Abstract
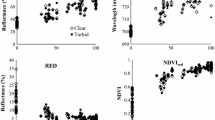
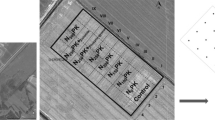
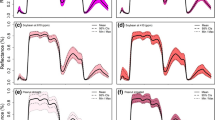
Canopy spectral reflectance (CSR) is a cost-effective, rapid, and non-destructive remote sensing and selection tool that can be employed in high throughput plant phenotypic studies. The objectives of the current study were to evaluate the predictive potential of vegetative indices as a high-throughput phenotyping tool for nitrogen use efficiency in soft red winter wheat (SRWW) (Triticum aestivum L.) and determine the optimum growth stage for employing CSR. A panel of 281 regionally developed SRWW genotypes was screened under low and normal N regimes in two crop seasons for grain yield, N uptake, nitrogen use efficiency for yield (NUEY) and nitrogen use efficiency for protein (NUEP). Vegetative indices were calculated from CSR and the data were analyzed by year and over the 2 years. Multiple regression and Pearson’s correlation were used to obtain the best predictive models and vegetative indices. The chosen models explained 84 and 83 % of total variation in grain yield and N uptake respectively, over two crop seasons. Models further accounted for 85 and 77 % of total variation in NUEY, and 85, and 81 % of total variation in NUEP under low and normal N conditions, respectively. In general, yield, NUEY and NUEP had greater than 0.6 R2 values in 2011–2012 but not in 2012–2013. Differences between years are likely a result of saturation of CSR indices due to high biomass and crop canopy coverage in 2012–2013. Heading was found to be the most appropriate crop growth stage to sense SRWW CSR data for predicting grain yield, N uptake, NUEY, and NUEP.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSR:
-
Canopy spectral reflectance
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- NIR:
-
Near infrared
- NUE:
-
Nitrogen use efficiency
- NUEP:
-
Nitrogen use efficiency for protein
- NUEY:
-
Nitrogen use efficiency for yield
- PRESS:
-
Predicted residual sum of squares
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error
- SRWW:
-
Soft red winter wheat
- VIF:
-
Variance inflation factor
References
Alley, M. M., Scharf, P., Brann, D. E., Baethgen, W. E., & Hammons, J.L. (1996). Nitrogen management for winter wheat: Principles and recommendations. Pub. No. 424-206 Virginia Cooperative Extension. Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg.
Araus, J. L., Slafer, G. A., Reynolds, M. P., & Royo, C. (2009). Breeding for yield potential. In S. Ceccarelli, et al. (Eds.), Plant breeding and farmer participation (pp. 449–478). Rome: FAO.
Austin, R. B. (1980). Physiological limitations to cereals yields and ways of reducing them by breeding. In R. G. Hurd, et al. (Eds.), Opportunities for increasing crop yields (pp. 3–19). London: Pitman.
Babar, M. A., Reynolds, M. P., Van Ginkel, M., Klatt, M., Raun, W. R., & Stone, M. L. (2006a). Spectral reflectance to estimate genetic variation for in-season biomass, leaf chlorophyll, and canopy temperature in wheat. Crop Science, 46, 1046–1057.
Babar, M. A., Reynolds, M. P., Van Ginkel, M., Klatt, M., Raun, W. R., & Stone, M. L. (2006b). Spectral reflectance indices as a potential indirect selection criteria for wheat yield under irrigation. Crop Science, 46, 578–588.
Barnes, E. M., Clarke, T. R., Richards, S. E., Colaizzi, P. D, Haberland, J., Kostrzewski, M., et al. (2000). Coincident detection of crop water stress, nitrogen status and canopy density using ground based multispectral data. In Unpaginated CD-ROM (13.pdf). In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Precision Agriculture, Bloomington. 16–19 July 2000. ASA, CSSA, & SSSA, Madison.
Blackburn, G. A. (1998). Quantifying chlorophylls and carotenoids at leaf and canopy scales: An evaluation of some hyper-spectral approaches. Remote Sensing of Environment, 66(3), 273–285.
Brann, D.E., Holshhouser, D.L., & Mullins, G.L. (2000). Agronomy handbook. Pub. No. 424-100, Virginia Cooperative Extension, Blacksburg.
Broge, N. H., Thomsen, A. G., & Andersen, P. B. (2003). Comparison of selected vegetation indices as indicators of crop status. In T. Benes (Ed.), Geoinformation for European-wide integration (pp. 591–596). Rotterdam: Millpress Science Publishers.
Knighton. N., & Bugbee, B. (2005). A mixture of barium sulfate and white paint is a low-cost substitute reflectance standard for spectralon. Crop physiology laboratory, Utah State University, Logan, UT. http://www.triticeaecap.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/12/Barium_Sulfate.pdf. Accessed 18 Oct 2014.
Cameron, S. (1993). Why is the R squared adjusted reported? Journal of Quantitative Economics, 9(1), 183–186.
Chappelle, E. W., Kim, M. S., & McMurtrey, J. E, I. I. I. (1992). Ratio analysis of reflectance spectra (RARS): An algorithm for the remote estimation of the concentrations of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids in soybean leaves. Remote Sensing of Environment, 39, 239–247.
Chen, P., Tremblay, N., Wang, J., & Vigneault, P., (2009). New spectral index for corn greenbiomass estimation. In Q. Tong & D. Li (Ed.), Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Earth Observation for Global Changes. Sichuan. China. May 25–29 2009. (pp. 507–514).
Cook, R. D. (1977). Detection of influential observations in linear regression. Technometrics, 19(1), 15–18.
Cormier, F., Faure, S., Dubreuil, P., Heumez, E., Beauchêne, K., Lafarge, S., et al. (2013). A multi-environmental study of recent breeding progress on nitrogen use efficiency in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 126(12), 3035–3048.
Datt, B. (1999). A new reflectance index for remote sensing of chlorophyll content in higher plants: tests using eucalyptus leaves. Journal of Plant Physiology, 154, 30–36.
Eitel, J. U., Keefe, R. F., Long, D. S., Davis, A. S., & Vierling, L. A. (2010). Active ground optical remote sensing for improved monitoring of seedling stress in nurseries. Sensors, 10, 2843–2850.
Eitel, J., & Long, D. (2007). Predicting wheat nitrogen status with remote sensing. (2007). In Dryland Agricultural Research Annual Report of 2007. (pp 30–35). http://extension.oregonstate.edu/catalog/html/sr/sr1074-e/06.pdf. Accessed 30 Sept 2014.
Feyerherm, A. M., Paulsen, G. M., & Sebaugh, J. L. (1984). Contribution of genetic improvement to recent wheat yield increases in the USA. Agronomy Journal, 76, 985–990.
Fitzgerald, G., Rodriguez, D., & O’Leary, G. (2010). Measuring and predicting canopy nitrogen nutrition in wheat using a spectral index—the canopy chlorophyll content index (CCCI). Field Crops Research, 116, 318–324.
Foulkes, M. J., Hawkesford, P. B., Barraclough, M. J., Holdsworth, S., Kerr, S., Kightley, S., et al. (2009). Identifying traits to improve the nitrogen economy of wheat: recent advances and future prospects. Field Crops Research, 114, 329–342.
Gaju, O., Allard, V., Martre, P., Snape, J. W., Heumez, E., LeGouis, J., et al. (2011). Identification of traits to improve the nitrogen-use efficiency of wheat genotypes. Field Crops Research, 123, 139–152.
Gamon, J., Penuelas, J., & Field, C. (1992). A narrow-waveband spectral index that tracks diurnal changes in photosynthetic efficiency. Remote Sensing of Environment, 41, 35–44.
Gitelson, A. A., Buschmann, C., & Lichtenthaler, H. K. (1999). The chlorophyll fluorescence ratio F735/F700 as an accurate measure of the chlorophyll content in plants. Remote Sensing of Environment, 69, 296–302.
Gitelson, A. A., Viña, A., Rundquist, D. C., Ciganda, V., & Arkebauer, T. J. (2005). Remote estimation of canopy chlorophyll content in crops. Geophysical Research Letters, 32, 108403.
Green, A. J., Berger, G., Griffey, C. A., Pitman, R., Thomason, W., Balota, M., et al. (2012). Genetic yield improvement in soft red winter wheat in the eastern united states from 1919 to 2009. Crop Science, 52, 2097–2108.
Guyot, G. (1990). Optical properties of vegetation canopies. In M. D. Stevens & J. A. Clark (Eds.), Applications of remote sensing in agriculture (pp. 19–43). Butterworth: London.
Hansen, P., & Schjoerring, J. (2003). Reflectance measurement of canopy biomass and nitrogen status in wheat crops using normalized difference vegetation indices and partial least squares regression. Remote Sensing of Environment, 86, 542–553.
Hatfield, J. L., Gitelson, A. A., Schepers, J. S., & Walthall, C. L. (2008). Application of spectral remote sensing for agronomic decisions. Agronomy Journal, 100, 117–131.
Hoaglin, D. C., & Welsch, R. E. (1978). The hat matrix in regression and ANOVA. The American Statistician, 32(1), 17–22.
Kent, N.L., & Evers, A.D. (1994). Technology of cereals: An introduction for students of food science and agriculture, Pergamon: Oxford [England].
Kipp, S., Mistele, B., Baresel, P., & Schmidhalter, U. (2014). High-throughput phenotyping early plant vigour of winter wheat. European Journal of Agronomy, 52, 271–278.
Kruse, J. (2010). Estimating demand for agricultural commodities to 2050. http://globalharvestinitiative.org/Documents/Kruse%20-%20Demand%20for%20Agricultural%20Commoditites.pdf. Accessed 28 Oct 2014.
Le Gouis, J., & Pluchard, P. (1996). Genetic variation for nitrogen use efficiency in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Euphytica, 92, 221–224.
Le Maire, G., Francois, C., & Dufrene, E. (2004). Towards universal broad leaf chlorophyll indices using PROSPECT simulated database and hyperspectral reflectance measurements. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89, 1–28.
Liew, O. W., Chong, P. C. J., Li, B., & Asundi, A. K. (2008). Signature optical cues: Emerging technologies for monitoring plant health. Sensors, 8, 3205–3239.
Lukina, E., Freeman, K., Wynn, K., Thomason, W., Mullen, R., Stone, M., et al. (2001). Nitrogen fertilization optimization algorithm based on in-season estimates of yield and plant nitrogen uptake. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 24(6), 885–898.
MacAdam, J. W., Volenec, J. J., & Nelson, C. J. (1989). Effects of nitrogen on mesophyll cell division and epidermal cell elongation in tall fescue leaf blades. Plant Physiology, 89, 549–556.
Mistele, B., & Schmidhalter, U. (2010). Tractor-based quadrilateral spectral reflectance measurements to detect biomass and total aerial nitrogen in winter wheat. Agronomy Journal, 102, 499–506.
Moll, R. H., Kamprath, E. J., & Jackson, W. A. (1982). Analysis and interpretation of factors which contribute to efficiency of nitrogen utilization. Agronomy Journal, 74, 562–564.
Montes, J. M., Melchinger, A. E., & Reif, J. C. (2007). Novel throughput phenotyping platforms in plant genetic studies. Trends in Plant Science, 12, 433–436.
Mortimer, N.D., Elsayed, M.A., & Horne, R.E. (2004). Energy and greenhouse gas emissions for bioethanol production from wheat grain and sugar beet, report for British sugar plc, Report No. 23/1, http://www.northenergy.co.uk Accessed 28 Oct, 2014.
Mourtzinis, S., Arriaga, F. J., Balkcom, K. S., & Ortiz, B. V. (2013). Corn grain and stover yield prediction at R1 growth stage. Agronomy Journal, 105, 1045–1050.
Mourtzinis, S., Rowntree, S. C., Suhre, J. J., Weidenbenner, N. H., Wilson, E. W., Davis, V. M., et al. (2014). The use of reflectance data for in-season soybean yield prediction. Agronomy Journal, 106, 1159–1168. doi:10.2134/agronj13.0577.
Naser, M.A. (2012). Active sensing: An innovative tool for evaluating grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency of multiple wheat genotypes. M.S. Thesis., Colarado State Univ., Fort Collins.
Ortiz-Monasterio, J.I., Manske, G.G.B., & Van Ginkel, M. (2001). Nitrogen and phosphorus use efficiency. In M.P Reynolds et al. (Ed.), Application of Physiology in Wheat Breeding. CIMMYT: Mexico (pp. 200–207).
Peleman, J. D., & van der Voort, J. R. (2003). Breeding by design. Trends in Plant Science, 8, 330–334.
Prasad, B., Carver, B. F., Stone, M. L., Babar, M. A., Raun, W. R., & Klatt, A. R. (2007). Potential use of spectral reflectance indices as a selection tool for grain yield in winter wheat under Great Plains conditions. Crop Science, 47, 1426–1440.
Raun, W. R., Solie, J. B., Stone, M. L., Martin, K. L., Freeman, K. W., Mullen, R. W., et al. (2005). Optical sensor based algorithm for crop nitrogen fertilization. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 36, 2759–2781.
Ray, S., Singh, J., & Panigrahy, S. (2010). Use of hyperspectral remote sensing data for crop stress detection: Ground-based studies. International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, XXXVIII, Part 8. Japan.
Reynolds, M., & Pfeiffer, W. (2000). Applying physiological strategies to improve yield potential. Durum wheat improvement in the Mediterranean region: New challenges. options. Mediterranèennes, 40, 95–103.
Reynolds, M. P., Rajaram, S., & Sayre, K. D. (1999). Physiological and genetic changes of irrigated wheat in the post-green revolution period and approaches for meeting projected global demand. Crop Science, 39, 1611–1621.
Rosengrant, M. W., Agcaoili-Sombilla, M., & Perez, N. D. (1995). In Global Food Projections to 2020: Implications for investment. Washington, D.C.: IFPRI.
Royo, C., & Villegas, D. (2011). Field measurements of canopy spectra for biomass assessment of small-grain cereals, In D. Matovic (Ed.), Biomass-detection, production and usage, InTech, (pp. 27–52). http://cdn.intechopen.com/pdfs/19066/InTech-field_measurements_of_canopy_spectra_for_biomass_assessment_of_small_grain_cereals.pdf Accessed 28 Oct 2014.
SAS Institute. (2012). SAS for windows v.9.3, SAS Inst., Cary.
Sheiner, L., & Beal, S. (1982). Some suggestions for measuring predictive performance. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics, 10, 229.
Siddique, K. H., Kirby, E. J. M., & Perry, M. W. (1989). Ear:stem ratio in old and modern wheat varieties: Relationship with improvement in number of grains per ear and yield. Field Crops Research, 21, 59–78.
Siegmann, B., Jarmer, T., Lilienthal, H., Richter, N., Selige, T., & Höfled, B. (2013). Comparison of narrow band vegetation indices and empirical models from hyperspectral remote sensing data for the assessment of wheat nitrogen concentration. http://koenigstuhl.geog.uni-heidelberg.de/publications/2013/Hoefle/Siegmann_et_al_2013_EARSeL.pdf. Accessed 28 Oct 2014.
Sims, D. A., & Gamon, J. A. (2002). Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sensing of Environment, 81, 337–354.
Slafer, G. A., & Rawson, H. (1994). Sensitivity of wheat phasic development to major environmental factors: A re-examination of some assumptions made by physiologists and modelers. Functional Plant Biology, 21, 393–426.
Thomason, W., Phillips, S., Davis, P., Warren, J., Alley, M., & Reiter, M. (2011). Variable nitrogen rate determination from plant spectral reflectance in soft red winter wheat. Precision Agriculture, 12, 666–681.
UCLA Statistical Consulting Group. (2013). Regression through the origin. www.ats.ucla.edu/stat/mult_pkg/faq/general/noconstant.htm Accessed 28 Oct 2014.
Van den Boogaard, R., Veneklaas, E. J., & Lambers, H. (1996). The association of biomass allocation with growth and water use efficiency of two Triticum aestivum cultivars. Australian Journal of Plant Physiology., 23, 751–761.
Van Sanford, D. A., & MacKown, C. T. (1986). Variation in nitrogen use efficiency among soft red winter wheat genotypes. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 72, 158–163.
Wu, C., Han, X., Ni, J., Niu, Z., & Huang, W. (2010). Estimation of gross primary production in wheat from in situ measurements. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation., 12, 183–189.
Wu, C., Niu, Z., Tang, Q., & Huang, W. (2008). Estimating chlorophyll content from hyperspectral vegetation indices: Modeling and validation. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 148, 1230–1241.
Zadoks, J. C., Chang, T. T., & Konzak, C. F. (1974). A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Research, 14, 415–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavuluri, K., Chim, B.K., Griffey, C.A. et al. Canopy spectral reflectance can predict grain nitrogen use efficiency in soft red winter wheat. Precision Agric 16, 405–424 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-014-9385-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-014-9385-2