Abstract
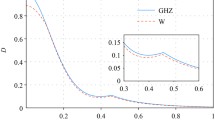
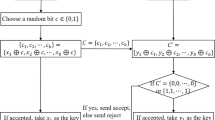
Quantum key agreement (QKA) permits participants to constitute a shared key on a quantum channel, and no participants are able to independently determine the shared key. In fact, particles are frequently affected by channel noise in the transmission process of quantum channel. Under the cover of noise, attackers can launch malicious attacks. In this thesis, on account of the usage of entanglement swapping of GHZ state and logical Bell states, we design two two-party QKA protocols which are immune to collective-dephasing noise and collective-rotation noise, respectively. In comparison with the existing QKA protocols of two parties, the proposed protocols have better quantum resource cost and the qubit efficiency in the global scope. Security analysis reveals that they can resist not only attacks by participants but also external attacks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175–179. New York: IEEE (1984)
Bennett, C.H.: Quantum cryptography using any two nonorthogonal states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 3121–3124 (1992)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40(18), 1149 (2004)
Hsueh, C.C., Chen, C.Y. In: Proceedings of the 14th Information Security Conference (ISC 2004), pp. 236–242. National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei (2004)
Hillery, M., Bužek, V., Berthiaume, A.: Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 59, 1829–1834 (1999)
Karlsson, A., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Quantum entanglement for secret sharing and secret splitting. Phys. Rev. A 59, 162–168 (1999)
Boström, K., Felbinger, T.: Deterministic secure direct communication using entanglement. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 187902 (2002)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302 (2002)
Yang, Y.G., Wen, Q.Y.: An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A: Math. Theor. 42(5), 055305 (2009)
Yang, Y.G., Cao, W.F., Wen, Q.Y.: Secure quantum private comparison. Phys. Scr. 80(6), 065002 (2009)
Chen, X.B., Xu, G., Niu, X.X., Wen, Q.Y., Yang, Y.X.: An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 283(7), 1561–1565 (2010)
Yang, C.-W., Hwang, T.: Quantum dialogue protocols immune to collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 12(6), 2131 (2013)
Yang, Y.-G., Liu, Z.-C., Li, J., Chen, X.-B., Zuo, H.-J., Zhou, Y.-H., Shi, W.-M.: Theoretically extensible quantum digital signature with starlike cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(1), 1–15 (2017)
Yang, Y.-G., Lei, H., Liu, Z.-C., Zhou, Y.-H., Shi, W.-M.: Arbitrated quantum signature scheme based on cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(6), 2487–2497 (2016)
Wang, T.-Y., Wei, Z.L.: One-time proxy signature based on quantum cryptography. Quantum Inf. Process. 11, 455–463 (2012)
Wang, T.-Y., Cai, X.Q., Ren, Y.L., Zhang, R.L.: Security of quantum digital signature. Sci. Rep. 5, 9231 (2015)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 22, 644–654 (1976)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283(6), 1192–1195 (2010)
Shukla, C., Alam, N., Pathak, A.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2391–2405 (2014)
Chong, S.K., Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: Improvement on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 50, 1793–1802 (2011)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with Bell states and Bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 921–932 (2013)
Xu, G.B., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., Qin, S.J.: Novel multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2587–2594 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement with five-particle entangled states. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15(03), 1750018 (2017)
Cai, B., Guo, G., Lin, S.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with teleportation. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 31(10), 1750102 (2017)
Cao, H., Ma, W.: Multiparty quantum key agreement based on quantum search algorithm. Sci. Rep. 7, 45046 (2017)
Sun, Z.W., Zhang, C., Wang, B.H., Li, Q., Long, D.Y.: Improvements on “multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles”. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 3411–3420 (2013)
Kwiat, P.G., Berglund, A.J., Altepeter, J.B., White, A.G.: Experimental verification of decoherence-free subspaces. Science (New York, N.Y.) 290(5491), 498–501 (2000)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement with EPR pairs and single particle measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 649–663 (2014)
Huang, W., Su, Q., Wu, X., Li, Y.B., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement against collective decoherence. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53, 2891 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement against collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 5023–5035 (2016)
Gao, H., Chen, X.G., Qian, S.R.: Two-party quantum key agreement protocols under collective noise channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 140 (2018)
Walton, Z.D., Abouraddy, A.F., Sergienko, A.V., et al.: Decoherence-free subspaces in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 087901 (2003)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., et al.: A simple participant attack on the Bradler–Dusek protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7(4), 329–334 (2007)
Gao, F., Guo, F.Z., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Comment on “Experimental demonstration of a quantum protocol for byzantine agreement and liar detection”. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 208901 (2008)
Qin, S., Gao, F., Wen, Q., Zhu, F.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against an attack with a fake signal. Phys. Lett. A 357, 101–103 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Long, G.L., Wang, Y., Xiao, L.: Increasing the efficiencies of random-choice-based quantum communication protocols with delayed measurement. Chin. Phys. Lett. 21, 2097 (2004)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Z.J.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005)
Li, X.H., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Improving the security of secure direct communication based on the secret transmitting order of particles. Phys. Rev. A 74, 054302 (2006)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5635–5638 (2000)
Yang, Y.G., Gao, S., Li, D., et al.: Two-party quantum key agreement over a collective noisy channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 74 (2019)
Xiangbin, Wang: Fault tolerant quantum key distribution protocol with collective random unitary noise. Phys. Rev. A 72(5), 762–776 (2005)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Zeng, W., et al.: Cross-center quantum identification scheme based on teleportation and entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 254(4–6), 380–388 (2005)
Gui-Tong, Wu, Nan-Run, Zhou, Li-Hua, Gong, et al.: Quantum dialogue protocols with identification over collection noisy channel without information leakage. Acta Phys. Sin. 63(6), 060302 (2014)
Jun, G., Po-Hua, L., Tzonelih, H.: Double C-NOT attack and counterattack on ‘Three-step semi-quantum secure direct communication protocol’. Quantum Inf. Process. 17(7), 182 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 4182006, 4162005) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61572053, 61472048, 61671087, U1636106, 61602019, 61502016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, YH., Wang, MF., Shi, WM. et al. Two-party quantum key agreement against collective noisy channel. Quantum Inf Process 19, 100 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-2593-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-2593-y