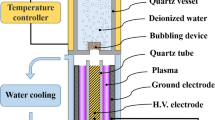
Abstract
Presently, the world is using different types of disinfectants for various applications such as disinfecting instrument surfaces in the medical field, sanitizers in airplanes, wash-rooms, etc. These disinfectants carry various harmful chemicals that harm our ecosystem. Hence in search of more eco-friendly disinfectants, our research leads us to explore plasma activated water (PAW). PAW can be produced with the help of plasma interaction with water. This interaction changes the physicochemical properties of water and makes it reactive to kill pathogens. PAW can be used for a wide variety of applications such as food preservation, fast germination, sterilization agents, etc. In the present work, PAW has been formed using non-thermal plasma and different gas or gas mixture as plasma forming gas. Its physicochemical properties have been studied to identify pH value, oxidation reduction potential, and chemical species formed after plasma interaction with a water surface. Further, the study has been carried out to determine the disinfectant ability of PAW for two types of pathogens named Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Different bactericidal methods have been adopted to confirm the results. SEM, fluorescence microscopy, and release of nucleic acids and proteins from raptured cell membrane of pathogens clearly show bactericidal efficacy of PAW. The important finding of the present work is the effective killing of pathogens by PAW in a short span of interaction time (≤ 10 s). The PAW has a strong possibility of using it as a disinfectant to kill a wide variety of pathogens and micro-organisms.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Finlay BB (1999) Bacterial disease in diverse hosts. Cell 96(3):315–318
Chan GJ, Lee AC, Baqui AH, Tan J, Black RE (2013) Risk of early-onset neonatal infection with maternal infection or colonization: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med 10(8):e1001502
Govaert M, Smet C, Verheyen D, Walsh JL, Van Impe JF (2019) Combined effect of cold atmospheric plasma and hydrogen peroxide treatment on mature Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium biofilms. Front Microbiol 10:2674
Freeda Blessie R, Varadharaju N, John Kennedy Z, Ganapathy S, Shridar B (2019) Effect of non-thermal plasma treatment on carrot slices. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 8(4):80–83
Lee J-Y, Kim K-H, Park S-Y, Yoon S-Y, Kim G-H, Lee Y-M, Rhyu I-C, Seol Y-J (2019) The bactericidal effect of an atmospheric-pressure plasma jet on Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilms on sandblasted and acid-etched titanium discs. J Periodontal Implant Sci 49(5):319–329
Hajhoseini A, Sharifan A, Yousefi H (2019) Effects of atmospheric cold plasma on microbial growth of Listeria innocua and Staphylococcus aureus in ready-to-eat fish products. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences
Nema SK, Vishal Jain, Adam Sanghariyat, Subroto Mukherjee, Nirav Jamnapara (2019) An apparatus for water treatment to activate water using atmospheric pressure hybrid plasma system. Indian Patent application no. 201621043562.
ten Bosch L, Köhler R, Ortmann R, Wieneke S, Viöl W (2017) Insecticidal effects of plasma treated water. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(12):1460
Thirumdas R, Kothakota A, Annapure U, Siliveru K, Blundell R, Gatt R, Valdramidis VP (2018) Plasma activated water (PAW): chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture. Trends Food Sci Technol 77:21–31
Tschang C-YT, Thoma M (2019) In vitro comparison of direct plasma treatment and plasma activated water on Escherichia coli using a surface micro-discharge. J Phys D Appl Phys 53(5):055201
Hongzhuan Z, Ying T, Xia S, Jinsong G, Zhenhua Z, Beiyu J, Yanyan C, Lulu L, Jue Z, Bing Y (2019) Preparation of the inactivated Newcastle disease vaccine by plasma activated water and evaluation of its protection efficacy. Applied microbiology and biotechnology:1–11
Wu H, Sun P, Feng H, Zhou H, Wang R, Liang Y, Lu J, Zhu W, Zhang J, Fang J (2012) Reactive oxygen species in a non-thermal plasma microjet and water system: generation, conversion, and contributions to bacteria inactivation—an analysis by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Plasma Processes Polym 9(4):417–424
Laurita R, Barbieri D, Gherardi M, Colombo V, Lukes P (2015) Chemical analysis of reactive species and antimicrobial activity of water treated by nanosecond pulsed DBD air plasma. Clin Plasma Med 3(2):53–61
Van Gils C, Hofmann S, Boekema B, Brandenburg R, Bruggeman P (2013) Mechanisms of bacterial inactivation in the liquid phase induced by a remote RF cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(17):175203
Shen J, Tian Y, Li Y, Ma R, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Fang J (2016) Bactericidal effects against S. aureus and physicochemical properties of plasma activated water stored at different temperatures. Sci Rep 6:28505
Naïtali M, Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry J-M, Bellon-Fontaine M-N, Brisset J-L (2010) Combined effects of long-living chemical species during microbial inactivation using atmospheric plasma-treated water. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(22):7662–7664
Zhang Q, Liang Y, Feng H, Ma R, Tian Y, Zhang J, Fang J (2013) A study of oxidative stress induced by non-thermal plasma-activated water for bacterial damage. Appl Phys Lett 102(20):203701
Lukes P, Dolezalova E, Sisrova I, Clupek M (2014) Aqueous-phase chemistry and bactericidal effects from an air discharge plasma in contact with water: evidence for the formation of peroxynitrite through a pseudo-second-order post-discharge reaction of H2O2 and HNO2. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 23(1):015019
Traylor MJ, Pavlovich MJ, Karim S, Hait P, Sakiyama Y, Clark DS, Graves DB (2011) Long-term antibacterial efficacy of air plasma-activated water. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(47):472001
Li Y, Pan J, Ye G, Zhang Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Fang J (2017) In vitro studies of the antimicrobial effect of non-thermal plasma-activated water as a novel mouthwash. Eur J Oral Sci 125(6):463–470
Sun P, Wu H, Bai N, Zhou H, Wang R, Feng H, Zhu W, Zhang J, Fang J (2012) Inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores in water by a direct-current, cold atmospheric-pressure air plasma microjet. Plasma Process Polym 9(2):157–164
Pan J, Li Y, Liu C, Tian Y, Yu S, Wang K, Zhang J, Fang J (2017) Investigation of cold atmospheric plasma-activated water for the dental unit waterline system contamination and safety evaluation in vitro. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 37(4):1091–1103
Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry J-M, Brisset J-L, Bellon-Fontaine M-N, Doubla A, Naïtali M (2008) Impact on disinfection efficiency of cell load and of planktonic/adherent/detached state: case of Hafnia alvei inactivation by plasma activated water. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81(3):449–457
Kamgang-Youbi G, Herry JM, Meylheuc T, Brisset JL, Bellon-Fontaine MN, Doubla A, Naïtali M (2009) Microbial inactivation using plasma-activated water obtained by gliding electric discharges. Lett Appl Microbiol 48(1):13–18
Kaushik NK, Ghimire B, Li Y, Adhikari M, Veerana M, Kaushik N, Jha N, Adhikari B, Lee S-J, Masur K (2018) Biological and medical applications of plasma-activated media, water and solutions. Biol Chem 400(1):39–62
Ercan UK, Wang H, Ji H, Fridman G, Brooks AD, Joshi SG (2013) Nonequilibrium plasma-activated antimicrobial solutions are broad-spectrum and retain their efficacies for extended period of time. Plasma Process Polym 10(6):544–555
Oehmigen K, Hähnel M, Brandenburg R, Wilke C, Weltmann KD, Von Woedtke T (2010) The role of acidification for antimicrobial activity of atmospheric pressure plasma in liquids. Plasma Process Polym 7(3–4):250–257
Tian Y, Ma R, Zhang Q, Feng H, Liang Y, Zhang J, Fang J (2015) Assessment of the physicochemical properties and biological effects of water activated by non-thermal plasma above and beneath the water surface. Plasma Process Polym 12(5):439–449
Zhang Q, Ma R, Tian Y, Su B, Wang K, Yu S, Zhang J, Fang J (2016) Sterilization efficiency of a novel electrochemical disinfectant against Staphylococcus aureus. Environ Sci Technol 50(6):3184–3192
Burlica R, Grim R, Shih KY, Balkwill D, Locke B (2010) Bacteria inactivation using low power pulsed gliding arc discharges with water spray. Plasma Process Polym 7(8):640–649
Xiang Q, Kang C, Niu L, Zhao D, Li K, Bai Y (2018) Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of plasma-activated water against Pseudomonas deceptionensis CM2. LWT 96:395–401
Schnabel U, Niquet R, Schmidt C, Stachowiak J, Schlüter O, Andrasch M, Ehlbeck J (2016) Antimicrobial efficiency of non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma processed water (PPW) against agricultural relevant bacteria suspensions. Int J Environ Agric Res 2:212–224
Bergendahl JA, Stevens L (2005) Oxidation reduction potential as a measure of disinfection effectiveness for chlorination of wastewater. Environ Prog 24(2):214–222
Suslow TV (2004) Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) for water disinfection monitoring, control, and documentation.
Hauser AR, Rello J (2012) Severe infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, vol 7. Springer, Berlin
Kluytmans J, Van Belkum A, Verbrugh H (1997) Nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: epidemiology, underlying mechanisms, and associated risks. Clin Microbiol Rev 10(3):505–520
Cole AM, Tahk S, Oren A, Yoshioka D, Kim Y-H, Park A, Ganz T (2001) Determinants of Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8(6):1064–1069
Fang Z, Xie X, Li J, Yang H, Qiu Y, Kuffel E (2009) Comparison of surface modification of polypropylene film by filamentary DBD at atmospheric pressure and homogeneous DBD at medium pressure in air. J Phys D Appl Phys 42(8):085204
Baron S (1996) Classification--Medical Microbiology. University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston,
Kimler A (1962) Evaluation of mediums for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Am J Clin Pathol 37(6):593–596
Zhang X, Xu D, Zhu C, Lundaa T, Scherr KE (2012) Isolation and identification of biosurfactant producing and crude oil degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. Chem Eng J 209:138–146
Garrity M, Bell A, Lilburn T (2005) Order IX Pseudomonadales Orla-Jensen 1921, 270 AL. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Part two The Proteobacteria, 2nd edn Springer, USA:384–402
Kushkevych I (2019) Isolation and Purification of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. In: Microorganisms. IntechOpen,
Li Q, Chen X, Jiang Y, Jiang C (2016) Cultural, physiological, and biochemical identification of actinobacteria. Actinobacteria-Basics and Biotechnological Applications:87–111
Association APH (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Aboubakr HA, Williams P, Gangal U, Youssef MM, El-Sohaimy SA, Bruggeman PJ, Goyal SM (2015) Virucidal effect of cold atmospheric gaseous plasma on feline calicivirus, a surrogate for human norovirus. Appl Environ Microbiol 81(11):3612–3622
Murtey MD, Ramasamy P (2016) Sample preparations for scanning electron microscopy–life sciences. In: Modern electron microscopy in physical and life sciences. IntechOpen,
Manchester KL (1996) Use of UV methods for measurement of protein and nucleic acid concentrations. Biotechniques 20(6):968–970
Musini A, Giri A (2019) Investigation of Mode of Action of Anti Bacterial Activity of Salacia Oblonga Extract Against Drug Resistant Pathogen. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 62
Paderog MJV, Suarez AFL, Sabido EM, Low ZJ, Saludes JP, Dalisay DS (2020) Anthracycline shunt metabolites from Philippine marine sediment-derived streptomyces destroy cell membrane integrity of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 11:743
Wilfinger WW, Mackey K, Chomczynski P (1997) Effect of pH and ionic strength on the spectrophotometric assessment of nucleic acid purity. Biotechniques 22(3):474–481
Groves WE, Davis FC Jr, Sells BH (1968) Spectrophotometric determination of microgram quantities of protein without nucleic acid interference. Anal Biochem 22(2):195–210
Stiefel P, Schmidt-Emrich S, Maniura-Weber K, Ren Q (2015) Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol 15(1):36
Coling D, Kachar B (1998) Principles and application of fluorescence microscopy. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 44(1):14.10.11-14.10.11
Salgado P, Frontela JL, Vidal G (2020) Optimization of fenton technology for recalcitrant compounds and bacteria inactivation. Catalysts 10(12):1483
Tomova I, Stoilova-Disheva M, Lazarkevich I, Vasileva-Tonkova E (2015) Antimicrobial activity and resistance to heavy metals and antibiotics of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from sediment and soil samples collected from two Antarctic islands. Front Life Sci 8(4):348–357
Sivachandiran L, Khacef A (2017) Enhanced seed germination and plant growth by atmospheric pressure cold air plasma: combined effect of seed and water treatment. RSC Adv 7(4):1822–1832
Lu P, Boehm D, Bourke P, Cullen PJ (2017) Achieving reactive species specificity within plasma-activated water through selective generation using air spark and glow discharges. Plasma Process Polym 14(8):1600207
Ma R, Wang G, Tian Y, Wang K, Zhang J, Fang J (2015) Non-thermal plasma-activated water inactivation of food-borne pathogen on fresh produce. J Hazard Mater 300:643–651
Vlad I-E, Anghel SD (2017) Time stability of water activated by different on-liquid atmospheric pressure plasmas. J Electrostat 87:284–292
Machala Z, Tarabova B, Hensel K, Spetlikova E, Sikurova L, Lukes P (2013) Formation of ROS and RNS in water electro-s prayed through transient spark discharge in air and their bactericidal effects. Plasma Process Polym 10(7):649–659
Jablonowski H, von Woedtke T (2015) Research on plasma medicine-relevant plasma–liquid interaction: what happened in the past five years? Clin Plasma Med 3(2):42–52
Oehmigen K, Winter J, Hähnel M, Wilke C, Brandenburg R, Weltmann KD, von Woedtke T (2011) Estimation of possible mechanisms of Escherichia coli inactivation by plasma treated sodium chloride solution. Plasma Process Polym 8(10):904–913
Chen B-M, Wang Z-H, Li S-X, Wang G-X, Song H-X, Wang X-N (2004) Effects of nitrate supply on plant growth, nitrate accumulation, metabolic nitrate concentration and nitrate reductase activity in three leafy vegetables. Plant Sci 167(3):635–643
Aslam M, Huffaker RC (1989) Role of nitrate and nitrite in the induction of nitrite reductase in leaves of barley seedlings. Plant Physiol 91(3):1152–1156
Laboratory NRCCoHSit (1980) Prudent practices for handling hazardous chemicals in laboratories. National Academies,
Xiang Q, Wang W, Zhao D, Niu L, Li K, Bai Y (2019) Synergistic inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by plasma-activated water and mild heat. Food Control 106:106741
Xu Y, Tian Y, Ma R, Liu Q, Zhang J (2016) Effect of plasma activated water on the postharvest quality of button mushrooms, Agaricus bisporus. Food Chem 197:436–444
Bălan GG, Roşca I, Ursu E-L, Doroftei F, Bostănaru A-C, Hnatiuc E, Năstasă V, Şandru V, Ştefănescu G, Trifan A (2018) Plasma-activated water: a new and effective alternative for duodenoscope reprocessing. Infect Drug Resist 11:727
Wyatt PJ (1970) Cell wall thickness, size distribution, refractive index ratio and dry weight content of living bacteria (Stapylococcus aureus). Nature 226(5242):277–279
Mai-Prochnow A, Clauson M, Hong J, Murphy AB (2016) Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria differ in their sensitivity to cold plasma. Sci Rep 6:38610
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the department of atomic energy (Government of India) graduate fellowship scheme (DGFS). Authors sincerely thank Dr. Vishal N. Jain, Mr. Chirayu Patil, and Mr. Adam Sanghariyat, Dr. Nirav I. Jamnapara, and Mr. Akshay Vaid for providing constant support and useful suggestions during this work.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Vikas Rathore and Divyesh Patel. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Vikas Rathore and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathore, V., Patel, D., Butani, S. et al. Investigation of Physicochemical Properties of Plasma Activated Water and its Bactericidal Efficacy. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 41, 871–902 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-021-10161-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-021-10161-y