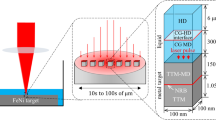
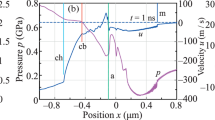
Abstract
Laser ablation through liquid is an important process that have to be studied for applications which use laser ablation in liquid (LAL) and laser shock peening (LSP). LAL is employed for production of suspensions of nanoparticles (NP), while LSP is applied to increase hardness and fatique/corrosion resistance properties of a surface layer. A bubble appears in liquid around the laser spot focused at a target surface after strong enough laser pulse. In the paper we connect the early quasi-plane heated layer created by a pulse in liquid and the bubble forming at much later stages. In the previous works these early stage from one side and the late stage from another side existed mainly as independent entities. At least, quantitative links between them were unknown. We consider how the quasi-plane heated layer of liquid forms thank to thermal conduction, how gradually conduction becomes weaker, and how the heated layer of liquid nearly adiabatically expands to few orders of magnitude in volume during the drop of pressure. Our molecular dynamics simulations show that the heated layer is filled by the diffusive atomic metal–liquid mixture. Metal atoms began to condense into NPs when they meet cold liquid outside the edge of mixing zone. This process limits diffusive expansion of metal atoms, because the diffusivity of NP is less than that of individual atoms. Thus the mixture expands together with hot liquid, and the NPs approximately homogeneously fill an interior of bubble.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amans, D., Cai, W., Barcikowski, S.: Status and demand of research to bring laser generation of nanoparticles in liquids to maturity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 488, 445–454 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.117
Ashitkov, S.I., Agranat, M.B., Kanel’, G.I., Komarov, P.S., Fortov, V.E.: Behavior of aluminum near an ultimate theoretical strength in experiments with femtosecond laser pulses. JETP Lett. 92(8), 516–520 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364010200051
Bailly, A.L., Correard, F., Popov, A., Tselikov, G., Chaspoul, F., Appay, R., Al-Kattan, A., Kabashin, A., Braguer, D., Esteve, M.A.: In vivo evaluation of safety, biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of laser-synthesized gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–12 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-48748-3
Bushman, A.V., Kanel’, G.I., Ni, A.L., Fortov, V.E.: Intense Dynamic Loading of Condensed Matter. Taylor & Francis, Abingdon (1993)
Byram, C., Moram, S.S.B., Soma, V.R.: SERS based detection of multiple analytes from dye/explosive mixtures using picosecond laser fabricated gold nanoparticles and nanostructures. Analyst 144, 2327–2336 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AN01276H
Calculation of the thermophysical properties of water and water vapor. http://www.ivpromenergo.ru/page/programs/watersteamcalculator.php
Correa, C., Peral, D., Porro, J., Díaz, M., Ruiz de Lara, L., García-Beltrán, A., Ocaña, J.: Random-type scanning patterns in laser shock peening without absorbing coating in 2024–T351 Al alloy: a solution to reduce residual stress anisotropy. Opt. Laser Technol. 73, 179–187 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2015.04.027
Demaske, B.J., Zhakhovsky, V.V., Inogamov, N.A., Oleynik, I.I.: Ultrashort shock waves in nickel induced by femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Rev. B 87(5), 054109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.87.054109
Fabbro, R., Fournier, J., Ballard, P., Devaux, D., Virmont, J.: Physical study of laser-produced plasma in confined geometry. J. Appl. Phys. 68(2), 775–784 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.346783
Hoppius, J.S., Maragkaki, S., Kanitz, A., Gregorčič, P., Gurevich, E.L.: Optimization of femtosecond laser processing in liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 467–468, 255–260 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.121
Inogamov, N.A., Zhakhovskii, V.V., Ashitkov, S.I., Khokhlov, V.A., Petrov, Y.V., Komarov, P.S., Agranat, M.B., Anisimov, S.I., Nishihara, K.: Two-temperature relaxation and melting after absorption of femtosecond laser pulse. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 9712–9716 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.04.139
Inogamov, N.A., Zhakhovskii, V.V., Khokhlov, V.A.: Dynamics of gold ablation into water. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 127(1), 79–106 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063776118070075
Kabashin, A.V., Singh, A., Swihart, M.T., Zavestovskaya, I.N., Prasad, P.N.: Laser-processed nanosilicon: a multifunctional nanomaterial for energy and healthcare. ACS Nano 13(9), 9841–9867 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b04610
Kanel, G.I.: Rate and temperature effects on the flow stress and tensile strength of metals. AIP Conf. Proc. 1426, 939–944 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3686432
Kanitz, A., Kalus, M.R., Gurevich, E.L., Ostendorf, A., Barcikowski, S., Amans, D.: Review on experimental and theoretical investigations of the early stage, femtoseconds to microseconds processes during laser ablation in liquid-phase for the synthesis of colloidal nanoparticles. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 28(10), 103001 (2019a). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6595/ab3dbe
Kanitz, A., Förster, D.J., Hoppius, J.S., Weber, R., Ostendorf, A., Gurevich, E.L.: Pump-probe microscopy of femtosecond laser ablation in air and liquids. Appl. Surf. Sci. 475, 204–210 (2019b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.184
Karthik, D., Swaroop, S.: Laser peening without coating-an advanced surface treatment: a review. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32(14), 1565–1572 (2017)
Kawashima, T., Sano, T., Hirose, A., Tsutsumi, S., Masaki, K., Arakawa, K., Hori, H.: Femtosecond laser peening of friction stir welded 7075–T73 aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 262, 111–122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.06.022
Khishchenko, K.V., Tkachenko, S.I., Levashov, P.R., Lomonosov, I.V., Vorobev, V.S.: Metastable states of liquid tungsten under subsecond wire explosion. Int. J. Thermophys. 23(5), 1359–1367 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019821126883
Krylach, I.V., Kudryashov, S.I., Olekhnovich, R.O., Moskvin, M.K., Uspenskaya, M.V.: Tuning water wetting angle of a steel surface via nanosecond laser ablative nano/microtexturing for chemical and biomedical microfluidic applications. Laser Phys. Lett. 16(10), 105602 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1612-202x/ab3d32
Kudryashov, S., Samokhvalov, A., Ageev, E., Petrov, A., Veiko, V.: Ultrasonic characterization of dry and wet nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 127, 1095–1100 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.08.104
Kudryashov, S.I., Saraeva, I.N., Lednev, V.N., Pershin, S.M., Rudenko, A.A., Ionin, A.A.: Single-shot femtosecond laser ablation of gold surface in air and isopropyl alcohol. Appl. Phys. Lett. 112(20), 203101 (2018b). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5026591
Kudryashov, S.I., Samokhvalov, A.A., Nastulyavichus, A.A., Saraeva, I.N., Mikhailovskii, V.Y., Ionin, A.A., Veiko, V.P.: Nanosecond-laser generation of nanoparticles in liquids: from ablation through bubble dynamics to nanoparticle yield. Materials 12(4), 562 (2019a). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12040562
Kudryashov, S.I., Samokhvalov, A.A., Ageev, E.I., Veiko, V.P.: Ultrafast broadband nonlinear spectroscopy of a colloidal solution of gold nanoparticles. JETP Lett. 109(5), 298–302 (2019b). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364019050096
Kudryashov, S.I., Samokhvalov, A.A., Ageev, E.I., Veiko, V.P.: Filamentation of an ultrashort laser pulse in a medium with artificial nonlinearity. JETP Lett. 109(7), 432–436 (2019c). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364019070087
Kudryashov, S.I., Levchenko, A.O., Danilov, P.A., Smirnov, N.A., Rudenko, A.A., Melnik, N.N., Busleev, N.I., Ionin, A.A.: Direct femtosecond-laser writing of optical-range nanoscale metagratings/metacouplers on diamond surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 115(7), 073102 (2019d). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5114630
Kudryashov, S.I., Nastulyavichus, A.A., Ivanova, A.K., Smirnov, N.A., Khmelnitskiy, R.A., Rudenko, A.A., Saraeva, I.N., Tolordava, E.R., Kharin, A.Y., Zavestovskaya, I.N., Romanova, Y.M., Zayarny, D.A., Ionin, A.A.: High-throughput laser generation of Si-nanoparticle based surface coatings for antibacterial applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 470, 825–831 (2019e). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.201
Lam, J., Lombard, J., Dujardin, C., Ledoux, G., Merabia, S., Amans, D.: Dynamical study of bubble expansion following laser ablation in liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108(7), 074104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4942389
Lemmon, E.W., McLinden, M.O., Friend, D.G.: NIST chemistry webbook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69 (National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD, 20899, 2019), chap. Thermophysical Properties of Fluid Systems. https://doi.org/10.18434/T4D303
Lomonosov, I.V.: Multi-phase equation of state for aluminum. Laser Part. Beams 25, 567–584 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263034607000687
Nastulyavichus, A.A., Kudryashov, S.I., Smirnov, N.A., Rudenko, A.A., Kharin, A.Y., Zayarny, D.A., Ionin, A.A.: Nanosecond-laser plasma-mediated generation of colloidal solutions from silver films of variable thickness: colloidal optical density versus pre-determined ablated mass. Opt. Laser Technol. 111, 75–80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.09.038
Pavlov, D.V., Zhizhchenko, A.Y., Honda, M., Yamanaka, M., Vitrik, O.B., Kulinich, S.A., Juodkazis, S., Kudryashov, S.I., Kuchmizhak, A.A.: Multi-purpose nanovoid array plasmonic sensor produced by direct laser patterning. Nanomaterials 9(10), 1348 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101348
Petrov, Y., Khokhlov, V., Zhakhovsky, V., Inogamov, N.: Hydrodynamic phenomena induced by laser ablation of metal into liquid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 492, 285–297 (2019a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.325
Petrov, Y.V., Inogamov, N.A., Zhakhovsky, V.V., Khokhlov, V.A.: Condensation of laser produced gold plasma during expansion and cooling in water environment. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 59(6), e201800180 (2019b). https://doi.org/10.1002/ctpp.201800180
Phipps, C.R., Turner, T.P., Harrison, R.F., York, G.W., Osborne, W.Z., Anderson, G.K., Corlis, X.F., Haynes, L.C., Steele, H.S., Spicochi, K.C., King, T.R.: Impulse coupling to targets in vacuum by KrF, HF, and CO2 single-pulse lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 64(3), 1083–1096 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.341867
Povarnitsyn, M.E., Itina, T.: Hydrodynamic modeling of femtosecond laser ablation of metallic targets in vacuum and in liquid. Appl. Phys. A 117(1), 175–178 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-014-8319-1
Povarnitsyn, M.E., Itina, T.E., Levashov, P.R., Khishchenko, K.V.: Mechanisms of nanoparticle formation by ultra-short laser ablation of metals in liquid environment. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15, 3108–3114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP42650A
Samarskii, A.A.: The Theory of Difference Schemes, vol. 786. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2001)
Sano, T., Eimura, T., Kashiwabara, R., Matsuda, T., Isshiki, Y., Hirose, A., Tsutsumi, S., Arakawa, K., Hashimoto, T., Masaki, K., Sano, Y.: Femtosecond laser peening of 2024 aluminum alloy without a sacrificial overlay under atmospheric conditions. J. Laser Appl. 29(1), 012005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2351/1.4967013
Saraeva, I.N., Luong, N.V., Kudryashov, S.I., Rudenko, A.A., Khmelnitskiy, R.A., Shakhmin, A.L., Kharin, A.Y., Ionin, A.A., Zayarny, D.A., Tung, D.H., Duong, P.V., Minh, P.H.: Laser synthesis of colloidal Si@Au and Si@Ag nanoparticles in water via plasma-assisted reduction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 360, 125–131 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.04.004
Saraeva, I., Kudryashov, S., Lednev, V., Makarov, S., Pershin, S., Rudenko, A., Zayarny, D., Ionin, A.: Single- and multishot femtosecond laser ablation of silicon and silver in air and liquid environments: plume dynamics and surface modification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 476, 576–586 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.01.092
Shepelev, V.V., Inogamov, N.A., Danilov, P.A., Kudryashov, S.I., Kuchmizhak, A.A., Vitrik, O.B.: Ultrashort pulse action onto thin film on substrate: qualitative model of shock propagation in substrate explaining phenomenon of fast growth of a hole with increase of absorbed energy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1147(1), 012065 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1147/1/012065
Shih, C.Y., Shugaev, M.V., Wu, C., Zhigilei, L.V.: Generation of subsurface voids, incubation effect, and formation of nanoparticles in short pulse laser interactions with bulk metal targets in liquid: molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. C 121(30), 16549–16567 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b02301
Shih, C.Y., Streubel, R., Heberle, J., Letzel, A., Shugaev, M.V., Wu, C., Schmidt, M., Gokce, B., Barcikowski, S., Zhigilei, L.V.: Two mechanisms of nanoparticle generation in picosecond laser ablation in liquids: the origin of the bimodal size distribution. Nanoscale 10, 6900–6910 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR08614H
Starinskiy, S.V., Shukhov, Y.G., Bulgakov, A.V.: Laser-induced damage thresholds of gold, silver and their alloys in air and water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 396, 1765–1774 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.11.221
Veiko, V.P., Volkov, S.A., Zakoldaev, R.A., Sergeev, M.M., Samokhvalov, A.A., Kostyuk, G.K., Milyaev, K.A.: Laser-induced microplasma as a tool for microstructuring transparent media. Quantum Electron. 47(9), 842–848 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1070/qel16377
Walsh, N., Costello, J., Kelly, T.: Optical diagnostics of laser-produced aluminium plasmas under water. Appl. Phys. B 123, 179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-017-6754-3
Xiao, J., Liu, P., Wang, C.X., Yang, G.W.: External field-assisted laser ablation in liquid: an efficient strategy for nanocrystal synthesis and nanostructure assembly. Prog. Mater. Sci. 87, 140–220 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2017.02.004
Zaretsky, E.B., Kanel, G.I.: Plastic flow in shock-loaded silver at strain rates from \(10^4\,\text{ s }^{-1}\) to \(10^7\,\text{ s }^{-1}\) and temperatures from 296 K to 1233 K. J. Appl. Phys. 110(7), 073502 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3642989
Zaretsky, E.B., Kanel, G.I.: Effect of temperature, strain, and strain rate on the flow stress of aluminum under shock-wave compression. J. Appl. Phys. 112, 073504 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4755792
Zhakhovskii, V.V., Inogamov, N.A.: Elastic–plastic phenomena in ultrashort stress waves. JETP Lett. 92(8), 521–526 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0021364010200063
Zhakhovsky, V.V., Budzevich, M.M., Inogamov, N.A., Oleynik, I.I., White, C.T.: Two-zone elastic–plastic single shock waves in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107(13), 135502 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.135502
Acknowledgements
The work of INA, VAKh, and YuVP was carried out under the state order of ITP RAS. The work of VVZ was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Grant Number 19-19-00697).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Fundamentals of Laser Assisted Micro- and Nanotechnologies.
Guest edited by Tigran Vartanyan, Vadim Veiko, Andrey Belikov and Eugene Avrutin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inogamov, N.A., Khokhlov, V.A., Petrov, Y.V. et al. Hydrodynamic and molecular-dynamics modeling of laser ablation in liquid: from surface melting till bubble formation. Opt Quant Electron 52, 63 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2168-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2168-2