bis(diphenylphosphino)aniline ligands and their complexes: X-ray crystal structure of palladium(II) and platinum(II) complexes, and application of palladium(II) complexes as pre-catalysts in Heck and Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Polyhedron 28:2313–2320
Chen X, Engle Keary M, Wang D-H, Yu J-Q (2009) Palladium(II)-catalyzed C-H activation/C–C cross-coupling reactions: versatility and practicality. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:5094–5115
Barnard BC (2008) Platin Met Rev 52:38–45
Röhlich C, Köhler K (2010) Macrocyclic palladium(II) complexes in C-C coupling reactions: efficient catalysis by controlled temporary release of active species. Adv Synth Catal 352:2263–2274
García-Melchor M, Fuentes B, Lledós A, Casares JA, Ujaque G, Espinet P (2011) Cationic intermediates in the Pd-catalyzed Negishi coupling. Kinetic and density functional theory study of alternative transmetalation pathways in the Me–Me coupling of ZnMe2 and trans-[PdMeCl(PMePh2)2]. J Am Chem Soc 133:13519–13526
Borah BJ, Saikia K, Saikia PP, Barua NC, Dutta DK (2012) PdO-nanoparticles stabilized by tripodal phosphine based ligands and their catalytic activities on carboncarbon bond formation reactions. Catal Today 198:174–183
Slagt VF, de Vries AHM, de Vries JG, Kellogg RM (2010) Practical aspects of carbon−carbon cross-coupling reactions using heteroarenes. Org Process Res Dev 14:30–47
Morgan BP, Galdamez GA, Gilliard JR Jr, Smith RC (2009) Canopied trans-chelating bis(N-heterocyclic carbene) ligand: synthesis, structure and catalysis. Dalton Trans. https://doi.org/10.1039/B815739A
Bakherad M, Keivanloo A, Bahramian B, Jajarmi S (2010) Copper- and solvent-free Sonogashira coupling reactions of aryl halides with terminal alkynes catalyzed by 1-phenyl-1,2-propanedione-2-oxime thiosemi-carbazone-functionalized polystyrene resin supported Pd(II) complex under aerobic conditions. Appl Catal A 390:135–140
Alizadeh A, Khodaei MM, Kordestani D, Beygzadeh M (2013) Highly efficient phosphine-free Suzuki aryl couplings mediated by an in situ generated Pd(OAc)2/metformin complex in green media. Tetrahedron Lett 54:291–294
Yang Q, Wu H, Zhan H, Hou J, Gao M, Su Q, Wu S (2020) Attapulgite-anchored Pd complex catalyst: a highly active and reusable catalyst for C-C coupling reactions. React Kinet Mech Cat. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-019-01698-3
Johansson Seechurn Carin CC, Kitching Matthew O, Colacot Thomas J, Snieckus V (2012) Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling: a historical contextual perspective to the 2010 Nobel Prize. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:5062–5085
Lu Z-L, Lindner E, Mayer HA (2002) Applications of sol–gel-processed interphase catalysts. Chem Rev 102:3543–3578
Kidwai M, Jain A, Bhardwaj S (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles catalyzed synthesis of diverse N-heterocycles. Mol Divers 16:121–128
Phan Nam TS, Gill Christopher S, Nguyen Joseph V, Zhang ZJ, Jones Christopher W (2006) Expanding the utility of one-pot multistep reaction networks through compartmentation and recovery of the catalyst. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:2209–2212
Abu-Reziq R, Alper H, Wang D, Post ML (2006) Metal supported on dendronized magnetic nanoparticles: highly selective hydroformylation catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 128:5279–5282
Ma’mani L, Sheykhan M, Heydari A, Faraji M, Yamini Y (2010) Sulfonic acid supported on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated-γ-Fe2O3 nanocrystallites as a magnetically Brønsted acid for N-formylation of amines. Appl Catal A 377:64–69
Teunissen W, Bol AA, Geus JW (1999) Magnetic catalyst bodies. Catal Today 48:329–336
Yoon T-J, Lee W, Oh Y-S, Lee J-K (2003) Magnetic nanoparticles as a catalyst vehicle for simple and easy recycling. N J Chem 27:227–229
Yoon H, Ko S, Jang J (2007) Nitrogen-doped magnetic carbon nanoparticles as catalyst supports for efficient recovery and recycling. Chem Commun 38(14):1468–1470
Yang H-H, Zhang S-Q, Chen X-L, Zhuang Z-X, Xu J-G, Wang X-R (2004) Magnetite-containing spherical silica nanoparticles for biocatalysis and bioseparations. Anal Chem 76:1316–1321
Lee D, Lee J, Lee H, Jin S, Hyeon T, Kim BM (2006) Filtration-free recyclable catalytic asymmetric dihydroxylation using a ligand immobilized on magnetic mesocellular mesoporous silica. Adv Synth Catal 348:41–46
Zhang Y, Li Z, Sun W, Xia C (2008) A magnetically recyclable heterogeneous catalyst: cobalt nano-oxide supported on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated γ-Fe2O3 nanocrystallites for highly efficient olefin oxidation with H2O2. Catal Commun 10:237–242
Deng J, Mo L-P, Zhao F-Y, Hou L-L, Yang L, Zhang Z-H (2011) Sulfonic acid supported on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated-[gamma]-Fe2O3 nanocrystallites as a magnetically separable catalyst for one-pot reductive amination of carbonyl compounds. Green Chem 13:2576–2584
Liu Y-H, Deng J, Gao J-W, Zhang Z-H (2012) Triflic acid-functionalized silica-coated magnetic nanoparticles as a magnetically separable catalyst for synthesis of gem-dihydroperoxides. Adv Synth Catal 354:441–447
Baleizao C, Corma A, Garcia H, Leyva A (2003) An oxime-carbapalladacycle complex covalently anchored to silica as an active and reusable heterogeneous catalyst for Suzuki cross-coupling in water. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/B211742H
Wang D, Astruc D (2014) Fast-growing field of magnetically recyclable nanocatalysts. Chem Rev 114:6949–6985
Stevens PD, Li G, Fan J, Yen M, Gao Y (2005) Recycling of homogeneous Pd catalysts using superparamagnetic nanoparticles as novel soluble supports for Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. Chem Commun. https://doi.org/10.1039/B505424A
Dálaigh CÓ, Corr Serena A, Gunko Y, Connon Stephen J (2007) N-dialkylaminopyridine catalyst: excellent reactivity combined with facile catalyst recovery and recyclability. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:4329–4332
Wight AP, Davis ME (2002) Design and preparation of organic–inorganic hybrid catalysts. Chem Rev 102:3589–3614
Tabatabaeian K, Zanjanchi MA, Mamaghani M, Dadashi A (2016) Diversity oriented synthesis of benzoxanthene and benzochromene libraries via one-pot, three-component reactions and their anti-proliferative activity. Res Chem Intermed 42:5049–5067
Khoobi M, Ma’mani L, Rezazadeh F, Zareie Z, Foroumadi A, Ramazani A, Shafiee A (2012) One-pot synthesis of 4H-benzo[b]pyrans and dihydropyrano[c]chromenes using inorganic–organic hybrid magnetic nanocatalyst in water. J Mol Catal A 359:74–80
Sheykhan M, Mohammadquli M, Heydari A (2012) A new and green synthesis of formamidines by γ-Fe2O3@SiO2-HBF4 nanoparticles as a robust and magnetically recoverable catalyst. J Mol Struct 1027:156–161
Mohsenimehr M, Mamaghani M, Shirini F, Sheykhan M, Moghaddam FA (2014) One-pot synthesis of novel pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines using HAp-encapsulated-γ-Fe2O3 supported sulfonic acid nanocatalyst under solvent-free conditions. Chin Chem Lett 25:1387–1391
Ma’mani L, Sheykhan M, Heydari A (2011) Nanosilver embedded on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated γ-Fe2O3: superparamagnetic catalyst for chemoselective oxidation of primary amines to N-monoalkylated hydroxylamines. Appl Catal A 395:34–38
Sheykhan M, Ma’mani L, Ebrahimi A, Heydari A (2011) Sulfamic acid heterogenized on hydroxyapatite-encapsulated γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as a magnetic green interphase catalyst. J Mol Catal A 335:253–261
Cullity BD (1956) Elements of X ray diffraction. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, London
Sabu Thomas KJ, Malhotra SK, Koichi G, Sreekala MS (2013) Polymer composites, nanocomposites. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Pastoriza-Santos I, Liz-Marzán LM (2009) N-dimethylformamide as a reaction medium for metal nanoparticle synthesis. Adv Funct Mater 19:679–688
Hajipour Abdol R, Karami K, Pirisedigh A (2009) Accelerated Heck reaction using ortho-palladated complex with controlled microwave heating. Appl Organomet Chem 23:504–511
Hajipour AR, Karami K, Pirisedigh A, Ruoho AE (2009) Application of dimeric orthopalladate complex of homoveratrylamine as an efficient catalyst in the Heck cross-coupling reaction. J Organomet Chem 694:2548–2554
Ma X, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zhu A, Jiang T, Han B (2008) Solvent-free Heck reaction catalyzed by a recyclable Pd catalyst supported on SBA-15 via an ionic liquid. Green Chem 10:59–66
Wu S, Ma H, Jia X, Zhong Y, Lei Z (2011) Biopolymer–metal complex wool–Pd as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst for Heck reaction in aqueous media. Tetrahedron 67:250–256
Firouzabadi H, Iranpoor N, Ghaderi A (2011) Solvent-free Mizoroki-Heck reaction catalyzed by palladium nano-particles deposited on gelatin as the reductant, ligand and the non-toxic and degradable natural product support. J Mol Catal A 347:38–45
Xu H-J, Zhao Y-Q, Zhou X-F (2011) Palladium-catalyzed Heck reaction of aryl chlorides under mild conditions promoted by organic ionic bases. J Org Chem 76:8036–8041
Meng L, Liu C, Zhang W, Zhou C, Lei A (2014) Palladium catalysed β-selective oxidative Heck reaction of an electron-rich olefin. Chem Commun 50:1110–1112
Polshettiwar V, Hesemann P, Moreau JJE (2007) Palladium containing nanostructured silica functionalized with pyridine sites: a versatile heterogeneous catalyst for Heck, Sonogashira, and cyanation reactions. Tetrahedron 63:6784–6790
Petrucci C, Cappelletti M, Piermatti O, Nocchetti M, Pica M, Pizzo F, Vaccaro L (2015) Immobilized palladium nanoparticles on potassium zirconium phosphate as an efficient recoverable heterogeneous catalyst for a clean Heck reaction in flow. J Mol Catal A 401:27–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barazandehdoust, M., Mamaghani, M. & Kefayati, H. A novel phosphine-free and recyclable palladium organic–inorganic hybrid magnetic nanocatalyst for Heck cross-coupling reactions. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 129, 1007–1026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01744-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-020-01744-5