Abstract
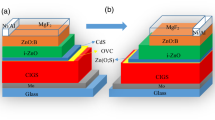
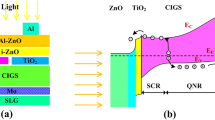
Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS) based thin film solar cells are the most efficient thin-film solar cells today. The non-toxic and wide band-gap zinc sulphide (ZnS) is a promising material to replace the cadmium sulfide (CdS) as the buffer layer in CIGS based solar cells. In this work we present a simulation study of a CIGS based solar cell with a buffer layer of ZnS, using the simulator Silvaco-Atlas. Our primary simulation shows a 22.6% efficiency of the CIGS solar cell with the CdS buffer layer which is comparable to reported and highest experimental results. However, the simulated efficiency of the CIGS solar cell with the ZnS buffer layer as high as 23.54% was achieved. The effects of layer parameters like the thickness, the acceptor and donor densities of the CIGS absorber and ZnS buffer layers and the CBO on the photovoltaic parameters of the ZnS/CIGS solar cell are optimized in order to improve the performance of the ZnS/CIGS solar cell. The highest efficiency of 27.33% is achieved when the ZnS buffer and the CIGS absorber layers have thicknesses of 0.025 µm and 4 µm with acceptor and donor densities of 6 × 1017 cm−3 and 1018 cm−3, respectively and a CBO in the range − 0.05 to 0.05 eV. The present results of simulation can help the development of the solar cells with higher conversion efficiency and low cost.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asaduzzaman, Md., Bahar, A.N., Bhuiyan, M.M.R.: Dataset demonstrating the modeling of a high performance Cu(In, Ga)Se2 absorber based thin film photovoltaic cell. Data Brief 11, 296–300 (2017a)
Asaduzzaman, Md, Billal Hosen, Md, Karamot Ali, Md, Newaz Bahar, A.: Non-toxic buffer layers in flexible Cu(In, Ga)Se2 photovoltaic cell applications with optimized absorber thickness. Int. J. Photoener. 2017, 187–191 (2017b)
Atlas User’s Manual device simulation software. Silvaco, Inc, Santa Clara, USA (2013)
Bechlaghem, S., Zebentout, B., Benamara, Z.: The major influence of the conduction-band-offset on Zn (O, S)/CuIn0.7Ga0.3Se2 solar cells. Results. Phys. 10, 650–654 (2018)
Chelvanathan, P., Hossain, M.I., Amin, N.: Performance analysis of copper–indium–gallium–diselenide (CIGS) solar cells with various buffer layers by SCAPS. Curr. Appl. Phys. 10(3), S387–S391 (2010)
Elbar, M., Tobbeche, S., Merazga, A.: Effect of top-cell CGS thickness on the performance of CGS/CIGS tandem solar cell. J. Sol. Energy. 125, 104–112 (2015)
Faraj, M.G., Ibrahim, K., Salhin, A.: Investigation of CIGS solar cells on polyethylene terephthalate substrates. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 60(10), 817–824 (2011)
Fridolin, T.N., Maurel, D.K.G., Ejuh, G.W., Bénédicte, T.T., Marie, N.J.: Highlighting some layer’s properties in performances optimization of CIGSe based solar cells: case of Cu (In, Ga) Se–ZnS. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2018.03.026
Friedlmeier, T.M., Jackson, P., Bauer, A., Hariskos, D., Kiowski, O., Wuerz, R., Powalla, M.: Improved photocurrent in Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cells: from 20.8% to 21.7% efficiency with CdS buffer and 21.0% Cd-free. J. Photovolt. 5, 1487–1491 (2015)
Gloeckler, M., Fahrenbruch, A.L., Sites, J.R.: Numerical modeling of CIGS and CdTe solar cells: setting the baseline. In: 3rd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, pp. 491–494 (2003)
Haque, F., Khan, N.A., Rahman, K.S., Islam, M.A., Alam, M.M., Sopian, K., Amin, N.: Prospects of zinc sulphide as an alternative buffer layer for CZTS solar cells from numerical analysis. In: 8th International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, pp. 504–507 (2014)
Hariskos, D., Spiering, S., Powalla, M.: Buffer layers in Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cells and modules. Thin Solid Films 480, 99–109 (2005)
Hosen, M.B., Bahar, A.N., Ali, M.K., Asaduzzaman, M.: Modeling and performance analysis dataset of a CIGS solar cell with ZnS buffer layer. Data Brief 14, 246–250 (2017)
Jackson, P., Wuerz, R., Hariskos, D., Lotter, E., Witte, W., Powalla, M.: Effects of heavy alkali elements in Cu(In, Ga)Se2 solar cells with efficiencies up to 22.6%. Phys. Status Solidi RRL 10, 583–586 (2016)
Khoshsirat, N., Yunus, N.A.M., Hamidon, M.N., Shafie, S., Amin, N.: Analysis of absorber layer properties effect on CIGS solar cell performance using SCAPS. Optik 126, 681–686 (2015)
Lindahl, J., Zimmermann, U., Szaniawski, P., Torndahl, T., Hultqvist, A., Salome, P., Platzer-Bjorkman, C., Edoff, M.: Inline Cu(In, Ga)Se2 Co-evaporation for high-efficiency solar cells and modules. IEEE. J. Photovolt. 3, 1100–1105 (2013)
Luo, K., Sun, Y., Zhou, L., Wang, F., Wu, F.: Theoretical simulation of performances in CIGS thin-film solar cells with cadmium-free buffer layer. J. Semicond. 38(8), 084006 (2017)
Martin Green, A., Emery, K., Hishikawa, Y., Warta, W., Ewan Dunlop, D., Dean Levi, H., Anita Ho-Baillie, W.Y.: Solar cell efficiency tables (Version 49). Prog. Photovolt.: Res. Appl. 25, 23–32 (2016)
Mostefaoui, M., Mazari, H., Khelifi, S., Bouraiou, A., Dabou, R.: Simulation of high efficiency CIGS solar cells with SCAPS-1D software. Energy Procedia 74, 736–744 (2015)
Movla, H.: Optimization of the CIGS based thin film solar cells: numerical simulation and analysis. Optik 125(1), 67–70 (2014)
Nakamura, M, Yamaguchi, K, Chiba, Y, Hakuma, H, Kobayashi, T, Nakada, T.: Achievement of 19.7% efficiency, with a small-sized Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 solar cells prepared by sulfurization after selenization process with Zn-based buffer. In: 39th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, pp. 0849–0852 (2013)
Park, J., Shin, M.: Numerical optimization of gradient bandgap structure for CIGS solar cell with ZnS buffer layer using technology computer-aided design simulation. Energies 11(7), 1785–1794 (2018)
Pettersson, J., Törndahl, T., Platzer-Björkman, C., Hultqvist, A., Edoff, M.: The influence of absorber thickness on Cu(In, Ga)Se solar cells with different buffer layers. IEEE. J. Photovolt. 3, 1376–1382 (2013)
Ramli, H., Rahim, S.K.A., Rahim, T.A., Aminuddin, M.M.: Optimization of zinc sulfide (ZnS) electron affinity in copper indium sulfide (CIS) based photovoltaic cell. Chal. Lett. 10(6), 189–195 (2013)
Richter, M., Schubbert, C., Eraerds, P., Riedel, I., Keller, J., Parisi, J., Dalibor, T., Avellán-Hampe, A.: Optical characterization and modeling of Cu(In, Ga)(Se, S)2 solar cells with spectroscopic ellipsometry and coherent numerical simulation. Thin Solid Films 535, 331–335 (2013)
Siebentritt, S.: Alternative buffers for chalcopyrite solar cells. Sol. Energy 77, 767–775 (2004)
Singh, P., Gautam, R., Sharma, S., Kumari, S., Verma, A.S.: Simulated solar cell device of CuGaSe2 by using CdS, ZnS and ZnSe buffer layers. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 42, 288–302 (2016)
Song, S.H., Nagaich, K., Aydil, E.S., Feist, R., Haley, R., Campbell, S.A.: Structure optimization for a high efficiency CIGS solar cell. In: 35th IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conference, pp. 2488–2492 (2010)
Sozzi, G., Troni, F., Menozzi, R.: On the combined effects of window/buffer and buffer/absorber conduction-band offsets, buffer thickness and doping on thin-film solar cell performance. Sol. Energy. Mater. Solar Cell. 121, 126–136 (2014)
Spiering, S., Nowitzki, A., Kessler, F., Igalson, M., Maksoud, H.A.: Optimization of buffer-window layer system for CIGS thin film devices with indium sulphide buffer by in-line evaporation. Sol. Energy. Mater. Sol. Cell. 144, 544–550 (2016)
Sylla, A., Touré, S., Vilcot, J.P.: Theoretical analysis of the effects of band gaps and the conduction band offset of ZnS-CIGS layers, as well as defect layer thickness. Int. J. Sci. Res. 6(11), 855–861. https://www.ijsr.net/archive/v6i11/v6i11.php. #ijsrnet (2017)
Törndahl, T., Hultqvist, A., Platzer-Björkman, C., Edoff, M.: Growth and characterization of ZnO-based buffer layers for CIGS solar cells. In: Oxide-Based Materials and Devices, vol. 7603, p. 76030D (2010)
Za’Abar, F., Zuhdi, A.W.M., Bahrudin, M.S., Abdullah, S.F., Harif, M.N., Hasani, A.H.: Optimization of baseline parameters and numerical simulation for Cu (In, Ga)Se2 solar cell. In: IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics (ICSE), pp. 209–213 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tobbeche, S., Kalache, S., Elbar, M. et al. Improvement of the CIGS solar cell performance: structure based on a ZnS buffer layer. Opt Quant Electron 51, 284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2000-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-019-2000-z