Abstract
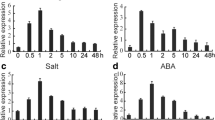
The calcineurin B-like (CBL) protein and the CBL-interacting protein kinase (CIPK) signaling pathway play important roles in plant abiotic stress tolerance. To investigate the molecular mechanism of salt stress tolerance of foxtail millet, SiCBL4 and SiCIPK24 were identified and functionally characterized. Both SiCBL4 and SiCIPK24 were induced by salt, abscisic acid (ABA), methyl viologen (MV), and heat shock stress in foxtail millet seedlings. Yeast two-hybrid and bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay showed that SiCBL4 interacted with SiCIPK24. The mutation of the N-myristoylation site of SiCBL4 changed the sub-cellular localization of SiCBL4 and directed the SiCBL4-SiCIPK24 protein complex from plasma membrane to cytoplasm, and disrupted its function in plant salt stress tolerance. Overexpression of SiCBL4 or SiCIPK24 in Arabidopsis sos3-1 or sos2-1 mutant plants rescued the mutant salt hypersensitivity phenotype. In addition, overexpression of SiCIPK24 also enhanced the salt stress tolerance of Arabidopsis wild-type plants. This work helps to understand the structure and function of the foxtail millet CBL and CIPK genes and confirmed that the foxtail millet CBL-CIPK pathway can be manipulated to enhance the plant salt stress tolerance.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batistic O, Sorek N, Schültke S, Yalovsky S, Kudla J (2008) Dual fatty acyl modification determines the localization and plasma membrane targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ signaling complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20(5):1346–1362
Bennetzen JL, Schmutz J, Wang H, Percifield R, Hawkins J, Pontaroli AC, Estep M, Feng L, Vaughn JN, Grimwood J, Jenkins J, Barry K, Lindquist E, Hellsten U, Deshpande S, Wang X, Wu X, Mitros T, Triplett J, Yang X, Ye CY, Mauro-Herrera M, Wang L, Li P, Sharma M, Sharma R, Ronald PC, Panaud O, Kellogg EA, Brutnell TP, Doust AN, Tuskan GA, Rokhsar D, Devos KM (2012) Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat Biotechnol 30(6):555–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2196
D'Angelo C, Weinl S, Batistic O, Pandey GK, Cheong YH, Schultke S, Albrecht V, Ehlert B, Schulz B, Harter K, Luan S, Bock R, Kudla J (2006) Alternative complex formation of the Ca-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J 48(6):857–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02921.x
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH, Willems AR, Woods RA (1995) Studies on the transformation of intact yeast cells by the LiAc/SS-DNA/PEG procedure. Yeast 11(4):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.320110408
Gu L, Han Z, Zhang L, Downie B, Zhao T (2013) Functional analysis of the 5′ regulatory region of the maize GALACTINOL SYNTHASE2 gene. Plant Sci 213:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.002
Gu L, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Li T, Dirk LM, Downie B, Zhao T (2016) ZmGOLS2, a target of transcription factor ZmDREB2A, offers similar protection against abiotic stress as ZmDREB2A. Plant Mol Biol 90(1–2):157–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0403-1
Hu DG, Li M, Luo H, Dong QL, Yao YX, You CX, Hao YJ (2012) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of MdSOS2 reveals its involvement in salt tolerance in apple callus and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 31(4):713–722
Jin X, Sun T, Wang X, Su P, Ma J, He G, Yang G (2016) Wheat CBL-interacting protein kinase 25 negatively regulates salt tolerance in transgenic wheat. Sci Rep 6:28884. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28884
Kanwar P, Sanyal SK, Tokas I, Yadav AK, Pandey A, Kapoor S, Pandey GK (2014) Comprehensive structural, interaction and expression analysis of CBL and CIPK complement during abiotic stresses and development in rice. Cell Calcium 56(2):81–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceca.2014.05.003
Kellogg EA, Brutnell TP, Tuskan GA, Panaud O, Doust AN, Ronald PC, Li P, Sharma M, Sharma R, Rokhsar D (2012) Reference genome sequence of the model plant Setaria. Nat Biotechnol 30(6):555–561
Kim BG, Waadt R, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Dominguez-Solis JR, Schultke S, Lee SC, Kudla J, Luan S (2007) The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J: Cell Mol Biol 52(3):473–484. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03249.x
Knight H, Trewavas AJ, Knight MR (1997) Calcium signalling in Arabidopsis thaliana responding to drought and salinity. Plant J: Cell Mol Biol 12(5):1067–1078
Kudla J, Xu Q, Harter K, Gruissem W, Luan S (1999) Genes for calcineurin B-like proteins in Arabidopsis are differentially regulated by stress signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(8):4718–4723
Li R, Zhang J, Wu G, Wang H, Chen Y, Wei J (2012) HbCIPK2, a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environment 35(9):1582–1600
Li P, Song A, Gao C, Wang L, Wang Y, Sun J, Jiang J, Chen F, Chen S (2015) Chrysanthemum WRKY gene CmWRKY17 negatively regulates salt stress tolerance in transgenic chrysanthemum and Arabidopsis plants. Plant Cell Rep 34(8):1365–1378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1793-x
Lin H, Yang Y, Quan R, Mendoza I, Wu Y, Du W, Zhao S, Schumaker KS, Pardo JM, Guo Y (2009) Phosphorylation of SOS3-LIKE CALCIUM BINDING PROTEIN8 by SOS2 protein kinase stabilizes their protein complex and regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 21(5):1607–1619. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.066217
Liu J, Zhu JK (1997) An Arabidopsis mutant that requires increased calcium for potassium nutrition and salt tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94(26):14960–14964
Liu J, Zhu JK (1998) A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280(5371):1943–1945
Luan S, Lan WZ, Lee SC (2009) Potassium nutrition, sodium toxicity, and calcium signaling: connections through the CBL-CIPK network. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.05.003
Mahajan S, Sopory SK, Tuteja N (2006) Cloning and characterization of CBL-CIPK signalling components from a legume (Pisum sativum). FEBS J 273(5):907–925. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05111.x
Martínez-Atienza J, Quintero FJ (2007) Conservation of the salt overly sensitive pathway in rice. Plant Physiol 143(2):1001–1012
Pandey GK, Grant JJ, Yong HC, Kim BG, Le GL, Sheng L (2008) Calcineurin-B-like protein CBL9 interacts with target kinase CIPK3 in the regulation of ABA response in seed germination. Mol Plant 1(2):238–248
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(12):8436–8441
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I, Zhang Y, Cao W, Yang Y, Shang M, Chen S, Pardo JM, Guo Y (2007) SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19(4):1415–1431. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.042291
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sánchez-Barrena MJ, Martínez-Ripoll M, Zhu JK, Albert A (2005) The structure of the Arabidopsis thaliana SOS3: molecular mechanism of sensing calcium for salt stress response. J Mol Biol 345(5):1253–1264
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10):2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tang RJ, Yang Y, Yang L, Liu H, Wang CT, MM Y, Gao XS, Zhang HX (2014) Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell Environ 37(3):573–588. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12178
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Wang M, Gu D, Liu T, Wang Z, Guo X, Hou W, Bai Y, Chen X, Wang G (2007) Overexpression of a putative maize calcineurin B-like protein in Arabidopsis confers salt tolerance. Plant Mol Biol 65(6):733–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-007-9238-8
Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ, Wang Y, Liu LL, He L, WH W (2006) A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125(7):1347–1360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.011
Zhang Y, Su J, Duan S, Ao Y, Dai J, Liu J, Wang P, Li Y, Liu B, Feng D, Wang J, Wang H (2011) A highly efficient rice green tissue protoplast system for transient gene expression and studying light/chloroplast-related processes. Plant Methods 7(1):30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-7-30
Zhang H, Liu WZ, Zhang Y, Deng M, Niu F, Yang B, Wang X, Wang B, Liang W, Deyholos MK (2014) Identification, expression and interaction analyses of calcium-dependent protein kinase (CPK) genes in canola ( Brassica napus L.) BMC Genomics 15(1):211
Zhao J, Sun Z, Zheng J, Guo X, Dong Z, Huai J, Gou M, He J, Jin Y, Wang J (2009) Cloning and characterization of a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from maize. Plant Mol Biol 69(6):661–674
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Yuanqing Jiang for providing us the Atsos3-1 and Atsos2-1 mutants. This research was supported by the special fund for transgenic research from the Ministry of Agriculture in China 2014ZX0800920B, the National Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province 2014JM3073 (to T.Z), and the National Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province 2015011071 (to J.Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Supplemental Figure 1
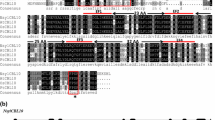
Phylogenetic relationship of CBL proteins from maize, rice, Arabidopsis and foxtail millet. Organism and accession numbers are listed in supplemental data set1. (JPEG 1861 kb)
ESM 1
The List of CBL and CIPK proteins from Arabidopsis, rice, mazie and foxtail millet genome. (XLS 40 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Linghu, J., Wang, D. et al. Foxtail Millet CBL4 (SiCBL4) Interacts with SiCIPK24, Modulates Plant Salt Stress Tolerance. Plant Mol Biol Rep 35, 634–646 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1051-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-017-1051-1