Abstract
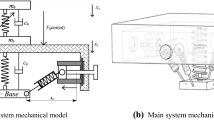
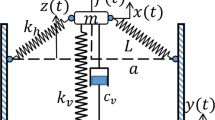
This paper investigates the stability problem of inerter-based semi-active n-degree-of-freedom (n-DOF) vibration systems containing semi-active switched elements, where the results can be applied to the design of many vibration control systems, such as building vibrations, vehicle suspensions, isolators, etc. Since introducing switched elements to n-DOF vibration systems may lead to instability, it is theoretically and practically meaningful to investigate the stability of n-DOF vibration systems containing semi-active switched elements. Necessary and sufficient conditions for the global asymptotic stability of a single-degree-of-freedom (SDOF) system containing at most one switched spring, one switched inerter, and one switched damper are derived, by solving the explicit solutions of the system states and analyzing the properties of energy functions. Based on the Lyapunov approach, a series of asymptotic stability conditions for the multi-degree-of-freedom (MDOF) system containing one semi-active switched inerter or one semi-active switched spring are derived. Finally, numerical simulation examples are presented to illustrate the stability results.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility Statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Smith, M.C.: Synthesis of mechanical networks: the inerter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 47(10), 1648–1662 (2002)
Chen, M.Z.Q., Hu, Y.: Inerter and its application in vibration control systems. Springer (2019)
Chen, M.Z.Q., Wang, K., Chen, G.: Passive network synthesis: advances with inerter. World Scientific (2019)
Wang, K., Chen, M.Z.Q.: On realizability of specific biquadratic impedances as three-reactive seven-element series-parallel networks for inerter-based mechanical control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 66(1), 340–345 (2020)
Hughes, T.H.: Minimal series-parallel network realizations of bicubic impedances. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 65(12), 4997–5011 (2020)
Shen, Y., Jiang, J.Z., Neild, S.A., Chen, L.: Vehicle vibration suppression using an inerter-based mechatronic device. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering 234(10–11), 2592–2601 (2020)
Alshabatat, N.T., Shaqarin, T.: Impact of using an inerter on the performance of vehicle active suspension. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 16(3), 331–339 (2022)
Liu, P., Ning, D., Luo, L., Zhang, N., Du, H.: An electromagnetic variable inertance and damping seat suspension with controllable circuits. IEEE Trans. Industr. Electron. 69(3), 2811–2821 (2021)
Zhang, S.Y., Neild, S., Jiang, J.Z.: Optimal design of a pair of vibration suppression devices for a multi-storey building. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 27(3), e2498 (2020)
Xu, K., Bi, K., Han, Q., Li, X., Du, X.: Using tuned mass damper inerter to mitigate vortex-induced vibration of long-span bridges: Analytical study. Eng. Struct. 182, 101–111 (2019)
Sarkar, S., Fitzgerald, B.: Vibration control of spar-type floating offshore wind turbine towers using a tuned mass-damper-inerter. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 27(1), e2471 (2020)
Lazar, I., Neild, S., Wagg, D.: Using an inerter-based device for structural vibration suppression. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 43(8), 1129–1147 (2014)
Zhang, S.Y., Jiang, J.Z., Neild, S.A.: Passive vibration control: a structure-immittance approach. In: Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 473(2201), 20170011 (2017)
Su, N., Bian, J., Chen, Z., Xia, Y.: A novel lever-type inerter-based vibration absorber. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 254, 108440 (2023)
Shen, Y., Hua, J., Fan, W., Liu, Y., Yang, X., Chen, L.: Optimal design and dynamic performance analysis of a fractional-order electrical network-based vehicle mechatronic ISD suspension. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 184, 109718 (2023)
Shi, B., Dai, W., Yang, J.: Performance analysis of a nonlinear inerter-based vibration isolator with inerter embedded in a linkage mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 109(2), 419–442 (2022)
Chowdhury, S., Banerjee, A.: The nonlinear dynamic analysis of optimum nonlinear inertial amplifier base isolators for vibration isolation. Nonlinear Dyn. 111, 12749–12786 (2023)
Chen, M.Z.Q., Hu, Y., Huang, L., Chen, G.: Influence of inerter on natural frequencies of vibration systems. J. Sound Vib. 333(7), 1874–1887 (2014)
Yamamoto, K.: Synthesis of passive interconnections in mass chains achieving a scale-free performance. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I: Journal of Systems and Control Engineering 235(9), 1709–1717 (2021)
Li, H., Chen, M.Z.Q.: Achievable dynamic responses of general undamped mass-chain systems. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 163, 108108 (2022)
Garrido, H., Curadelli, O., Ambrosini, D.: On the assumed inherent stability of semi-active control systems. Eng. Struct. 159, 286–298 (2018)
Hu, Y., Chen, M.Z.Q., Sun, Y.: Comfort-oriented vehicle suspension design with skyhook inerter configuration. J. Sound Vib. 405, 34–47 (2017)
Ribakov, Y., Gluck, J.: Active control of MDOF structures with supplemental electrorheological fluid dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 28(2), 143–156 (1999)
Bitaraf, M., Ozbulut, O.E., Hurlebaus, S., Barroso, L.: Application of semi-active control strategies for seismic protection of buildings with mr dampers. Eng. Struct. 32(10), 3040–3047 (2010)
Wang, Y., Meng, H., Zhang, B., Wang, R.: Analytical research on the dynamic performance of semi-active inerter-based vibration isolator with acceleration-velocity-based control strategy. Struct. Control. Health Monit. 26(4), e2336 (2019)
Min, C., Dahlmann, M., Sattel, T.: Steady state response analysis for a switched stiffness vibration control system based on vibration energy conversion. Nonlinear Dyn. 103, 239–254 (2021)
Corless, M., Leitmann, G.: Destabilization via active stiffness. Dyn. Control 7(3), 263–268 (1997)
Hu, Y., Hua, T., Chen, M.Z.Q., Shi, S., Sun, Y.: Instability analysis for semi-active control systems with semi-active inerters. Nonlinear Dyn. 105(1), 99–112 (2021)
Ramaratnam, A., Jalili, N.: A switched stiffness approach for structural vibration control: Theory and real-time implementation. J. Sound Vib. 291(1–2), 258–274 (2006)
Hu, Y., Hua, T., Chen, M.Z.Q., Shi, S., Sun, Y.: Inherent stability analysis for multibody systems with semi-active inerters. J. Sound Vib. 535, 117073 (2022)
Chen, C.T.: Linear system theory and design. Oxford University Press (1999)
Khalil, H.K.: Nonlinear Systems. Pearson (2013)
Banner, A.: The calculus lifesaver: all the tools you need to excel at calculus. Princeton University Press (2007)
Kwak, M.K.: Dynamic Modeling and Active Vibration Control of Structures. Springer (2022)
Liberzon, D.: Switching in systems and control. Springer (2003)
Makihara, K., Ecker, H., Dohnal, F.: Stability analysis of open-loop stiffness control to suppress self-excited vibrations. J. Vib. Control 11(5), 643–669 (2005)
Shimizu, K., Yamada, T., Tagami, J., Kurino, H.: Vibration tests of actual buildings with semi-active switching oil damper. In: Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, pp. 1–6. Vancouver, B.C., Canada (2004)
Hu, Y., Chen, M.Z.Q., Xu, S., Liu, Y.: Semiactive inerter and its application in adaptive tuned vibration absorbers. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 25(1), 294–300 (2016)
Du, G., Huang, X., Li, Y., Ouyang, Q., Wang, J.: Performance of a semi-active/passive integrated isolator based on a magnetorheological elastomer and spring. Smart Mater. Struct. 26(9), 095024 (2017)
Liao, G.J., Gong, X.L., Xuan, S.H., Kang, C.J., Zong, L.H.: Development of a real-time tunable stiffness and damping vibration isolator based on magnetorheological elastomer. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 23(1), 25–33 (2012)
Liu, Y., Waters, T., Brennan, M.: A comparison of semi-active damping control strategies for vibration isolation of harmonic disturbances. J. Sound Vib. 280(1–2), 21–39 (2005)
Wang, Y., Ding, H., Chen, L.Q.: Averaging analysis on a semi-active inerter-based suspension system with relative-acceleration-relative-velocity control. J. Vib. Control 26(13–14), 1199–1215 (2020)
Xu, W., Wang, K., Chen, M.Z.Q.: Supplementary material to: Stability analysis of inerter-based n-DOF vibration systems containing semi-active switched elements. supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09573-0
Cruz, C., Miranda, E.: Damping ratios of the first mode for the seismic analysis of buildings. J. Struct. Eng. 147(1), 04020300 (2021)
Wang, F.C., Su, W.J.: Impact of inerter nonlinearities on vehicle suspension control. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 46(7), 575–595 (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62373166, 61873129, the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province under Grant BK20211234, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant 2022M71136.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Wang, K. & Chen, M.Z.Q. Stability analysis of inerter-based n-DOF vibration systems containing semi-active switched elements. Nonlinear Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09573-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-024-09573-0