Abstract
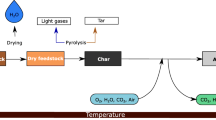
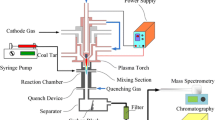
Thermal plasma-assisted processing is an effective process for the synthesis of gas (CO and H2) and carbonaceous materials production from industrial waste. In this paper, a DC plasma torch designed with two vortices chambers has been developed, and its characteristics have been experimentally tested. The plasma torch operates with different plasma working gases, including steam. The results of coal tar pitch (CTP) processing will be presented as a possible ecological application. CTP is a waste from the steel industry mainly composed of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. The experimental results will be discussed with thermodynamic calculations and numerical simulation of the heat and mass transfer in the DC plasma torch and the chemical reaction chamber. The simulations were carried out to clarify the regions of gas flow and temperatures for producing synthesis gas and carbon nanomaterial. The results enable one to predict the produced gas composition and carbon nanomaterial properties. The physicochemical properties of carbon nanomaterial and synthesis gas show high efficiency in converting CTP into high-value-added products.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminian J, Arshad AK (2020) ScienceDirect performance analysis of syngas production in a water thermal plasma reactor. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:30017–30028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.128
Billoux T, Cressault Y, Gleizes A (2015) Net emission coefficient for CO – H 2 thermal plasmas with the consideration of molecular systems. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 166:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2015.07.011
Ruj B, Ghosh S (2014) Technological aspects for thermal plasma treatment of municipal solid waste—a review. Fuel Process Technol 126:298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.05.011
Materazzi M, Lettieri P, Taylor R, Chapman C (2016) Performance analysis of RDF gasification in a two stage fluidized bed-plasma process. Waste Manag 47:256–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.016
Ren J, Cao J, Zhao X, Liu Y (2021) Fundamentals and applications of char in biomass tar reforming. Fuel Process Technol 216:106782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2021.106782
Kim SC, Lim MS, Chun YN (2013) Hydrogen-rich gas production from a biomass pyrolysis gas by using a plasmatron. Int J Hydrogen Energy 38:14458–14466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.004
Favas J, Monteiro E, Rouboa A (2017) Hydrogen production using plasma gasification with steam injection. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:10997–11005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.109
Kahraman N, Tangöz S, Akansu SO (2018) Numerical analysis of a gas turbine combustor fueled by hydrogen in comparison with jet—a fuel. Fuel 217:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.071
Gobbato P, Masi M, Toffolo A, Lazzaretto A (2011) Numerical simulation of a hydrogen fuelled gas turbine combustor. Int J Hydrog Energy 36:7993–8002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.01.045
Verhelst S, Wallner T, Sierens R (2014) Hydrogen-Fueled internal combustion engines. Handb Hydrog Energy 1:821–902. https://doi.org/10.1201/b17226
White CM, Steeper RR, Lutz AE (2006) The hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engine: a technical review. Int J Hydrog Energy 31:1292–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2005.12.001
Eriksson ELV, Gray EMA (2017) Optimization and integration of hybrid renewable energy hydrogen fuel cell energy systems—a critical review. Appl Energy 202:348–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.132
Goicoechea S, Ehrich H, Arias PL, Kockmann N (2015) Thermodynamic analysis of acetic acid steam reforming for hydrogen production. J Power Sources 279:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.012
Hlina M, Hrabovsky M, Kavka T, Konrad M (2014) Production of high quality syngas from argon/water plasma gasification of biomass and waste. Waste Manag 34:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.09.018
Fabry F, Rehmet C, Rohani V, Fulcheri L (2013) Waste gasification by thermal plasma: a review. Waste Biomass Valoriz 4:421–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9201-7
Lebouvier A, Iwarere SA, D’Argenlieu P et al (2013) Assessment of carbon dioxide dissociation as a new route for syngas production: a comparative review and potential of plasma-based technologies. Energy Fuels 27:2712–2722. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef301991d
Li J, Liu K, Yan S et al (2016) Application of thermal plasma technology for the treatment of solid wastes in China: an overview. Waste Manag 58:260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.06.011
Ojha A, Reuben AC, Sharma D (2012) Solid waste management in developing countries through plasma arc gasification—an alternative approach. APCBEE Proc 1:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcbee.2012.03.031
Ma WC, Chu C, Wang P et al (2020) Hydrogen-rich syngas production by DC thermal plasma steam gasification from biomass and plastic mixtures. Adv Sustain Syst 4:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202000026
Mašláni A, Hrabovský M, Křenek P et al (2021) Pyrolysis of methane via thermal steam plasma for the production of hydrogen and carbon black. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46:1605–1614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.10.105
Yan B, Xu P, Li X et al (2012) Experimental study of liquid hydrocarbons pyrolysis to acetylene in H 2/Ar plasma. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32:1203–1214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-012-9400-1
Cheng Y, Yan B, Li T, et al (2015) Experimental study on coal tar pyrolysis in thermal, pp 401–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-014-9608-3
Prado ESP, Miranda FS, Marquesi AR et al (2021) Theoretical and experimental approach of fuel gas and carbon black production from coal tar pitch by thermal plasma process. Environ Technol (UK) 1:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.2003437
Sikarwar VS, Hrabovský M, Van Oost G et al (2020) Progress in waste utilization via thermal plasma. Prog Energy Combust Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2020.100873
Mazzoni L, Almazrouei M, Ghenai C, Janajreh I (2017) A comparison of energy recovery from MSW through plasma gasification and entrained flow gasification. Energy Procedia 142:3480–3485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.12.233
Amaral-Labat G, Munhoz MGC, da Silva Fonseca BC et al (2021) Xerogel-like materials from sustainable sources: Properties and electrochemical performances. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14237977
Mukherjee R, Paul T, Soren JP et al (2019) Acidophilic α-amylase production from aspergillus niger RBP7 using potato peel as substrate: a waste to value added approach. Waste Biomass Valoriz 10:851–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0114-8
Flórez Vergara DE, Kondo Lopes BH, Quirino SF et al (2019) Frequency selective surface properties of microwave new absorbing porous carbon materials embedded in epoxy resin. Mater Res 22:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2018-0834
Liu S, Xue J, Liu X et al (2020) Pitch derived graphene oxides: characterization and effect on pyrolysis and carbonization of coal tar pitch. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 145:104746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2019.104746
Li J, He F, Luo Y et al (2003) A new grade carbon black produced by thermal plasma process. Plasma Sci Technol 5:1815–1819. https://doi.org/10.1088/1009-0630/5/3/010
Kim KS, Seo JH, Nam JS et al (2005) Production of hydrogen and carbon black by methane decomposition using DC-RF hybrid thermal plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 33:813–823. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPS.2005.844526
Mohsenian S, Esmaili MS, Fathi J, Shokri B (2016) Hydrogen and carbon black nano-spheres production via thermal plasma pyrolysis of polymers. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:16656–16663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.150
Moothi K, Iyuke SE, Meyyappan M, Falcon R (2012) Coal as a carbon source for carbon nanotube synthesis. Carbon N Y 50:2679–2690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2012.02.048
Fulcheri L, Probst N, Flamant G et al (2002) Plasma processing: a step towards the production of new grades of carbon black. Carbon NY 40:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00169-5
da Costa Labanca AR (2020) Carbon black and hydrogen production process analysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 45:25698–25707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.081
De WuM, Li GC, Li MS et al (2021) Effect of nickel cobalt co-catalyst on catalytic activity of molybdenum naphthenate for the hydroprocessing of coal tar pitch in suspension bed. J Fuel Chem Technol 49:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(21)60002-6
Yudin VE, Goykhman MY, Balik K et al (2002) Carbon/carbon composites based on a polyimide matrix with coal tar pitch. Carbon N Y 40:1427–1433. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(01)00313-X
Ibrahimoglu B, Demircan CA, Kizisar SE, et al (2018) Energy recovery from waste tires with plasma method. ISMSIT 2018—2nd Int Symp Multidiscip Stud Innov Technol Proc, pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMSIT.2018.8567305
Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products and Lubricants 2015.
Standard Test Method for Sulfur in the Analysis Sample of Coal and Coke Using High-Temperature Tube Furnace Combustion 2014.
Standard practice for ultimate analysis of coal and coke 2015.
Standard Test Method for Ash from Petroleum Products 2013.
Standard Test Method for Water in Petroleum Products and Bituminous Materials by Distillation 2013.
Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter 2014.
COMSOL Multiphysics
Murphy AB, Arundelli CJ (1994) Transport coefficients of argon, nitrogen, oxygen, argon-nitrogen, and argon-oxygen plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 14:451–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01570207
Zhukov MF, Zasypkin IM, Timoshevskii AN et al (2007) Thermal plasma torches: design, characteristics. Cambridge International Science Publishing, Cambridge, Application
Golish VI, Karpenko EI et al (2009) Long-service-life plasma arc torch. High Energy Chem 43:318–323. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018143909040134
Gorokhovski M, Karpenko EI, Lockwood FC et al (2005) Plasma technologies for solid fuels: experiment and theory. J Energy Inst 78:157–171. https://doi.org/10.1179/174602205X68261
Brunauer S, Emmett PH, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am ChemSoc 60:309–319
Dubinin MM (1989) Fundamentals of the theory of adsorption in micropores of carbon adsorbents: characteristics of their adsorption properties and microporous structures. Carbon N Y 27:457–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(89)90078-X
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, surface area and porosity. Acad Press, London
Tarazona P (1995) Solid-fluid transition and interfaces with density functional approaches. Surf Sci 331–333:989–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(95)00170-0
Kalinenko RA, Kuznetsov AP, Levitsky AA et al (1993) Pulverized coal plasma gasification. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 13:141–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01447176
Liu CJ, Xu GH, Wang T (1999) Non-thermal plasma approaches in CO2 utilization. Fuel Process Technol 58:119–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3820(98)00091-5
Malik MA, Jiang XZ (1999) The CO2 reforming of natural gas in a pulsed corona discharge reactor. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 19:505–512. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021882410379
Daugey N, Bergeat A, Schuck A et al (1997) Vibrational distribution in CN(X 2Σ+) from the N + C2 → CN + C reaction. Chem Phys 222:87–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0104(97)00181-X
He X, Ma T, Qiu J et al (2004) Mechanism of coal gasification in a steam medium under arc plasma conditions. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 13:446–453. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-0252/13/3/011
Amaral-Labat G, da Silva EL, Cuña A et al (2020) A sustainable carbon material from kraft black liquor as nickel-based electrocatalyst support for ethanol electro-oxidation. Waste Biomass Valoriz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-020-01201-3
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemienewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). PAC Pure Appl. Chem. 57:603
Okoye CO, Jones I, Zhu M et al (2021) Manufacturing of carbon black from spent tyre pyrolysis oil—a literature review. J Clean Prod 279:123336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123336
Guo XF, Kim GJ (2010) Synthesis of Ultrafine carbon black by pyrolysis of polymers using a direct current thermal plasma process. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30:75–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-009-9198-7
Sun DL, Wang F, Hong RY, Xie CR (2016) Preparation of carbon black via arc discharge plasma enhanced by thermal pyrolysis. Diam Relat Mater 61:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diamond.2015.11.004
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the fellowship awarded by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) to Eduardo Sant'Ana Petraconi Prado [grant number 141130/2021-0]. We also thank the support given by the National Institute for Space Research (INPE) and the Plasma and Processes Laboratory of the Aeronautics Institute of Technology (LPP-ITA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prado, E.S.P., Essiptchouk, A., Amaral-Labat, G. et al. Coal Tar Pitch Processing: Experimental and Theoretical Characteristics of Thermal Plasma Process Using DC Plasma Torch. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 43, 25–46 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-022-10303-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-022-10303-w