Abstract
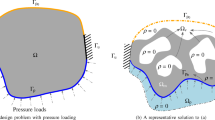
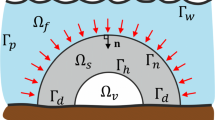
Homogenization method is applied to topology optimization of a weakly coupled two physics problem, where structures are made of periodically perforated material. The microscopic periodic cell is macroscopically modulated, where the design is characterized by the material density and its homogenized Hooke’s law at each point of the domain. The coupling is weak because the two physics involved are solved consecutively: first, the coupled fluid is determined using Biot–Darcy’s law and second, the fluid-structure problem by solving the linear poro-elasticity system; our aim is to optimize the homogenized formulation of this two-physic problem. This approach permits a computationally low cost of evaluation of load sensitivities using the adjoint-state method. Numerical two-dimensional test cases are presented using the alternate directions algorithm. It is demonstrated how the implementation can address a variety of design problems.
























Similar content being viewed by others
Code availibility
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no codes available as supplementary material because this work is carried out as part of a thesis in partnership with IFPEN. The latter holds the intellectual rights.
References
Abad KME, Khanoki AS, Pasini DF (2013) Fatigue design of lattice materials via computational mechanics: application to lattices with smooth transitions in cell geometry. Int J Fatigue 47:126–136
Allaire G (2002) Shape optimization by the homogenization method. Springer Appl Math Sci 146
Allaire G (2007) Conception optimale de structures. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Allaire G, Kohn RV (1993) Optimal design for minimum weight and compliance in plane stress using extremal microstructures. Eur J Mech A/Solids 12(6):839–878
Allaire G, Geoffroy-Donders P, Pantz O (2019) Topology optimization of modulated and oriented periodic microstructures by the homogenization method. Comput Math Appl 78(7):2197–2229
Batchelor G (2000) An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization: theory, methods, and applications. Springer Science and Business Media, Berlin
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1(4):193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bourdin B, Chambolle A (2003) Design-dependent loads in topology optimization. ESAIM Control Optim Calc Var 9:19–48
Céa J (1986) Conception optimale ou identification de formes, calcul rapide de la dérivée directionnelle de la fonction coût. ESAIM Math Modell Numer Anal 30(6):371–402
Du J, Olhoff N (2004) Topological optimization of continuum structures with design-dependent surface loading - part i: new computational approach for 2D problems. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 27(3):151–165
Feppon F (2019) Optimisation topologique de systèmes mutiphysiques, Hal, archives-ouvertes.fr (Thèse, École Polytechnique Université Paris Saclay)
Feppon F, Allaire G, Bordeu F, Cortial J, Dapogny C (2019) Shape Optimization of a Coupled Thermal Fluid-Structure Problem in a Level Set Mesh Evolution Framework. J Boletin de la Sociedad Española de Matemática Aplicada 76(3):413–458
Fuchs MB, Shemesh NNY (2004) Density-based topological design of structures subjected to water pressure using a parametric loading surface. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 28(1):11–19
Geoffroy-Donders P (2018) Homogenization method for topology optimization of structures built with lattice materials, PhD thesis, Université Paris Saclay (COmUE)
Hammer VB, Olhoff N (2000) Topology optimization of continuum structures subjected to pressure loading. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 19(2):85–92
Hashin Z, Shtrikman S (1963) A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials. J Mech Phys Solids 11(2):127–140
Hecht F (2012) New development in freefem++. J Numer Math 20(3–4):251–266
Hübner D, Rohan E, Lukeš V, Stingl M (2019) Optimization of the porous material described by the Biot model, Elsevier. Int J Solids Struct 156–157:216–233
Kohn RV, Strang G (1986) Optimal design and relaxation of variational problems. I. Comm Pure Appl Math 39(1):113–137
Kumar P (2023) TOPress: a MATLAB implementation for topology optimization of structures subjected to design-dependent pressure loads. Struct Multidiscip Optim 66:97
Kumar P, Frouws JS, Langelaar M (2020) Topology optimization of fluidic pressure loaded structures and compliant mechanisms using the Darcy Method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 61:1637–1655
Lee E, Martins JRRA (2012) Structural topology optimization with design-dependent pressure loads. J Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 40–48:233–236
Li Zm, Yu J, Yu Y, Xu L (2018) Topology optimization of pressure structures based on regional contour tracking technology. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 58(2):687–700
Lurie KA, Cherkaev AV, Fedorov AV (1982) Regularization of optimal design problems for bars and plates, I. II. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 37(4):499–522
Mendes E, Sivapuram R, Rodriguez R, Sampaio M, Picelli R (2022) Topology optimization for stability problems of submerged structures using the TOBS method. Comput Struct 259:106–685
Murat F (1997) Contre-exemples pour divers problèmes où le controle intervient dans les coefficients. Ann Mat Pura Appl 112:49–68
Murat F, Tartar L (1985) Calcul des variations et homogénéisation, Les lectures de l’homogénéisation : théorie et applications en physique, (Eyrolles), 319–369
Neuber H (1961) Theory of notch stresses: principles for exact calculation of strength with reference to structural form and material, USAEC Office of Technical Information, 4547
Pantz O, Trabelsi K (2008) A post-treatment of the homogenization method for shape optimization. SIAM J Control Optim 47(3):1380–1398
Picelli R, Neofytou A, Kim HA (2019) Topology optimization for design-dependent hydrostatic pressure loading via the level-set method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 60(4):1313–1326
Picelli R, Neofytou A, Kim HA (2019) Topology optimization for design-dependent hydrostatic pressure loading via the level-set method, Struct and Multidiscip Optim 60(4):1313-1326
Suzuki K, Kikuchi N (1991) A homogenization method for shape and topology optimization. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 93:291–318
Vigdergauz S (2013) Energy-minimizing inclusions in a planar elastic structure with macroisotropy. Struct Optim 17(2–3):104–112
Wang C, Zhao M, Ge T (2016) Structural topology optimization with design-dependent pressure loads. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(5):1005–1018
Wang C, Zhao M, Ge T (2016) Structural topology optimization with design-dependent pressure loads. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(5):1005–1018
Zheng B, Chang CJ, Gea HC (2009) Topology optimization with design-dependent pressure loading. J Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(6):535–543
Acknowledgements
This research project was fully sponsored by IFPEN: IFP energies nouvelles.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
n behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oheneba Agyekum, G., Cangémi, L. & Jouve, F. Homogenization based topology optimization of fluid-pressure loaded structures using the Biot–Darcy Model. Optim Eng 25, 459–490 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-023-09811-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-023-09811-1