Abstract
Background
The characteristics of boron (B) isotopes in different organ samples of Brassica napus L. provide powerful insights for better understanding the nutrient effect and acquisition mechanism of B in plants.
Method
Hydroponic experiments with B sources and constant pH controlled in the nutrient solution were carried out to explore the B isotopic signals in different plant organs during the growth of B. napus.
Results
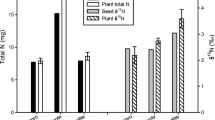
The B contents and δ11B values showed an increasing trend from roots to leaves and a decreasing trend from leaves to flowers. B absorption at the interface of plant-nutrient solution system is controlled by equilibrium process in a closed system with light isotopes preferentially absorbed into roots in B-sufficient and B-deficient media. A Rayleigh fractionation model was used to fit the fractionation of B isotopes with the accumulated distribution fraction during plant growth. The kinetic fractionation process of absorption causes the increased fractionation of B isotopes from the lower to upper compartment in different diffusion manners of B(OH)3. The light isotope preferentially bonds with pectin by chelate crosslinking group to form the cell wall with more 11B left in the sap.
Conclusions
The results also suggest that the B isotope tool has the potential to enable identification of the B nutrient effect and the physiochemical mechanism in plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- B:
-
Boron
- MC‒ICP‒MS:
-
Multicollector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- ICP‒MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
- a :
-
Isotopic fractionation factor
References
Bailey DG, Lupulescu MV, Darling RS, Singer JW, Chamberlain SC (2019) A review of boron-bearing minerals (excluding Tourmaline) in the Adirondack Region of New York State. Minerals 9:644–678. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9100644
Balistrieri LS, Borrok DM, Wanty RB, Ridley WI (2008) Fractionation of Cu and Zn isotopes during adsorption onto amorphous Fe(III) oxyhydroxide: Experimental mixing of acid rock drainage and ambient river water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:311–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.11.013
Bariya H, Bagtharia S, Patel A (2014) Boron: A promising nutrient for increasing growth and yield of plants. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland, pp 153–170
Blevins DG, Lukaszewski KM (1998) Boron in plant structure and function. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:481–500. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.481
Brown PH, Bellaloui N, Wimmer MA, Bassil ES, Ruiz J, Hu H, Pfeffer H, Dannel F, Römheld V. Boron in plant biology. Plant Biol 2002;4:205–223. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2002-25740
Camacho-Cristóbal JJ, Rexach J, González-Fontes A (2008) Boron in plants: deficiency and toxicity. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1247–1255. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00742.x
Carrano CJ, Schellenberg S, Amin SA, Green DH, Küpper FC (2009) Boron and marine life: a new look at an enigmatic bioelement. Mar Biotechnol 11:431–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-009-9191-4
Chalk PM (2020) Natural variations in stable boron isotopes (δ11B) as tracers in terrestrial ecosystems. Isot Environ Heal S 56:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256016.2020.1773458
Chetelat B, Liu CQ, Gaillarde J, Wang QL, Zhao ZQ, Liang CS, Xiao YK (2009) Boron isotopes geochemistry of the Changjiang basin rivers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:6084–6097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.07.026
Dannel F, Pfeffer H, Römheld V (2000) Characterization of root boron pool, boron uptake and boron translocation in sunflower using the stable isotopes 10B and 11B. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:397–405. https://doi.org/10.1071/PP99086
Das BC, Thapa P, Karki R, Schinke C, Das S, Kambhampati S, Banerjee SK, Van Veldhuizen P, Verma A, Weiss LM (2013) Boron chemicals in diagnosis and therapeutics. Future Med Chem 5:653–676. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.38
Donald HK, Foster GL, Fröhberg N, Swann GEA, Poulton AJ, Moore CM, Humphreys MP (2020) The pH dependency of the boron isotopic composition of diatom opal (Thalassiosira weissflogii). Biogeosci 17:2825–2837. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-17-2825-2020
Elmaci G, Icten O, Ay AN, Birgül ZK (2015) Boron isotopic fractionation in aqueous boric acid solutions over synthetic minerals: Effect of layer and surface charge on fractionation factor. Appl Clay Sci 107:117–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.01.011
Ercolani C, Lemarchand D, Dosseto A (2019) Insights on catchment-wide weathering regimes from boron isotopes in riverine material. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 261:35–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2019.07.002
Farmer JR, Branson O, Uchikawa J, Penman DE, Hönisch B, Zeebe RE (2019) Boric acid and borate incorporation in inorganic calcite inferred from B/Ca, boron isotopes and surface kinetic modeling. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 244:229–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.10.008
Geilert S, Vogl J, Rosner M, Eichert T (2019) Boron isotope variability related to boron speciation (change during uptake and transport) in bell pepper plants and SI traceable n(11B)/n(10B) ratios for plant reference materials. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 33:1137–1147. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcm.8455
Gonzalez-Fontes A, Fujiwara T (2020) Advances in plant boron. Int J Mol Sci 21:4107–4109. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114107
He J, Cui JZ, Zhu DW, Zhou WB, Liao SJ, Geng MJ (2015) The use of boron isotopes to evaluate boron uptake by rape grown in acid soil treated with boron containing goethite. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 178:935–943. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.201400336
He MY, Xiao YK, Jin ZD, Ma YQ, Xiao J, Zhang YL, Luo CG, Zhang F (2013) Accurate and precise determination of boron isotopic ratios at low concentration by positive thermal ionization mass spectrometry using static multicollection of Cs2BO2+ ions. Anal Chem 85:6248–6253. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400066r
He MY, Deng L, Lu H, Jin ZD (2019) Elimination of boron memory effect for rapid and accurate boron isotope analysis by MC-ICP-MS using NaF. J Anal Atom Spectro 34:1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9JA00007K
Klochko K, Kaufman AJ, Yao W, Byrne RH, Tossell JA (2006) Experimental measurement of boron isotope fractionation in seawater. Earth Planet Sci Lett 248:276–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.05.034
Köster MH, Williams LB, Kudejova P, Gilg HA (2019) The boron isotope geochemistry of smectites from sodium, magnesium and calcium bentonite deposits. Chem Geol 510:166–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.12.035
Lei F, Wei HZ, Yi SW, Zeng L, Lu HY (2021) Variations of the East Asian monsoon over the past 800 kyr constrained by the boron isotope composition of paleo-rainwater inferred from loess-paleosol deposits in NE China. Earth Planet Sc Lett 561:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2021.116826
Li YC, Chen HW, Wei HZ, Jiang SY, Palmer MR, van de Ven TGM, Hohl S, Lu JJ, Ma J (2020) Exploration of driving mechanisms of equilibrium boron isotope fractionation in tourmaline group minerals and fluid: A density functional theory study. Chem Geol 536:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119466
Li YC, Wei HZ, Palmer MR, Jiang SY, Liu X, Williams-Jones AE, Ma J, Lu JJ, Lin YB, Dong G (2021) Boron coordination and B/Si ordering controls over equilibrium boron isotope fractionation among minerals, melts, and fluids. Chem Geol 561:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.120030
Liu T, He T, Shi QH, Ni Q (2019) Rapid determination of boron in 61 soil, sediment, and rock reference materials by ICP-MS. Atom Spectrosc 40:55–62 https://doi.org/10.46770/AS.2019.02.004
Mao HR, Liu CQ, Zhao ZQ (2019) Source and evolution of dissolved boron in rivers: Insights from boron isotope signatures of end-members and model of boron isotopes during weathering processes. Earth Sci Rev 190:439–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.01.016
Marschall HR, Meyer C, Wunder B, Ludwig T, Heinrich W (2009) Experimental boron isotope fractionation between tourmaline and fluid: confirmation from in situ analyses by secondary ion mass spectrometry and from Rayleigh fractionation modelling. Contrib Mineral Petrol 158:675–681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-009-0403-8
Mavromatis V, Montouillout V, Noireaux J, Gaillardet J, Schott J (2015) Characterization of boron incorporation and speciation in calcite and aragonite from co-precipitation experiments under controlled pH, temperature and precipitation rate. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 150:299–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.10.024
Milka BJ (2020) Boron toxicity and deficiency in agricultural plants. Int J Mol Sci 21:1424–1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21041424
Morse SA (2008) The internal magma reservoir of large intrusions revealed by multiphase Rayleigh fractionation. J Petrol 49:2081–2098. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egn059
O’Neill MA, Ishii T, Albersheim P, Darvill AG (2004) Rhamnogalacturonan II: structure and function of a borate cross-linked cell wall pectic polysaccharide. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:109–139. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141750
Pereira GL, Siqueira JA, Willian BS, Cardoso FB, Adriano NN, Araújo WL (2020) Boron: more than an essential element for land plants? Front Plant Sci 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.610307
Roux P, Turpault MP, Kirchen G, Redon PO, Lemarchand D (2017) Boron dissolved and particulate atmospheric inputs to a forest ecosystem (Northeastern France). Environ Sci Technol 51:14038–14046. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03226
Rosner M, Pritzkow W, Vogl J, Voerkelius S (2011) Development and validation of a method to determine the boron isotopic composition of crop plants. Anal Chem 83:2562–2568. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac102836h
Santesteban LG, Miranda C, Barbarin I, Royo JB (2015) Application of the measurement of the natural abundance of stable isotopes in viticulture: a review. Aus J Grape Wine Res 21:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajgw.12124
Schmitt AD, Cobert F, Bourgeade P, Ertlen D, Labolle F, Gangloff S, Badot PM, Chabaux F, Stille P. Calcium isotope fractionation during plant growth under a limited nutrient supply. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 2013;110:70–83 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2013.02.002.
Sun AD, Gou DD, Dong YL, Xu QC, Cao GJ (2019) Extraction and analysis of available boron isotopes in soil using multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 67:7183–7189. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01455
Sun AD, Xu QC, Ren LY, Cao GJ, Gou DD (2017) Non-equilibrium ultrasound-assisted solid–liquid extraction of boron present in different phases within plants by ICP-OES. RSC Adv 7:49890–49894. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07078K
Sun AD, Xu QC, Wei GJ, Zhu HY, Chen XF (2018) Differentiation analysis of boron isotopic fractionation in different forms within plant organ samples. Phytochem 147:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2017.12.012
Takano J, Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2008) Boron transport mechanisms: collaboration of channels and transporters. Trends Plant Sci 13:451–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.05.007
Wang NN, Wei QJ, Yan TS, Pan ZY, Liu YZ, Peng SA (2016) Improving the boron uptake of boron-deficient navel orange plants under low boron conditions by inarching boron-efficient rootstock. Sci Hortic 199:49–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2015.12.014
Wei GJ, Wei JX, Liu Y, Ke T, Ren ZY, Ma JL, Xu YG (2013) Measurement on high-precision boron isotope of silicate materials by a single column purification method and MC-ICP-MS. J Anal Atom Spectrom 28:606–612. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ja30333k
Wei HZ, Zhao Y, Liu X, Wang YJ, Lei F, Wang WQ, Li YC, Lu HY (2021) Evolution of paleo-climate and seawater pH from the late Permian to postindustrial periods recorded by boron isotopes and B/Ca in biogenic carbonates. Earth Sci Rev 215:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103546
Wiggenhauser M, Moore RET, Wang P, Bienert GP, Laursen KH, Blotevogel S (2022) Stable Isotope Fractionation of Metals and Metalloids in Plants: A Review. Front Plant Sci 13:840941. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.840941
Xiao J, Xiao YK, Jin ZD, He MY, Liu CQ (2013) Boron isotope variations and its geochemical application in nature. Aus J Earth Sci 60:431−447 https://doi.org/10.1080/08120099.2013.813585
Xiao J, Vogl J, Rosner M, Deng L, Jin ZD (2019) A validated analytical procedure for boron isotope analysis in plants by MC-ICP-MS. Talanta 196:389−394 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.087
Xiao J, Vogl J, Rosner M, Jin ZD (2022) Boron isotope fractionation in soil-plant systems and its influence on biogeochemical cycling. Chem Geol 606:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.120972
Xu QC, Dong YL, Zhu HY, Sun AD (2015) Separation and analysis of boron isotope in high plant by thermal ionization mass spectrometry. Int J Anal Chem 2015:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/364242
Yang L, Zhang Q, Dou JN, Li L, Guo LF, Shi L, Xu FS (2013) Characteristics of root boron nutrition confer high boron efficiency in Brassica napus cultivars. Plant Soil 371:95–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1669-1
Young ED, Manning CE, Schauble EA, Shahar A, Macris CA, Lazar C, Jorda M. High-temperature equilibrium isotope fractionation of non-traditional stable isotopes: experiments, theory, and applications. Chem Geol 2015;395:176–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.12.013.
Zhou WB, Qiu BS (2004) Measurement of Intracellular pH in Plants. Plant Physiol Commun 40:724–728 https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2004.06.030
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Program for Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41673007 and 42173017) and the Program of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (grant no. ZR2020KC040).
Funding
This work was supported by the Program for Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 41673007 and 42173017) and the Program of Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (grant no. ZR2020KC040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Zhiqun Chen, Aide Sun and Li Yan. Jinxin Peng Zhijie Hu, and Zhiqun Chen analyzed the data. Zhiqun Chen, Aide Sun and Li Yan wrote this manuscript. Zhiqun Chen, Aide Sun and Li Yan designed the experiment and revised this manuscript, Qingcai Xu revised this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This research did not involve human participants or animals.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ad C. Borstlap.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Hu, Z., Peng, J. et al. Boron isotopic fractionation in Brassica napus L. plants during plant growth under hydroponic conditions. Plant Soil 485, 411–423 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05839-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05839-x