Abstract
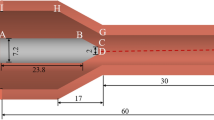
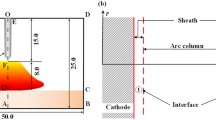
In this paper, the three-dimensional (3-D) two-temperature modeling on the characteristics of the dual-jet DC arc argon plasmas under different plasma working gas flow rates ranging from 0 to 15 slpm or the chamber pressures increasing from 0.4 to 1.0 atm are conducted at a fixed arc current of 80 A. The modeling results reveal a significant 3-D feature of the temperature and flow fields of the plasma arc-jet due to the declination of the electrodes to each other geometrically, and an obvious deviation from the local thermodynamic equilibrium (LTE) state resulting from the interactions between the high temperature plasma and the cold walls or cold surrounding gas. With other parameters being unchanged, the spatial distributions of the LTE plasma region changed significantly with increasing the plasma working gas flow rate; and the decrease of the chamber pressure leads to the expansion of the high-temperature region and the shrink of the LTE plasma region, which shows a more significant non-LTE feature of the plasma arc-jet. The calculated heavy-particle temperature distributions and the arc voltages are qualitatively consistent with the experimental measurements.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsu KC, Etemadi K, Pfender E (1983) J Appl Phys 54:1293–1301
Murphy A (1997) Phys Rev E 55:7473–7494
Chen X, Li H-P (2001) Int J Heat Mass Transf 44:2541–2553
Bachmann B, Kozakov R, Gött G, Ekkert K, Bachmann J, Marques J, Schöpp H, Uhrlandt D, Schein J (2013) J Phys D Appl Phys 46:125203
Gleizes A, Gonzalez JJ, Freton P (2005) J Phys D Appl Phys 38:R153–R183
Hsu KC, Pfender E (1983) J Appl Phys 54:4359–4366
Fauchais P (2004) J Phys D Appl Phys 37:R86–R108
Trelles J, Chazelas C, Vardelle A, Heberlein J (2009) J Therm Spray Technol 18:728–752
Murphy A (2011) J Phys D Appl Phys 44:194009
Lowke JJ (2013) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 22:023002
Polyakov SP, Rozenberg MG (1977) J Eng Phys Thermophys 32:675–682
Polyakov SP, Pechenkin VI (1982) J Eng Phys Thermophys 43:1293–1296
Zhang H, Wu G-Q, Li H-P, Bao C-Y (2009) IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 37:1129–1135
Wang Z, Wu G-Q, Ge N, Li H-P, Bao C-Y (2010) IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 38:2906–2913
Inaba T, Kikuchi M, Li H-P, Iwao T (2006) Proceedings of the XVI international conference on gas discharges and their applications. Xi’an, China
Megy S, Bousrih S, Baronnet J-M, Ershov-Pavlov E, Williams J, Iddles D (1995) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 15:309–331
Tang K-M, Yan J-D, Chapman C, Fang M (2010) J Phys D Appl Phys 43:345201
Colombo V, Conceal A, Ghedini E (2008) IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 36:1038–1039
Colombo V, Ghedini E, Boselli M, Sanibondi P, Concetti A (2011) J Phys D Appl Phys 44:194005
Li H-P, Benilov MS (2007) J Phys D Appl Phys 40:2010–2017
Zhou X, Heberlein J (1994) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 3:564–574
Li H-P, Pfender E, Chen X (2003) J Phys D Appl Phys 36:1084–1096
Gonzalez JJ, Freton P, Gleizes A (2002) J Phys D Appl Phys 35:3181–3191
Trelles JP, Heberlein J, Pfender E (2007) J Phys D Appl Phys 40:5937–5952
Mitchner M, Kruger CH (1973) Partially ionized gases. Wiley, New York
Devoto RS (1973) Phys Fluids 16:616–623
Freton P, Gonzalez JJ, Masquere M, Reichert F (2011) J Phys D Appl Phys 44:345202
Chen X, Li H-P (2002) Int J Heat Mass Transf 46:1443–1454
Lide DR (2003) The CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. CRC Press, New York
Chen X (2009) Heat transfer and fluid flow under thermal plasma conditions, Chap. 8. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Patankar SV (1980) Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, Washington
Griem HR (1964) Plasma spectroscopy. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
Benilov MS, Benilova LG, Li H-P, Wu G-Q (2012) J Phys D Appl Phys 45:355201
Shkol’nik SM (2011) Plasma Sources Sci Technol 20:013001
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11035005, 61104204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Heng Guo and Gui-Qing Wu have contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, H., Wu, GQ., Li, HP. et al. Three-Dimensional Non-equilibrium Modeling on the Characteristics of the Dual-Jet Direct-Current Arc Plasmas. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 35, 75–89 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-014-9586-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-014-9586-5