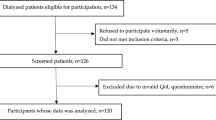
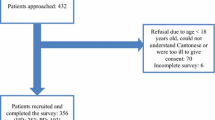
Abstract
Purpose
To identify relationships between health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and nutritional status in hemodialysis (HD) patients.
Method
Secondary data from a cross-sectional survey was utilized. HRQOL was assessed for 379 HD patients using the generic Short Form 36 (SF-36) and disease-specific Kidney-Disease Quality of Life-36 (KDQOL-36). Malnutrition was indicated by malnutrition inflammation score (MIS) ≥ 5, and presence of protein-energy wasting (PEW). The individual nutritional parameters included the domains of physical status, serum biomarkers, and dietary intake. Multivariate associations were assessed using the general linear model.
Results
MIS ≥ 5 was negatively associated with SF-36 scores of physical functioning (MIS < 5 = 73.4 ± 8.0 SE vs MIS ≥ 5 = 64.6 ± 7.7 SE, P < 0.001), role-limitation-physical (MIS < 5 = 65.3 ± 14.3 SE vs MIS ≥ 5 = 52.9 ± 14.0 SE, P = 0.006), general health (MIS < 5 = 53.7 ± 7.5 SE vs MIS ≥ 5 = 47.0 ± 7.1 SE, P = 0.003), and PCS-36 (MIS < 5 = 40.5 ± 3.3 SE vs MIS ≥ 5 = 35.9 ± 3.1 SE, P < 0.001); and KDQOL-36 score of symptoms/problems (MIS < 5 = 78.9 ± 5.6 SE vs MIS ≥ 5 = 74.8 ± 5.4 SE, P = 0.022), but not with PEW by any tool. Of individual nutritional parameters, underweight (68.1 ± 5.4 SE, P = 0.031), normal weight (63.8 ± 2.8 SE, P = 0.023), and overweight (64.3 ± 2.9 SE, P = 0.003) patients had significantly higher physical functioning scores compared to obese patients (44.8 ± 5.5 SE). Serum albumin levels were positively associated with physical functioning (P = 0.041) score. HGS was also positively associated with physical functioning (P = 0.036), and vitality (P = 0.041) scores. Greater dietary phosphorus intakes were significantly associated with lower scores for role limitation-physical (P = 0.008), bodily pain (P = 0.043), and PCS-36 (P = 0.024).
Conclusion
Malnutrition diagnosis by MIS, but not PEW, indicated associations with HRQOL in HD patients. Individual nutritional parameters that related to higher HRQOL were BMI < 30 kg/m2, better dietary phosphorus control, greater muscle strength and higher visceral protein pool.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalantar-Zadeh, Kopple, Block, & Humphreys. (2001). Association among SF-36 quality of life measures and nutrition, hospitalization, and mortality in hemodialysis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 12(12), 2797–2806.
Hall, R. K., Luciano, A., Pieper, C., & Colon-Emeric, C. S. (2018). Association of Kidney Disease Quality of Life (KDQOL-36) with mortality and hospitalization in older adults receiving hemodialysis. BMC Nephrology, 19(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0801-5
Peng, Y.-S., Chiang, C.-K., Hung, K.-Y., Chang, C.-H., Lin, C.-Y., Yang, C.-S., Chen, T.-W., Hsia, C.-C., Chen, D.-L., & Hsu, W.-D. (2010). Are both psychological and physical dimensions in health-related quality of life associated with mortality in hemodialysis patients: A 7-year Taiwan cohort study. Blood Purification, 30(2), 98–105. https://doi.org/10.1159/000319002
Perl, J., Karaboyas, A., Morgenstern, H., Sen, A., Rayner, H. C., Vanholder, R. C., Combe, C., Hasegawa, T., Finkelstein, F. O., & Lopes, A. A. (2016). Association between changes in quality of life and mortality in hemodialysis patients: Results from the DOPPS. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 32(3), 521–527. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfw233
Ambriz Murillo, Y., Menor Almagro, R., Campos-González, I. D., & Cardiel, M. H. (2015). Health-related quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, diabetes mellitus, end stage renal disease and geriatric subjects. Experience from a general hospital in Mexico. Reumatología Clínica (English Edition), 11(2), 68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reumae.2014.03.014
James, S. L., Abate, D., Abate, K. H., Abay, S. M., Abbafati, C., Abbasi, N., Abbastabar, H., Abd-Allah, F., Abdela, J., Abdelalim, A., Abdollahpour, I., Abdulkader, R. S., Abebe, Z., Abera, S. F., Abil, O. Z., Abraha, H. N., Abu-Raddad, L. J., Abu-Rmeileh, N. M. E., Accrombessi, M. M. K., et al. (2018). Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet, 392(10159), 1789–1858. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7
Urquhart-Secord, R., Craig, J. C., Hemmelgarn, B., Tam-Tham, H., Manns, B., Howell, M., Polkinghorne, K. R., Kerr, P. G., Harris, D. C., Thompson, S., Schick-Makaroff, K., Wheeler, D. C., van Biesen, W., Winkelmayer, W. C., Johnson, D. W., Howard, K., Evangelidis, N., & Tong, A. (2016). Patient and caregiver priorities for outcomes in hemodialysis: An International Nominal Group Technique Study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 68(3), 444–454. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.02.037
Cukor, D., Cohen, S. D., Peterson, R. A., & Kimmel, P. L. (2007). Psychosocial aspects of chronic disease: ESRD as a paradigmatic illness. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 18(12), 3042–3055. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2007030345
Jacobson, J., Ju, A., Baumgart, A., Unruh, M., O’Donoghue, D., Obrador, G., Craig, J. C., Dapueto, J. M., Dew, M. A., & Germain, M. (2019). Patient perspectives on the meaning and impact of fatigue in hemodialysis: A systematic review and thematic analysis of qualitative studies. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.01.034
Cleary, J., & Drennan, J. (2005). Quality of life of patients on haemodialysis for end-stage renal disease. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 51(6), 577–586. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03547.x
Dwyer, J. T., Larive, B., Leung, J., Rocco, M., Burrowes, J. D., Chumlea, W. C., Frydrych, A., Kusek, J. W., & Uhlin, L. (2002). Nutritional status affects quality of life in Hemodialysis (HEMO) Study patients at baseline. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 12(4), 213–223. https://doi.org/10.1053/jren.2002.35297
Mazairac, A. H. A., de Wit, G. A., Penne, E. L., van der Weerd, N. C., Grooteman, M. P. C., van den Dorpel, M. A., Nubé, M. J., Buskens, E., Lévesque, R., ter Wee, P. M., Bots, M. L., & Blankestijn, P. J. (2011). Protein-energy nutritional status and kidney disease-specific quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 21(5), 376-386.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2010.08.004
Md Yusop, N. B., Yoke Mun, C., Shariff, Z. M., & Beng Huat, C. (2013). Factors associated with quality of life among hemodialysis patients in Malaysia. PLoS ONE, 8(12), e84152. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0084152
Vero, L. M., Byham-Gray, L., Parrott, J. S., & Steiber, A. L. (2013). Use of the subjective global assessment to predict health-related quality of life in chronic kidney disease stage 5 patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 23(2), 141–147. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2012.03.003
Donciu, M.-D., Florea, L., Mititiuc, L.-I., Popescu, E.-R., & Chirita, R. (2019). Biochemical and bioimpedance orrelation with quality of life and illness perception in hemodialysis patients. Revista de Chimie, 70(2), 679–684. https://doi.org/10.37358/RC.19.2.6984
Chiang, C. K., Peng, Y. S., Chiang, S. S., Yang, C. S., He, Y. H., Hung, K. Y., Wu, K. D., Wu, M. S., Fang, C. C., Tsai, T. J., & Chen, W. Y. (2004). Health-related quality of life of hemodialysis patients in Taiwan: A multicenter study. Blood Purification, 22(6), 490–498. https://doi.org/10.1159/000081730
Germin-Petrović, D., Mesaros-Devcić, I., Lesac, A., Mandić, M., Soldatić, M., Vezmar, D., Petrić, D., Vujicić, B., Basić-Jukić, N., & Racki, S. (2011). Health-related quality of life in the patients on maintenance hemodialysis: The analysis of demographic and clinical factors. Collegium Antropologicum, 35(3), 687–693.
Carrero, J. J., Johansen, K. L., Lindholm, B., Stenvinkel, P., Cuppari, L., & Avesani, C. M. (2016). Screening for muscle wasting and dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney International, 90(1), 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.025
Fouque, D., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kopple, J., Cano, N., Chauveau, P., Cuppari, L., Franch, H., Guarnieri, G., Ikizler, T. A., Kaysen, G., Lindholm, B., Massy, Z., Mitch, W., Pineda, E., Stenvinkel, P., Trevino-Becerra, A., & Wanner, C. (2008). A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney International, 73(4), 391–398. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002585
Sahathevan, S., Khor, B.-H., Ng, H.-M., Abdul Gafor, A. H., Mat Daud, Z. A., Mafra, D., & Karupaiah, T. (2020). Understanding development of malnutrition in hemodialysis patients: A narrative review. Nutrients, 12(10), 3147. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12103147
Giglio, J., Kamimura, M. A., Lamarca, F., Rodrigues, J., Santin, F., & Avesani, C. M. (2018). Association of sarcopenia with nutritional parameters, quality of life, hospitalization, and mortality rates of elderly patients on hemodialysis. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 28(3), 197–207. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2017.12.003
Noori, N., Sharma Parpia, A., Lakhani, R., Janes, S., & Goldstein, M. B. (2018). Frailty and the quality of life in hemodialysis patients: The importance of waist circumference. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 28(2), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2017.07.007
Brown, E. A., Zhao, J., McCullough, K., Fuller, D. S., Figueiredo, A. E., Bieber, B., Finkelstein, F. O., Shen, J., Kanjanabuch, T., Kawanishi, H., Pisoni, R. L., & Perl, J. (2021). Burden of kidney disease, health-related quality of life, and employment among patients receiving peritoneal dialysis and in-center hemodialysis: Findings from the DOPPS program. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.02.327
Carrero, J. J., Thomas, F., Nagy, K., Arogundade, F., Avesani, C. M., Chan, M., Chmielewski, M., Cordeiro, A. C., Espinosa-Cuevas, A., Fiaccadori, E., Guebre-Egziabher, F., Hand, R. K., Hung, A. M., Ikizler, T. A., Johansson, L. R., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Karupaiah, T., Lindholm, B., Marckmann, P., … Kovesdy, C. P. (2018). Global prevalence of protein-energy wasting in kidney disease: A meta-analysis of contemporary observational studies from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 28(6), 380–392. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2018.08.006
Borges, M. C. C., Vogt, B. P., Martin, L. C., & Caramori, J. C. T. (2017). Malnutrition-inflammation score cut-off predicting mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, 17, 63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2016.10.006
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kopple, J. D., Block, G., & Humphreys, M. H. (2001). A malnutrition-inflammation score is correlated with morbidity and mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 38(6), 1251–1263. https://doi.org/10.1053/ajkd.2001.29222
Ma, L., & Zhao, S. (2017). Risk factors for mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Cardiology, 238, 151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.02.095
Carrero, J. J., Stenvinkel, P., Cuppari, L., Ikizler, T. A., Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kaysen, G., Mitch, W. E., Price, S. R., Wanner, C., Wang, A. Y., ter Wee, P., & Franch, H. A. (2013). Etiology of the protein-energy wasting syndrome in chronic kidney disease: A consensus statement from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM). Journal of Renal Nutrition, 23(2), 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2013.01.001
Opiyo, R. O., Nyasulu, P. S., Olenja, J., Zunza, M., Nguyen, K. A., Bukania, Z., Nabakwe, E., Mbogo, A., & Were, A. O. (2019). Factors associated with adherence to dietary prescription among adult patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis in national referral hospitals in Kenya: A mixed-methods survey. Renal Replacement Therapy, 5(1), 41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-019-0237-4
Kawate, Y., & Miyata, H. (2017). The importance of nutritional intervention by dietitians for hyperphosphatemia in maintained hemodialysis patients. Renal Replacement Therapy, 3(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-017-0095-x
Clark-Cutaia, M. N., Sevick, M. A., Thurheimer-Cacciotti, J., Hoffman, L. A., Snetselaar, L., Burke, L. E., & Zickmund, S. L. (2019). Perceived barriers to adherence to hemodialysis dietary recommendations. Clinical Nursing Research, 28(8), 1009–1029. https://doi.org/10.1177/1054773818773364
Zimmerer, J. L., Leon, J. B., Covinsky, K. E., Desai, U., & Sehgal, A. R. (2003). Diet monotony as a correlate of poor nutritional intake among hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 13(2), 72–77. https://doi.org/10.1053/jren.2003.50025
Sualeheen, A., Khor, B. H., Balasubramanian, G. V., Sahathevan, S., Ali, M. S. M., Narayanan, S. S., Chinna, K., Daud, Z. A. M., Khosla, P., Gafor, A. H. A., & Karupaiah, T. (2020). Habitual dietary patterns of patients on hemodialysis indicate nutritional risk. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 30(4), 322–332. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2019.09.010
Zabel, R., Ash, S., King, N., Juffs, P., & Bauer, J. (2012). Relationships between appetite and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Appetite, 59(1), 194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2012.02.016
Feroze, U., Noori, N., Kovesdy, C. P., Molnar, M. Z., Martin, D. J., Reina-Patton, A., Benner, D., Bross, R., Norris, K. C., Kopple, J. D., & Kalantar-Zadeh, K. (2011). Quality-of-life and mortality in hemodialysis patients: Roles of race and nutritional status. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 6(5), 1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.07690910
Al-Ali, F., Bieber, B., Pisoni, R., Ezzat, H., AlGhonaim, M., AlHejaili, F., AlGhareeb, S., Saleh, A., Al Maimani, Y., Alyousef, A., Ahmed, H., Hamad, A., & GCC-DOPPS 5 Study Group. (2016). Nutritional status and outcomes in hemodialysis patients from the Gulf Cooperation Council countries enrolled in the dialysis outcome and practice patterns study phase 5 (2012–2015). Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation, 27(7), 31–41. https://doi.org/10.4103/1319-2442.194888
Broers, N. J., Usvyat, L. A., Kooman, J. P., van der Sande, F. M., Lacson, E., Jr., Kotanko, P., & Maddux, F. W. (2015). Quality of life in dialysis patients: A retrospective cohort study. Nephron, 130(2), 105–112. https://doi.org/10.1159/000430814
Allen, K. L., Miskulin, D., Yan, G., Dwyer, J. T., Frydrych, A., Leung, J., & Poole, D. (2002). Association of nutritional markers with physical and mental health status in prevalent hemodialysis patients from the HEMO study. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 12(3), 160–169. https://doi.org/10.1053/jren.2002.33512
Moreira, A. C., Carolino, E., Domingos, F., Gaspar, A., Ponce, P., & Camilo, M. E. (2013). Nutritional status influences generic and disease-specific quality of life measures in haemodialysis patients. Nutricion Hospitalaria, 28(3), 951–957. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2013.28.3.6454
dos Santos, A. C. B., do Carmo Machado, M., Pereira, L. R., Abreu, J. L. P., & Lyra, M. B. (2013). Association between the level of quality of life and nutritional status in patients undergoing chronic renal hemodialysis. Brazilian Journal of Nephrology, 35(4), 279–288. https://doi.org/10.5935/0101-2800.20130047
Veerappan, I., Arvind, R. M., & Ilayabharthi, V. (2012). Predictors of quality of life of hemodialysis patients in India. Indian Journal of Nephrology, 22(1), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-4065.91185
Sohrabi, Z., Eftekhari, M. H., Eskandari, M. H., Rezaeianzadeh, A., & Sagheb, M. M. (2015). Malnutrition-inflammation score and quality of life in hemodialysis patients: Is there any correlation? Nephro-Urology Monthly, 7(3), e27445–e27445. https://doi.org/10.5812/numonthly.7(3)2015.27445
de Roij van Zuijdewijn, C., Grooteman, M., Bots, M., Blankestijn, P., van den Dorpel, M., Nubé, M., & ter Wee, P. (2016). Comparing tests assessing protein-energy wasting: Relation with quality of life. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 26(2), 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2015.09.003
Han, H., Burrowes, J. D., Houser, R., Chung, M.-C., & Dwyer, J. T. (2012). What is the impact of nutritional status on health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients? Journal of Renal Nutrition, 22(2), 237–243. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2011.05.003
Bilgic, A., Akgul, A., Sezer, S., Arat, Z., Ozdemir, F. N., & Haberal, M. (2007). Nutritional status and depression, sleep disorder, and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 17(6), 381–388. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2007.08.008
Rambod, M., Bross, R., Zitterkoph, J., Benner, D., Pithia, J., Colman, S., Kovesdy, C. P., Kopple, J. D., & Kalantar-Zadeh, K. (2009). Association of malnutrition-inflammation score with quality of life and mortality in hemodialysis patients: A 5-year prospective cohort study. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 53(2), 298–309. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.09.018
Fouque, D., Vennegoor, M., Ter Wee, P., Wanner, C., Basci, A., Canaud, B., Haage, P., Konner, K., Kooman, J., & Martin-Malo, A. (2007). EBPG guideline on nutrition. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation, 22(suppl_2), ii45–ii87. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm020
K/DOQI. (2020). Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI) clinical practice guideline for nutrition in chronic kidney disease: 2020 update. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006
Memmer, D. (2013). Implementation and practical application of the nutrition care process in the dialysis unit. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 23(1), 65–73. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2012.01.025
Swan, W. I., Vivanti, A., Hakel-Smith, N. A., Hotson, B., Orrevall, Y., Trostler, N., Beck Howarter, K., & Papoutsakis, C. (2017). Nutrition care process and model update: Toward realizing people-centered care and outcomes management. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 117(12), 2003–2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2017.07.015
Wight, J., Edwards, L., Brazier, J., Walters, S., Payne, J., & Brown, C. (1998). The SF-36 as an outcome measure of services for end stage renal failure. BMJ Quality & Safety, 7(4), 209–221. https://doi.org/10.1136/qshc.7.4.209
Hays, R. D., Kallich, J. D., Mapes, D. L., Coons, S. J., & Carter, W. B. (1994). Development of the kidney disease quality of life (KDQOL) instrument. Quality of Life Research, 3(5), 329–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451725
Aiyegbusi, O. L., Kyte, D., Cockwell, P., Marshall, T., Gheorghe, A., Keeley, T., Slade, A., & Calvert, M. (2017). Measurement properties of patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs) used in adult patients with chronic kidney disease: A systematic review. PLoS ONE, 12(6), e0179733. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179733
Black, A. E. (2000). Critical evaluation of energy intake using the Goldberg cut-off for energy intake: Basal metabolic rate. A practical guide to its calculation, use and limitations. International Journal of Obesity, 24(9), 1119. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801376
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and psychological measurement, 30(3), 607–610.
Sararaks, S., Azman, A., Low, L., Rugayah, B., Aziah, A., Hooi, L., Razak, M. A., Norhaya, M., Lim, K., & Azian, A. (2005). Validity and reliability of the SF-36: The Malaysian context. Medical Journal of Malaysia, 60(2), 163.
Goh, K. K. K., Lai, P. S. M., & Lim, S. K. (2019). Cross cultural adaptation and validation of the Malay Kidney Disease Quality of Life (KDQOL-36). BMC Nephrology, 20(1), 226. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-019-1397-8
Joshi, V. D., Mooppil, N., & Lim, J. F. Y. (2010). Validation of the Kidney Disease Quality of Life-Short Form: A cross-sectional study of a dialysis-targeted health measure in Singapore. BMC Nephrology, 11(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2369-11-36
Ware, J. E. (1993). SF-36 health survey: Manual and interpretation guide. The Health Institute, New England Medical Center.
Ware, J. E., Kosinski, M. A., & Keller, S. D. (1995). SF-36 physical and mental health summary scales: A user’s manual. The Health Institute, New England Medical Center.
Peipert, J. D., Nair, D., Klicko, K., Schatell, D. R., & Hays, R. D. (2019). Kidney Disease Quality of Life 36-Item Short Form Survey (KDQOL-36) normative values for the united states dialysis population and new single summary score. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 30(4), 654–663. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2018100994
Ware, J., Kosinski, M., & Susan, K. (1995). SF-12: How to score the SF-12 Physical and Mental Health Summary Scales. The Health Institute, New England Medical Center.
Khor, B.-H., Sualeheen, A., Sahathevan, S., Chinna, K., Gafor, A. H. A., Bavanandan, S., Goh, B.-L., Morad, Z., Daud, Z. A. M., Khosla, P., Wang, A.Y.-M., Karupaiah, T., Bee, B. C., Ahmad, G., Lim, S. K., Wahab, M. Z. A., Visvanathan, R., Yahya, R., & Pa, T. C. H. I. (2020). Association of dietary patterns with serum phosphorus in maintenance haemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 12278. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68893-4
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kopple, J. D., Humphreys, M. H., & Block, G. (2004). Comparing outcome predictability of markers of malnutrition-inflammation complex syndrome in haemodialysis patients. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 19(6), 1507–1519. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfh143
Pisetkul, C., Chanchairujira, K., Chotipanvittayakul, N., Ong-Ajyooth, L., & Chanchairujira, T. (2010). Malnutrition-inflammation score associated with atherosclerosis, inflammation and short-term outcome in hemodialysis patients. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 93(Suppl 1), S147–S156.
Frisancho, A. R. (1981). New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 34(11), 2540–2545. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/34.11.2540
K/DOQI. (2000). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for nutrition in chronic renal failure. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 37(1), S66–S70.
Tee, E., Ismail, M., Nasir, M., & Khatijah, I. (1997). Nutrient composition of Malaysian foods. Malaysian food composition database programme (p. 310). Institute for Medical Research, Kuala Lumpur
Singapore Health Promotion Board. (2003). Food composition guide Singapore. Singapore Health Promotion Board.
Organization, W. H. (1995). Physical status: The use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organization Technical Report Series, 854, 1–452.
James, G., Witten, D., Hastie, T., & Tibshirani, R. (2013). An introduction to statistical learning (Vol. 112). Springer.
Beto, J. A., Ramirez, W. E., & Bansal, V. K. (2014). Medical nutrition therapy in adults with chronic kidney disease: Integrating evidence and consensus into practice for the generalist registered dietitian nutritionist. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 114(7), 1077–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jand.2013.12.009
Mak, R. H., Ikizler, A. T., Kovesdy, C. P., Raj, D. S., Stenvinkel, P., & Kalantar-Zadeh, K. (2011). Wasting in chronic kidney disease. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle, 2(1), 9–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13539-011-0019-5
Vogt, B. P., & Caramori, J. C. T. (2016). Are nutritional composed scoring systems and protein-energy wasting score associated with mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients? Journal of Renal Nutrition, 26(3), 183–189. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2015.11.003
Toledo, F. R., Antunes, A. A., Vannini, F. C., Silveira, L. V., Martin, L. C., Barretti, P., & Caramori, J. C. (2013). Validity of malnutrition scores for predicting mortality in chronic hemodialysis patients. International Urology and Nephrology, 45(6), 1747–1752. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0482-3
Gracia-Iguacel, C., González-Parra, E., Mahillo, I., & Ortiz, A. (2019). Criteria for classification of protein–energy wasting in dialysis patients: Impact on prevalence. British Journal of Nutrition, 121(11), 1271–1278. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114519000400
Takahashi, H., Inoue, K., Shimizu, K., Hiraga, K., Takahashi, E., Otaki, K., Yoshikawa, T., Furuta, K., Tokunaga, C., Sakakibara, T., & Ito, Y. (2017). Comparison of nutritional risk scores for predicting mortality in Japanese chronic hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 27(3), 201–206. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2016.12.005
de Roij van Zuijdewijn, C. L. M., ter Wee, P. M., Chapdelaine, I., Bots, M. L., Blankestijn, P. J., van den Dorpel, M. A., Nubé, M. J., & Grooteman, M. P. C. (2015). A comparison of 8 nutrition-related tests to predict mortality in hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 25(5), 412–419. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2015.02.005
Lopes, M. B., Silva, L. F., Lopes, G. B., Penalva, M. A., Matos, C. M., Robinson, B. M., & Lopes, A. A. (2017). Additional Contribution of the Malnutrition-Inflammation Score to predict mortality and patient-reported outcomes as compared with its components in a cohort of African descent hemodialysis patients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 27(1), 45–52. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2016.08.006
Johansen, K. L., Kutner, N. G., Young, B., & Chertow, G. M. (2006). Association of body size with health status in patients beginning dialysis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83(3), 543–549.
Forhan, M., & Gill, S. V. (2013). Obesity, functional mobility and quality of life. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 27(2), 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2013.01.003
Tong, A., Manns, B., Wang, A. Y. M., Hemmelgarn, B., Wheeler, D. C., Gill, J., Tugwell, P., Pecoits-Filho, R., Crowe, S., Harris, T., Van Biesen, W., Winkelmayer, W. C., Levin, A., Thompson, A., Perkovic, V., Ju, A., Gutman, T., Bernier-Jean, A., Viecelli, A. K., … ONG Implementation Workshop Investigators. (2018). Implementing core outcomes in kidney disease: Report of the Standardized Outcomes in Nephrology (SONG) implementation workshop. Kidney International, 94(6), 1053–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.08.018
Evangelidis, N., Tong, A., Manns, B., Hemmelgarn, B., Wheeler, D. C., Tugwell, P., Crowe, S., Harris, T., Van Biesen, W., & Winkelmayer, W. C. (2017). Developing a set of core outcomes for trials in hemodialysis: An international Delphi survey. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 70(4), 464–475. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.11.029
Chan, W., Chin, S. H., Whittaker, A. C., Jones, D., Kaur, O., Bosch, J. A., & Borrows, R. (2019). The associations of muscle strength, muscle mass, and adiposity with clinical outcomes and quality of life in prevalent kidney transplant recipients. Journal of Renal Nutrition, 29(6), 536–547. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2019.06.009
Sayer, A. A., Syddall, H. E., Martin, H. J., Dennison, E. M., Roberts, H. C., & Cooper, C. (2006). Is grip strength associated with health-related quality of life? Findings from the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. Age and Ageing, 35(4), 409–415. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afl024
Jakobsen, L. H., Rask, I. K., & Kondrup, J. (2010). Validation of handgrip strength and endurance as a measure of physical function and quality of life in healthy subjects and patients. Nutrition, 26(5), 542–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2009.06.015
Kang, S. Y., Lim, J., & Park, H. S. (2018). Relationship between low handgrip strength and quality of life in Korean men and women. Quality of Life Research, 27(10), 2571–2580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-1920-6
Nishikawa, H., Enomoto, H., Yoh, K., Iwata, Y., Sakai, Y., Kishino, K., Ikeda, N., Takashima, T., Aizawa, N., Takata, R., Hasegawa, K., Ishii, N., Yuri, Y., Nishimura, T., Iijima, H., & Nishiguchi, S. (2018). Health-related quality of life in chronic liver diseases: A strong impact of hand grip strength. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 7(12), 553. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7120553
Sayer, A. A., Dennison, E. M., Syddall, H. E., Gilbody, H. J., Phillips, D. I., & Cooper, C. (2005). Type 2 diabetes, muscle strength, and impaired physical function: The tip of the iceberg? Diabetes Care, 28(10), 2541–2542. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.10.2541
McNicholl, T., Curtis, L., Dubin, J. A., Mourtzakis, M., Nasser, R., Laporte, M., & Keller, H. (2020). Handgrip strength predicts length of stay and quality of life in and out of hospital. Clinical Nutrition, 39(8), 2501–2509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2019.11.006
Oliveira, M. C., Bufarah, M. N. B., & Balbi, A. L. (2018). Handgrip strength in end stage of renal disease—A narrative review. Nutrire, 43(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41110-018-0073-2
Martin-Alemañy, G., de los Ángeles Espinosa-Cuevas, M., Pérez-Navarro, M., Wilund, K. R., Miranda-Alatriste, P., Cortés-Pérez, M., García-Villalobos, G., Gómez-Guerrero, I., Cantú-Quintanilla, G., Ramírez-Mendoza, M., & Valdez-Ortiz, R. (2020). Effect of oral nutritional supplementation with and without exercise on nutritional status and physical function of adult hemodialysis patients: A Parallel Controlled Clinical Trial (AVANTE-HEMO Study). Journal of Renal Nutrition, 30(2), 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jrn.2019.06.010
Lopes, A. A., Bragg-Gresham, J. L., Goodkin, D. A., Fukuhara, S., Mapes, D. L., Young, E. W., Gillespie, B. W., Akizawa, T., Greenwood, R. N., Andreucci, V. E., Akiba, T., Held, P. J., & Port, F. K. (2007). Factors associated with health-related quality of life among hemodialysis patients in the DOPPS. Quality of Life Research, 16(4), 545–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-006-9143-7
Keller, U. (2019). Nutritional laboratory markers in malnutrition. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(6), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8060775
Hanafusa, N., Nitta, K., Okazaki, M., Komatsu, M., Shiohira, S., Kawaguchi, H., & Tsuchiya, K. (2017). Serum albumin level adjusted with C-reactive protein predicts hemodialysis patient survival. Renal Replacement Therapy, 3(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-016-0085-4
Kalantar-Zadeh, K., Kuwae, N., Wu, D. Y., Shantouf, R. S., Fouque, D., Anker, S. D., Block, G., & Kopple, J. D. (2006). Associations of body fat and its changes over time with quality of life and prospective mortality in hemodialysis patients. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 83(2), 202–210. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/83.2.202
Kalender, B., Ozdemir, A. C., Dervisoglu, E., & Ozdemir, O. (2007). Quality of life in chronic kidney disease: Effects of treatment modality, depression, malnutrition and inflammation. International Journal of Clinical Practice, 61(4), 569–576. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01251.x
Nowak, K. L., & Chonchol, M. (2018). Does inflammation affect outcomes in dialysis patients? Seminars in Dialysis, 31(4), 388–397. https://doi.org/10.1111/sdi.12686
K/DOQI. (2003). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in chronic kidney disease. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 42(4 Suppl 3), S1-201.
Lacson, E., Jr., Xu, J., Lin, S. F., Dean, S. G., Lazarus, J. M., & Hakim, R. (2009). Association between achievement of hemodialysis quality-of-care indicators and quality-of-life scores. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 54(6), 1098–1107. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.07.017
Ware, J. E., Jr., Gandek, B., Kosinski, M., Aaronson, N. K., Apolone, G., Brazier, J., Bullinger, M., Kaasa, S., Leplège, A., & Prieto, L. (1998). The equivalence of SF-36 summary health scores estimated using standard and country-specific algorithms in 10 countries: Results from the IQOLA project. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 51(11), 1167–1170. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0895-4356(98)00108-5
Lam, C. L., Eileen, Y., Gandek, B., & Fong, D. Y. (2005). The SF-36 summary scales were valid, reliable, and equivalent in a Chinese population. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 58(8), 815–822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2004.12.008
Yarlas, A. S., White, M. K., Yang, M., Saris-Baglama, R. N., Bech, P. G., & Christensen, T. (2011). Measuring the health status burden in hemodialysis patients using the SF-36(R) health survey. Quality of Life Research, 20(3), 383–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-010-9764-8
Acknowledgements
Members of PaTCH (Malaysia) Investigators are Dr. Bee Boon Cheak (Hospital Selayang, Malaysia), Dr. Lim Soo Kun (Universiti Malaya, Malaysia), Dr. Ravindran Visvanathan (Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia), Dr. Rosnawati Yahya (Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia), and Dr. Sunita Bavanandan (Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, HM., Khor, BH., Sahathevan, S. et al. Is malnutrition a determining factor of health-related quality of life in hemodialysis patients? A cross-sectional design examining relationships with a comprehensive assessment of nutritional status. Qual Life Res 31, 1441–1459 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-021-03018-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-021-03018-6