Abstract
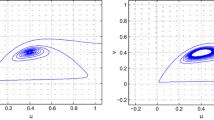
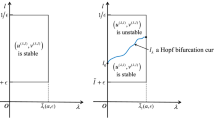
In this paper, the predator–prey model with Michaelis–Menten functional response subject to the Neumann boundary conditions is considered. The stability of the positive equilibrium and the direction of the Hopf bifurcations for the corresponding ordinary differential equation and partial differential equation are studied, respectively. To this end, the normal form method and the center manifold theorem are applied to determine the direction of the Hopf bifurcation and the stability of the bifurcated limit cycle when the diffusion terms are present. It is shown that the corresponding system can undergo either the supercritical or subcritical Hopf bifurcation at the equilibrium point within certain parameter range. Meanwhile, the Turing instability conditions for the equilibrium and the limit cycle bifurcated from the Hopf bifurcation are derived. As a result, some patterns occur in the model. Numerical simulations are carried out to verify the theoretical analysis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turing, A.M.: The chemical basis of morphogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci 237, 37–72 (1952)
Epstein, I.R., Pojman, J.A.: An Introduction to Nonlinear Chemical Dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1998)
Lengyel, I., Epstein, I.R.: Modeling of Turing structure in the chlorite-iodide-malonic acid-starch reaction system. Science 251, 650–652 (1991)
Li, X., Jiang, W.H., Shi, J.P.: Hopf bifurcation and Turing instability in the reaction–diffusion Holling–Tanner predator–prey model. IMA J. Appl. Math. 78, 287–306 (2013)
Peng, R., Wang, M.X.: On pattern formation in the Gray-Scott model. J. Sci. China Ser. A Math. 50, 377–386 (2007)
Ruan, S.G.: Diffusion-driven instability in the Gierer–Meinhardt model of morphogenesis. Nat. Resour. Modell. 11, 131–142 (1998)
Faria, T.: Stability and bifurcation for a delayed predator–prey model and the effect of diffusion. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 254, 433–463 (2001)
Chen, F.D.: On a nonlinear nonautonomous predator–prey model with diffusion and distributed delay. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 180, 33–49 (2005)
Ko, W., Ryu, K.: Qualitative analysis of a predator-prey model with Holling type II functional response incorporating a prey refuge. J. Differ. Equ. 231, 534–550 (2006)
Xiao, Y.N., Chen, L.S.: A ratio-dependent predator–prey model with disease in the prey. Appl. Math. Comput. 131, 397–414 (2002)
Jiang, G.R., Lu, Q.S.: Impulsive state feedback control of a predator–prey model. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 200, 193–207 (2007)
Du, Y.H., Hsu, S.B.: A diffusive predator–prey model in heterogeneous environment. J. Differ. Equ. 203, 331–364 (2004)
Xiao, D.M., Li, W.X., Han, M.A.: Dynamics in a ratio-dependent predator–prey model with predator harvesting. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 324, 14–29 (2006)
Kar, T.K., Ghorai, A.: Dynamic behaviour of a delayed predator–prey model with harvesting. Appl. Math. Comput. 217, 9085–9104 (2011)
Hu, D.P., Cao, H.J.: Stability and bifurcation analysis in a predator–prey system with Michaelis–Menten type predator harvesting. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 33, 58–82 (2017)
Wang, K.: Periodic solutions to a delayed predator-prey model with Hassell–Varley type functional response. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 12, 137–145 (2011)
Chen, W.Y., Wang, M.X.: Qualitative analysis of predator–prey models with Beddington–De Angelis functional response and diffusion. Math. Comput. Modell. 42, 31–44 (2005)
Chen, J.P., Zhang, H.D.: The qualitative analysis of two species predator–prey model with Holling’s type III functional response. J. Biomath. 7, 77–86 (1986)
Wang, Q., Dai, B.X., Chen, Y.M.: Multiple periodic solutions of an impulsive predator–prey model with Holling-type IV functional response. Math. Comput. Modell. 49, 1829–1836 (2009)
Liu, X.Q., Zhong, S.M., Tian, B.D., Zheng, F.X.: Asymptotic properties of a stochastic predator–prey model with Crowley–Martin functional response. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 43, 479–490 (2013)
Seo, G., Kot, M.: A comparison of two predator–prey models with Holling type I functional response. Math. Biosci. 212, 161–179 (2008)
May, R.M., Beddington, J.R., et al.: Management of multispecies fisheries. Science 205, 267–277 (1979)
Hsu, S.B., Huang, T.W.: Global stability for a class of predator–prey system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55, 763–783 (1995)
Beddington, J.R., May, R.M.: Maximum sustainable yields in systems subject to harvesting at more than one trophic level. Math. Biosci. 51, 261–281 (1980)
Beddington, J.R., Cooke, J.G.: Harvesting from a prey–predator complex. Ecol. Modell. 14, 155–177 (1982)
Zhu, C.R., Lan, K.Q.: Phase portraits, Hopf bifurcation and limit cycles of Leslie–Gower predator-prey systems with harvesting rates. Discr. Cont. Dynam. Syst. Ser. B. 14, 289–306 (2010)
Gong, Y.J., Huang, J.C.: Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation in a Leslie–Gower predator–prey model with prey harvesting. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. Eng. Ser. 30, 239–244 (2014)
Kar, T.K., Chaudhuri, K.S.: Regulation of a prey–predator fishery by taxation: a dynamic reaction model. J. Biol. Syst. 11, 173–187 (2003)
Bairagi, N., Chakraborty, S., Pal, S.: Heteroclinic bifurcation and multistability in a ratio-dependent predator–prey system with Michaelis–Menten type harvesting rate. Proc. World Congr. Eng. 1, 4–6 (2012)
Clark, C.W.: Aggregation and fishery dynamics: a theoretical study of schooling and the purse seine tuna fisheries. Fish. Bull. 77, 317–337 (1979)
Yi, F.Q., Wei, J.J., Shi, J.P.: Diffusion-driven instability and bifurcation in the Lengyel–Epstein system. Nonlinear Anal. RWA 9, 1038–1051 (2008)
Sambath, M., Gnanavel, S., Balachandran, K.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation of a diffusive predator–prey model with predator saturation and competition. Appl. Anal. 92, 2439–2456 (2012)
Wang, L., Zhao, H.Y.: Hopf bifurcation and Turing instability of 2-D Lengyel–Epstein system with reaction–diffusion terms. Appl. Math. Comput. 219, 9229–9244 (2013)
Peng, Y.H., Zhang, T.H.: Turing instability and pattern induced by cross-diffusion in a predator–prey system with Allee effect. Appl. Math. Comput. 275, 1–12 (2016)
Chen, J.X., Zhang, H., et al.: Interaction of excitable waves emitted from two defects by pulsed electric fields. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 54, 202–209 (2018)
Chen, J.X., Guo, M.M., Ma, J.: Termination of pinned spirals by local stimuli. EPL 113, 38004 (2016)
Chen, J.X., Peng, L., Zhao, Y.H., You, S.P., Wu, N.J., Ying, H.P.: Dynamics of spiral waves driven by a rotating electric field. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19, 60–66 (2014)
Ma, J., Xu, Y., Ren, G.D., Wang, C.N.: Prediction for breakup of spiral wave in a regular neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 84, 497–509 (2016)
Wiggins, S.: Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (1990)
Yi, F.Q., Wei, J.J., Shi, J.P.: Bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator–prey system. J. Differ. Equ. 246, 1944–1977 (2009)
Hassard, B.D., Kazarinoff, N.D., Wan, Y.H.: Theory and Application of Hopf Bifurcation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1981)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No.11571016, 61403115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, R., Chen, M., Liu, B. et al. Hopf bifurcation and Turing instability in a predator–prey model with Michaelis–Menten functional response. Nonlinear Dyn 91, 2033–2047 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-4001-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-4001-4