Abstract
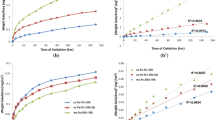
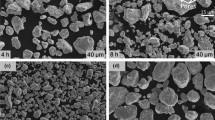
Oxidation behavior of nanocrystalline and microcrystalline Fe–20Cr–3Al alloys was investigated at high temperatures (500–800 °C) in the present study. The nanocrystalline Fe–20Cr–3Al alloy was synthesized by high-energy ball milling followed by spark plasma sintering. The synthesized nanocrystalline Fe–20Cr–3Al alloy was annealed to prepare its microcrystalline counterparts. The nanocrystalline alloy exhibited superior oxidation resistance than its microcrystalline counterparts, which is explained by oxidation kinetics and nature of oxide formed on both the alloys. The presence of higher grain boundary area in the nanocrystalline alloy enhances the diffusivity on metal and as a result, a considerably more protective oxide layer formed on the nanocrystalline alloy. On the other hand, a considerably less protective oxide layer formed on the microcrystalline alloy due to limited diffusion of metal. Additionally, both the nanocrystalline and microcrystalline alloys exhibited superior oxidation resistance at 800 °C than that of 700 °C, which is contrary to common steels.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Z. Liu, W. Gao, K. L. Dahm, and F. Wang, Acta Materialia 46, 1691 (1998).
W. Gao, Z. Liu, and Z. Li, Advanced Materials 13, 1001 (2001).
S. E. Sadique, A. H. Mollah, M. S. Islam, M. M. Ali, M. H. H. Megat, and S. Basri, Oxidation of Metals 54, 385 (2000).
F. H. Stott and G. C. Wood, Materials Science and Engineering 87, 267 (1987).
H. Asteman and M. Spiegel, Corrosion Science 50, 1734 (2008).
H. Josefsson, F. Liu, J. E. Svensson, M. Halvarsson, and L. G. Johansson, Materials and Corrosion 56, 801 (2005).
W. J. Quadakkers, D. Naumenko, E. Wessel, and V. Kochubey, Oxidation of Metals 61, 17 (2004).
R. K. Singh Raman and R. K. Gupta, Corrosion Science 51, 316 (2009).
R. K. Singh-Raman, Metals (Basel) 11, 695 (2021).
F. H. Stott, G. C. Wood, and J. Stringert, Oxidation of Metals 44, 113 (1995).
R. Prescott and M. J. Graham, Oxidation of Metals 38, 233 (1992).
P. Tomaszewicz and G. R. Wallwork, Reviews on High-Temperature Materials 4, 75 (1978).
Z. G. Zhang, P. Y. Hou, F. Gesmundo, and Y. Niu, Applied Surface Science 253, 881 (2006).
Z. G. Zhang, F. Gesmundo, P. Y. Hou, and Y. Niu, Corrosion Science 48, 741 (2006).
Z. G. Zhang, X. L. Zhang, L. Sheng, and X. Teng, Open Corrosion Journal 2, 37 (2009).
E. Airiskallio, E. Nurmi, M. H. Heinonen, et al., Corrosion Science 52, 3394 (2010).
Y. Niu, S. Wang, F. Gao, Z. G. Zhang, and F. Gesmundo, Corrosion Science 50, 345 (2008).
J. Engkvist, S. Canovic, K. Hellström, et al., Oxidation of Metals 73, 233 (2010).
P. T. Moseley, K. R. Hyde, B. A. Bellamy, and G. Tappin, Corrosion Science 24, 547 (1984).
F. Liu, H. Götlind, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, Corrosion Science 50, 2272 (2008).
F. Liu, H. Josefsson, J. E. Svensson, L. G. Johansson, and M. Halvarsson, Materials at High Temperatures 22, 521 (2005).
H. Gleiter, Physica Status Solidi 41, 41 (1992).
Z. B. Wang, N. R. Tao, W. P. Tong, J. Lu, and K. Lu, Acta Materialia 51, 4319 (2003).
H. Echsler, E. A. Martinez, L. Singheiser, and W. J. Quadakkers, Materials Science and Engineering A 384, 1 (2004).
F. Wang, Oxidation of Metals 48, 215 (1997).
B. V. Mahesh and R. K. Singh Raman, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 45, 5799 (2014).
T. Ungár, I. Dragomir, Á. Révész, and A. Borbély, Journal of Applied Crystallography 32, 992 (1999).
R. Kumar, J. Joardar, R. K. Singh Raman, V. S. Raja, S. V. Joshi, and S. Parida, Journal of Alloys and Compounds 671, 164 (2016).
V. S. Rao, R. G. Baligidad, and V. S. Raja, Intermetallics 10, 73 (2002).
A. W. Bowen and G. M. Leak, Metallurgical Transactions 1, 1695 (1970).
J. Takada, S. Yamamoto, S. Kikuchi, and M. Adachi, Oxidation of Metals 25, 93 (1986).
F. S. Buffington, K. Hirano, and M. Cohen, Acta Metallurgica 9, 434 (1961).
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (Rajiv Kumar) acknowledges to IITB-Monash Research Academy for providing financial support for the research work. The authors also acknowledge Prof. B. S. Murty for facilitating ball milling and spark plasma sintering work at Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai. The authors also acknowledge the Central Surface Analytical Facility (ESCA) at IIT Bombay for providing the facilities for XPS.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The authors’ contributions in the research paper are as follows: RK was involved in investigation, methodology, validation, writing—original draft preparation. RKSR, SRB, VSR and SP were involved in writing—reviewing and editing. RKSR, VSR and SP were involved in supervision. SRB collected resources.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
All authors have made substantial contributions to the manuscript.
Consent for Publication
All authors have approved the manuscript for publication.
Ethics Approval
No ethical approval is required for the current study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Singh Raman, R.K., Bakshi, S.R. et al. Effect of Nanocrystalline Structure on the Oxidation Behavior of Fe–20Cr–3Al Alloy at High Temperatures. Oxid Met 97, 307–321 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-021-10090-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-021-10090-3