Abstract
Background
The yield potential of super hybrid rice has been increased by nearly 10% compared to ordinary hybrid or inbred rice. To further explain the reasons for the yield advantage of hybrids, we conducted investigations into the underlying physiological mechanism by considering leaf photosynthesis in combination with assimilate translocation.
Methods
Field experiments were conducted from 2020 to 2021 to compare the yield, photosynthetic performance, and efficiency of assimilate translocation-related traits between super hybrid rice (Yliangyou5867 and Yliangyou3218) and inbred super rice (Zhendao11 and Nanjing9108) under two nitrogen (N) levels.
Results
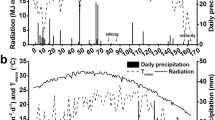
The average yield of hybrids across N levels was respectively 15.7% and 25.3% higher than that of inbreds in 2020 and 2021. Before heading, the biomass of hybrids was significantly higher than that of inbreds, and hybrids exhibited a higher harvest index. The higher radiation use efficiency (RUE) in hybrids was primarily due to an improved photosynthetic rate (Pn). Dry matter translocation from stem and leaf to panicle of hybrids was higher than that of inbreds. The hybrids also exhibited greater fluctuation in day-night sugar content and higher phloem sugar content which indicated higher assimilate translocation efficiency with hybrids.
Conclusions
Our results revealed that the higher RUE was responsible for the higher aboveground biomass before heading in hybrids. Furthermore, the improved biomass partitioning and remobilization, as demonstrated by an increase in assimilate translocation efficiency, contributed to higher harvest index and grain yield in hybrids. Crop breeders should focus on coordinating light utilization and assimilate translocation efficiency in super hybrid rice.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ainsworth EA, Bush DR (2011) Carbohydrate export from the leaf: a highly regulated process and target to enhance photosynthesis and productivity. Plant Physiol 155:64–69. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.167684
Bueno CS, Lafarge T (2009) Higher crop performance of rice hybrids than of elite inbreds in the tropics: 1. Hybrids accumulate more biomass during each phenological phase. Field Crop Res 112:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2009.03.006
Burnett AC, Rogers A, Rees M, Osborne CP (2016) Carbon source-sink limitations differ between two species with contrasting growth strategies. Plant Cell Environ 39:2460–2472. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12801
Busch FA, Sage RF (2017) The sensitivity of photosynthesis to O2 and CO2 concentration identifies strong rubisco control above the thermal optimum. New Phytol 213:1036–1051. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14258
Chen L-Y, Xiao Y-H, Tang W-B, Lei D-Y (2007) Prospect and practice of three-procedure breeding on super hybrid rice. Zhongguo Shuidao Kexue 21:90–94
Chen L, Deng Y, Zhu HL, Hu YX, Jiang ZR, Tang S, Wang SH, Ding YF (2019) The initiation of inferior grain filling is affected by sugar translocation efficiency in large panicle rice. Rice 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0333-7
Cheng SH, Cao LY, Zhuang JY, Chen SG, Zhan XD, Fan YY, Zhu DF, Min SK (2007) Super hybrid rice breeding in China: achievements and prospects. J Integr Plant Biol 49:805–810. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00514.x
Cheng YX, Xiao F, Huang DY, Yang Y, Cheng WD, Jin SC, Li GH, Ding YF, Paul MJ, Liu ZH (2024) High canopy photosynthesis before anthesis explains the outstanding yield performance of rice cultivars with ideal plant architecture. Field Crop Res 306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2023.109223
Corbin JL, Walker TW, Orlowski JM, Krutz LJ, Gore J, Cox MS, Golden BR (2016) Evaluation of trinexapac-ethyl and nitrogen management to minimize lodging in rice. Agron J 108:2365–2370. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2016.04.0185
De Costa W, Weerakoon WMW, Herath H, Amaratunga KSP, Abeywardena RMI (2006) Physiology of yield determination of rice under elevated carbon dioxide at high temperatures in a subhumid tropical climate. Field Crop Res 96:336–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2005.08.002
Deng J, Sheng T, Zhong XF, Ye JY, Wang CH, Huang LY, Tian XH, Liu K, Zhang YB (2023) Delayed leaf senescence improves radiation use efficiency and explains yield advantage of large panicle-type hybrid rice. Plants-Basel 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12234063
Elhakeem A, van der Werf W, Bastiaans L (2021) Radiation interception and radiation use efficiency in mixtures of winter cover crops. Field Crop Res 264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2020.108034
Fabre D, Yin XY, Dingkuhn M, Clement-Vidal A, Roques S, Rouan L, Soutiras A, Luquet D (2019) Is triose phosphate utilization involved in the feedback inhibition of photosynthesis in rice under conditions of sink limitation? J Exp Bot 70:5773–5785. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz318
Huang JL, He F, Cui KH, Buresh RJ, Xu B, Gong WH, Peng SB (2008) Determination of optimal nitrogen rate for rice varieties using a chlorophyll meter. Field Crop Res 105:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.07.006
Huang M, Chen JN, Cao FB, Jiang LG, Zou YB (2015) Root morphology was improved in a late-stage vigor super rice cultivar. PLoS One 10:9. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142977
Huang M, Shan SL, Zhou XF, Chen JN, Cao FB, Jiang LG, Zou YB (2016) Leaf photosynthetic performance related to higher radiation use efficiency and grain yield in hybrid rice. Field Crop Res 193:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.03.009
Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (2016) Climate change 2016. Synthesis report. Vol. AR5. Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change, Geneva
Katsura K, Maeda S, Horie T, Shiraiwa T (2007) Analysis of yield attributes and crop physiological traits of Liangyoupeijiu, a hybrid rice recently bred in China. Field Crop Res 103:170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2007.06.001
Khush GS (2013) Strategies for increasing the yield potential of cereals: case of rice as an example. Plant Breed 132:433–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.1991
Lafarge T, Bueno CS (2009) Higher crop performance of rice hybrids than of elite inbreds in the tropics: 2. Does sink regulation, rather than sink size, play a major role? (vol 112, pg 238, 2009). Field Crop Res 114:433–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2009.08.010
Liu K, Yang R, Deng J, Huang LY, Wei ZW, Ma GH, Tian XH, Zhang YB (2020) High radiation use efficiency improves yield in the recently developed elite hybrid rice Y-liangyou 900. Field Crops Res 253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2020.107804
Mitchell PL, Sheehy JE (2006) Supercharging rice photosynthesis to increase yield. New Phytol 171:688–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01855.x
Normile D (2008) Reinventing rice to feed the world. Science 321:330–333. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.321.5887.330
Okamura M, Arai-Sanoh Y, Yoshida H, Mukouyama T, Adachi S, Yabe S, Nakagawa H, Tsutsumi K, Taniguchi Y, Kobayashi N, Kondo M (2018) Characterization of high-yielding rice cultivars with different grain-filling properties to clarify limiting factors for improving grain yield. Field Crop Res 219:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2018.01.035
Pan YH, Gao S, Xie KL, Lu ZF, Meng XS, Wang SY, Lu JW, Guo SW (2020) Higher radiation use efficiency produces greater biomass before heading and grain yield in super hybrid rice. Agronomy-Basel 10:13. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10020209
Paul MJ, Foyer CH (2001) Sink regulation of photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 52:1383–1400. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.360.1383
Paul MJ, Pellny TK (2003) Carbon metabolite feedback regulation of leaf photosynthesis and development. J Exp Bot 54:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erg052
Peng S (2000) Single-leaf and canopy photosynthesis of rice. Redesigning Rice Photosynth Increase Yield 7:213–228
Peng SB, Khush GS, Virk P, Tang QY, Zou YB (2008) Progress in ideotype breeding to increase rice yield potential. Field Crop Res 108:32–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2008.04.001
Sharkey TD, Bernacchi CJ, Farquhar GD, Singsaas EL (2007) Fitting photosynthetic carbon dioxide response curves for C3 leaves. Plant Cell Environ 30:1035–1040. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01710.x
Tartachnyk II, Blanke MM (2004) Effect of delayed fruit harvest on photosynthesis, transpiration and nutrient remobilization of apple leaves. New Phytol 164:441–450. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01197.x
Wang L, Lu Q, Wen X, Lu C (2015) Enhanced sucrose loading improves rice yield by increasing grain size. Plant Physiol 169:2848–2862. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01170
Wei H, Meng T, Li X, Dai Q, Zhang H, Yin X (2018) Sink-source relationship during rice grain filling is associated with grain nitrogen concentration. Field Crop Res 215:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.09.029
Weichert N, Saalbach I, Weichert H, Kohl S, Erban A, Kopka J, Hause B, Varshney A, Sreenivasulu N, Strickert M, Kumlehn J, Weschke W, Weber H (2010) Increasing sucrose uptake capacity of wheat grains stimulates storage protein synthesis. Plant Physiol 152:698–710. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.150854
White AC, Rogers A, Rees M, Osborne CP (2016) How can we make plants grow faster? A source-sink perspective on growth rate. J Exp Bot 67:31–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv447
Xu FY, Wang K, Yuan W, Xu WF, Shuang L, Kronzucker HJ, Chen GL, Miao R, Zhang MX, Ding M, Xiao L, Kai L, Zhang JH, Zhu YY (2019) Overexpression of rice aquaporin OsPIP1;2 improves yield by enhancing mesophyll CO2 conductance and phloem sucrose transport. J Exp Bot 70:671–681. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery386
Yang WH, Peng SB, Laza RC, Visperas RM, Dionisio-Sese ML (2007) Grain yield and yield attributes of new plant type and hybrid rice. Crop Sci 47:1393–1400. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.07.0457
Yang JT, Preiser AL, Li ZR, Weise SE, Sharkey TD (2016) Triose phosphate use limitation of photosynthesis: short-term and long-term effects. Planta 243:687–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2436-8
Yuan LP (2017) Progress in super-hybrid rice breeding. Crop J 5:100–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2017.02.001
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U2003210) and National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1900704-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shiwei Guo, Xusheng Meng and Yonghui Pan conceived and designed the experiments; Xusheng Meng, Yixiao Chai, Yu Ji, Haisu Du, and Jian Huang performed the experiments; Xusheng Meng and Shengxian Chen analysed the data and wrote the paper; Yonghui Pan, Min Wang, and Shiwei Guo helped in analysis of the results and manuscript writing; all authors discussed the results and reviewed the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: M. Iqbal R. Khan.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 706 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Pan, Y., Chai, Y. et al. Higher light utilization and assimilate translocation efficiency produced greater grain yield in super hybrid rice. Plant Soil (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06639-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-024-06639-1