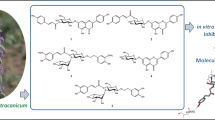
Inhibition of α-glucosidase is a therapeutic approach that slows down the hydrolysis of oligosaccharides and disaccharides to glucose. Therefore, delaying the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates by inhibiting α-glucosidase can reduce blood glucose levels. Herein, the methanol extract of Scutellaria barbata D. Don was screened for α-glucosidase inhibitors using an in vitro inhibition assay and chromatographic techniques (column chromatography, TLC, and HPLC). Six known flavonoids were isolated, including chrysin (1), wogonin (2), apigenin (3), hispidulin (4), pinocembrin (5) and 6-methoxyaringenin (6), and their structures were identified by spectroscopic methods (NMR and MS) and by comparing their spectral data to reported values. Compounds 1 – 6 exhibited higher inhibitory activities against α-glucosidase with IC50 values between 17 μM and 192 μM compared to the reference drug acarbose (1463.0 ± 29.5 μM). The kinetic analysis showed that flavonoid 1 was a competitive inhibitor, flavonoids 2 and 4 were mixed-type inhibitors, while flavonoids 3, 5 and 6 were noncompetitive inhibitors of α-glucosidase. Computer modeling showed that the primary amino acid residue interacted with the flavonoids primarily through hydrogen bonding, with binding energies ranging from –5.44 to –1.85 kcal/mol. These results indicate that compounds 1 – 6 are potential α-glucosidase inhibitors.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Xiao, G. Kai, K. Yamamoto, et al., Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 53 (8), 818 – 836 (2013).
S. Li, J. Li, X. L. Guan, et al., Fitoterapia, 82(7), 1081 – 1085 (2011).
Y. Hu, Z. Hou, R. Yi, et al., Food Funct., 8(8), 2803 – 2816 (2017).
A. P. de Oliveira, J. S. Coppede, B. W. Bertoni, et al., Chem. Biodivers., 15(1), e1700421 (2018).
B. Shan, J. Zhang, and X. Du, Chin. J. Integr. Trad. West. Med., 21(5), 370 – 374 (2001).
W. Y. Gu, J. Chen, Y. Y. Tang, et al., Chem Nat. Compd., 55(3), 469 – 470 (2019).
V. Malikov and M. Yuldashev, Chem. Nat. Compd., 38(4), 358 – 406 (2002).
H. Xu, J. Luo, J. Huang, et al., Medicine, 97(19), e0686 (2018).
L. Zeng, H. Ding, X. Hu, et al., Food Chem., 271, 70 – 79 (2019).
L. Zeng, G. Zhang, S. Lin, et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 64(37), 6939 – 6949 (2016).
V. Morocho, A. Valle, J. Garcia, et al., Molecules, 23(1), 146 (2018).
Y. S. Lin, C. R. Chen, W. H. Wu, et al., J. Agric. Food Chem., 63(28), 6393 – 6401 (2015).
W. J. Hu, L. Yan, D. Park, et al., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 50(3), 694 – 700 (2012).
Y. Meng, A. Su, S. Yuan, et al., Plant Foods Hum. Nutr., 71(4), 444 – 449 (2016).
G. Maeda, J. J. Munissi, S. Lindblad, et al., J. Nat. Prod., 83(2), 316 – 322.
X. D. Cao, Z. S. Ding, F. S. Jiang, et al, Nat. Prod. Res., 26(22), 2089 – 2094 (2012).
M. Xu, L. Shen, and K. Wang, Fitoterapia, 80(8), 461 – 464 (2009).
T. Mitsui, S. Hotta, S. Tazawa, et al., Biosc. Biotechnol. Biochem., 82(3), 417 – 421 (2018).
R. H. Liu, X. C. Wen, F. Shao, et al., Chin. Herb. Med., 8(1), 89 – 93 (2016).
O. Spring, N. Heil, and B. Vogler, Phytochemistry, 46(8), 1369 – 1373 (1997).
S. R. Lee, M. S. Kim, S. Kim, et al., Chem. Biodivers., 14(11), e1700231 (2017).
J. Yang, X. Wang, C. Zhang, et al., Food Chem., 347, 129056 (2021).
K. Tadera, Y. Minami, K. Takamatsu, et al., J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 52(2), 149 – 153 (2006).
C. Proença, M. Freitas, D. Ribeiro, et al., J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem., 32(1), 1216 – 1228 (2017).
Z. Xiong, W. Liu, L. Zhou, et al., Food Chem., 203, 430 – 439 (2016).
J. P. Zhang, Q. X. Chen, K. K. Song, et al., Food Chem., 95(4), 579 – 584 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Shu-Chi Lin and Ms Lih-Mei Sheu for their technical assistance with the MS measurements in the Instrumentation Centre at National Tsing Hua University and National Chung Hsing University. The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer (NMR) was conducted in the Precision Instruments Centre of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (Grant MOST 105-2320-B-020- 002-MY3 and MOST 108-2320-B-020-003) and NPUST-KMU Joint Research Project (KP109005 and NPUST-KM-109-P006).
SUPPLEMENTARYMATERIAL
The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of compounds 1 – 6 are available as supplementary material by request from the authors.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dlamini, B.S., Chen, CR., Kuo, YH. et al. Bio-Assay Guided Isolation of Flavonoids from Scutellaria barbata D. Don and Their Mechanism of α-Glucosidase Inhibition. Pharm Chem J 56, 683–691 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02695-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11094-022-02695-y