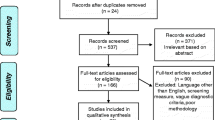
Abstract
Differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from normal aging and other dementia etiologies is imperative for disease specific treatment options and long-term care planning. Neuropathological confirmation is the gold standard for neurodegenerative disease diagnosis, yet most published studies examining the use of neuropsychological tests in the differential diagnosis of dementia rely upon clinical diagnostic outcomes. The present study undertook a meta-analytic review of the literature to identify cognitive tests and domains that allow for the differentiation of individuals with AD pathology from individuals with dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) pathology and pathology-free individuals. A comprehensive literature search yielded 14 studies that met the inclusion criteria for the present meta-analysis. Six studies comprised 222 decedents with AD compared to 433 normal controls, and eight studies comprised 431 cases of AD compared to 155 decedents with DLB. Results revealed that the effect of having neuropathologically confirmed AD versus DLB lowered performance in the memory domain, and having DLB decreased performance in the visuospatial domain. No single test differed significantly across the AD and DLB groups. For the AD and pathology free comparison, results indicated that that AD was associated with poorer performance on the memory and language domains. With respect to specific cognitive tests, AD produced lower scores on list learning tests, category fluency, and the Digit Symbol substitution test. The limited number of studies meeting inclusion criteria warrants formulation of guidelines for reporting in clinico-pathological studies; suggested guidelines are provided.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis
Ahmed, S., de Jager, C. A., Haigh, A. M., & Garrard, P. (2013). Semantic processing in connected speech at a uniformly early stage of autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychology. doi:10.1037/a0031288.
Albert, M. S., Moss, M. B., Tanzi, R., & Jones, K. (2001). Preclinical prediction of AD using neuropsychological tests. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. doi:10.1017/S1355617701755105.
Albert, Albert, M. S. DeCarli, C. DeKosky, S. De Leon, M. Foster, N. L. Fox, … Khachaturian, Z. (2005). The use of MRI and PET for clinical diagnosis of dementia and investigation of cognitive impairment: A consensus report. In Alzheimer's Association.
Bäckman, L., Jones, S., Berger, A. K., Laukka, E. J., & Small, B. J. (2005). Cognitive impairment in preclinical Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychology. doi:10.1037/0894-4105.19.4.520.
* Ballard, C., Holmes, C., McKeith, I., Neill, D., O’Brien, J., Cairns, N., et al. (1999). Psychiatric morbidity in dementia with Lewy bodies: a prospective clinical and neuropathological comparative study with Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 1039–1045.
* Beach, T. G., Adler, C. H., Lue, L., Sue, L. I., Bachalakuri, J., Henry-Watson, J., et al. (2009). Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathologica. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0538.
Beach, T. G., Monsell, S. E., Phillips, L. E., & Kukull, W. (2012). Accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer disease at National Institute on Aging Alzheimer disease centers, 2005–2010. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e31824b211b.
* Bennett, D. A., Schneider, J. A., Arvanitakis, Z., Kelly, J. F., Aggarwal, N. T., Shah, R. C., & Wilson, R. S. (2006). Neuropathology of older persons without cognitive impairment from two community-based studies. Neurology. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000219668.47116.e6.
Bossuyt, P. M., Reitsma, J. B., Bruns, D. E., Gatsonis, C. A., Glasziou, P. P., Irwig, L. M., et al. (2003). The STARD statement for reporting studies of diagnostic accuracy: explanation and elaboration. Annals of Internal Medicine, 138, W1–12. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-138-1-200301070-00012-w1.
Caramelli, P., Robitaille, Y., LarocheCholette, A., Nitrini, R., Gauvreau, D., Joanette, Y., & Lecours, A. R. (1998). Structural correlates of cognitive deficits in a selected group of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, 11, 184–190.
Chen, P., Ratcliff, G., Belle, S. H., Cauley, J. A., DeKosky, S. T., & Ganguli, M. (2001). Patterns of cognitive decline in presymptomatic Alzheimer disease: a prospective community study. Archives of General Psychiatry. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.58.9.853.
Christensen, H., Hadzi-Pavlovic, D., & Jacomb, P. (1991). The psychometric differentiation of dementia from normal aging: A meta-analysis. Psychological Assessment: A Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. doi:10.1037//1040-3590.3.2.147.
Chui, H. C., Zarow, C., Mack, W. J., Ellis, W. G., Zheng, L., Jagust, W. J., et al. (2006). Cognitive impact of subcortical vascular and Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Annals of Neurology. doi:10.1002/ana.21009.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analyses for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Collerton, D., Burn, D., McKeith, I., & O’Brien, J. (2003). Systematic review and meta-analysis show that dementia with Lewy bodies is a visual-perceptual and attentional-executive dementia. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders. doi:10.1159/000072807.
Davis, D. G., Schmitt, F. A., Wekstein, D. R., & Markesbery, W. R. (1999). Alzheimer neuropathologic alterations in aged cognitively normal subjects. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. doi:10.1097/00005072-199904000-00008.
Development Core Team, R. (2015). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing Available from http://www.R-project.org.
Driscoll, I., Resnick, S. M., Troncoso, J. C., An, Y., O'Brien, R., & Zonderman, A. B. (2006). Impact of Alzheimer's pathology on cognitive trajectories in nondemented elderly. Annals of Neurology. doi:10.1002/ana.21031.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., DeKosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., et al. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: revising the NINCDS–ADRDA criteria. The Lancet Neurology. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(07)70178-3.
Elfgren, C., Brun, A., Gustafson, L., Johanson, A., Minthon, L., Passant, U., & Risberg, J. (1994). Neuropsychological tests as discriminators between dementia of Alzheimer type and frontotemporal dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry. doi:10.1002/gps.930090807.
Elias, M., Beiser, A., Wolf, P., Au, R., White, R., & D’Agostino, R. (2000). The preclinical phase of Alzheimer disease: a 22- year prospective study of the Framingham cohort. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.57.6.808.
Ferman, T. J., Smith, G. E., Boeve, B. F., Graff-Radford, N. R., Lucas, J. A., Knopman, D. S., et al. (2006). Neuropsychological differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. The Clinical Neuropsychologist. doi:10.1080/13854040500376831.
Field, A. P., & Gillett, R. (2010). How to do a meta-analysis. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology. doi:10.1348/000711010X502733.
Galasko, D., Hansen, L. A., Katzman, R., Wiederholt, W., Masliah, E., Terry, R., et al. (1994). Clinical-neuropathological correlations in Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.1994.00540210060013.
* Galasko, D., Katzman, R., Salmon, D. P., & Hansen, L. (1996). Clinical and neuropathological findings in Lewy body dementias. Brain and Cognition. doi:10.1006/brcg.1996.0040.
Galvin, J. E., Powlishta, K. K., Wilkins, K., McKeel, D. W., Xiong, C., Grant, E., et al. (2005). Predictors of preclinical Alzheimer disease and dementia: a clinicopathologic study. Archives of Neurology, 62, 758–765.
Galvin, J. E., Boeve, B. F., Duda, J. E., Galasko, D. R., Kaufer, D., Leverenz, J. B., … Lopez, O. L. (2008). Current issues in Lewy body dementia diagnosis, treatment and research. Retrieved from Lewy Body Dementia Association website: http://www.lbda.org/sites/default/files/current_issues.pdf.
Gaugler, J. E., Ascher-Svanum, H., Roth, D. L., Fafowora, T., Siderowf, A., & Beach, T. G. (2013). Characteristics of patients misdiagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease and their medication use: An analysis of the NACC-UDS database. BMC Geriatrics, 13. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-13-137.
* Goldman, W. P., Price, J. L., Storandt, M., Grant, E. A., McKeel, D. W., Rubin, E. H., & Morris, J. C. (2001). Absence of cognitive impairment or decline in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. doi:10.1212/WNL.56.3.361.
* Hamilton, J. M., Salmon, D. P., Galasko, D., Delis, D. C., Hansen, L. A., Masliah, E., et al. (2004). A comparison of episodic memory deficits in neuropathologically-confirmed dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer's disease. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society. doi:10.1017/S1355617704105043.
Hamilton, J. M., Salmon, D. P., Galasko, D., Raman, R., Emond, J., Hansen, L. A., et al. (2008). Visuospatial deficits predict rate of cognitive decline in autopsy-verified dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuropsychology. doi:10.1037/a0012949.
Henry, J. D., Crawford, J. R., & Phillips, L. H. (2004). Verbal fluency performance in dementia of the Alzheimer’s type: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.02.001.
Hirni, D. I., Kivisaari, S. L., Monsch, A. U., & Taylor, K. I. (2016). Distinct neuroanatomical bases of episodic and semantic memory performance in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2013.01.013.
Hulette, C. M., Welsh-Bohmer, K. A., Murray, M. G., Saunders, A. M., Mash, D. C., & McIntyre, L. M. (1998). Neuropathological and neuropsychological changes in “normal” aging: evidence for preclinical Alzheimer disease in cognitively normal individuals. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. doi:10.1097/00005072-199812000-00009.
Hutchinson, A. D., & Mathais, J. L. (2007). Neuropsychological deficits in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analytic review. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2006.100669.
Hyman, B. T., Phelps, C. H., Beach, T. G., Bigio, E. H., Cairns, N. J., Carrillo, M. C., et al. (2012). National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 8, 1–13.
Jacobs, D. M., Sano, M., Dooneief, G., Marder, K., Bell, K. L., & Stern, Y. (1995). Neuropsychological detection and characterization of preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. doi:10.1212/WNL.45.5.957.
John, S. E., Gurnani, A. S., Bussell, C. A., Saurman, J. L., Griffin, J. W., & Gavett, B. E. (in press). The effectiveness and unique contribution of neuropsychological tests and the δ latent dementia phenotype in the differential diagnosis of dementia in the uniform data set. Neuropsychology.
Johns, E. K., Phillips, N. A., Belleville, S., Goupil, D., Babins, L., Kelner, L., et al. (2009). Executive functions in frontotemporal dementia and Lewy body dementia. Neuropsychology. doi:10.1037/a0016792.
Johnson, D. K., & Galvin, J. E. (2011). Longitudinal changes in cognition in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, doi, 1159/000323570.
Johnson, D. K., Morris, J. C., & Galvin, J. E. (2005). Verbal and visuospatial deficits in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000180964.60708.c2.
* Johnson, D. K., Storandt, M., Morris, J. C., Langford, Z. D., & Galvin, J. E. (2008). Cognitive profiles in dementia: Alzheimer disease vs healthy brain aging. Neurology. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000335972.35970.70.
Johnson, D. K., Storandt, M., Morris, J. C., & Galvin, J. E. (2009). Longitudinal study of the transition from healthy aging to Alzheimer’s disease. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2009.158.
Josephs, K. A., Tsuboi, Y., Cookson, N., Watt, H., & Dickson, D. W. (2004). Apolipoprotein E ε4 is a determinant for Alzheimer-type pathologic features in tauopathies, synucleinopathies, and frontotemporal degeneration. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.61.10.1579.
Kanne, S. M., Balota, D. A., Storandt, M., McKeel, D. W., & Morris, J. C. (1998). Relating anatomy to function in Alzheimer’s disease: neuropsychological profiles predict regional neuropathology 5 years later. Neurology. doi:10.1212/WNL.50.4.979.
Kazee, A. M., Eskin, T. A., Lapham, L. W., Gabriel, K. R., McDaniel, K. D., & Hamill, R. W. (1993). Clinicopathologic correlates in Alzheimer disease: assessment of clinical and pathologic diagnostic criteria. Alzheimer Disease & Associated Disorders, 7, 152–164.
Khachaturian, Z. S. (1985). Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Archives of Neurology, 42, 1097–1105. doi:10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029.
Konstantopoulos, S. (2011). Fixed effects and variance components estimation in three-level meta-analysis. Research Synthesis Methods. doi:10.1002/jrsm.35.
Kraybill, M. L., Larson, E. B., Tsuang, D. W., Teri, L., McCormick, W. C., Bowen, J. D., et al. (2005). Cognitive differences in dementia patients with autopsy-verified Alzheimer’s disease, Lewy body pathology, or both. Neurology, 64, 2069–2073.
Lamar, M., Price, C. C., Davis, K. L., Kaplan, E., & Libon, D. J. (2002). Capacity to maintain mental set in dementia. Neuropsychologia. doi:10.1016/S0028-3932(01)00125-7.
Lezak, M. D., Howieson, D. B., Bigler, E. D., & Tranel, D. (2012). Neuropsychological assessment (5th ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Lopez, O. L., Wisniewski, S. R., Becker, J. T., Boller, F., & DeKosky, S. T. (1999). Psychiatric medication and abnormal behavior as predictors of progression in probable Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology, 56, 1266–1272.
Mathais, J. L., & Burke, J. (2009). Cognitive functioning in Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. Neuropsychology. doi:10.1037/a0015384.
McKeith, I. G., Burn, D., O’Brien, J., Perry, R., & Perry, E. (2002). Dementia with Lewy bodies. In K. L. Davis, D. Charney, J. T. Koyle, & C. Nemeroff (Eds.), Neuropsychopharmacology: The fifth generation of progress (pp. 1301–1315). Brentwood, TN: American college of neuropsychophamacology.
McKeith, I. G., Dickson, D. W., Lowe, J. J., Emre, M. M., O'Brien, J. T., Feldman, H. H., et al. (2005). Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB consortium. Neurology. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000187889.17253.b1.
McKhann, G. M., Knopman, D. S., Chertkow, H., Hyman, B. T., Jack Jr., C. R., Kawas, C. H., et al. (2011). The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005.
Meehl, P. E. (1995). Bootstraps taxometrics: solving the classification problem in psychopathology. American Psychologist. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.50.4.266.
* Minoshima, S., Foster, N. L., Sima, A. A., Frey, K. A., Albin, R. L., & Kuhl, D. E. (2001). Alzheimer's disease versus dementia with Lewy bodies: cerebral metabolic distinction with autopsy confirmation. Annals of Neurology. doi:10.1002/ana.1133.
Mitchell, A. J. (2009). A meta-analysis of the accuracy of the mini-mental state examination in the detection of dementia and mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Psychiatric Research. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.04.014.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed1000097.
Mollenhauer, B., Förstl, H., Deuschl, G., Storch, A., Oertel, W., & Trenkwalder, C. (2010). Lewy body and Parkinsonian dementia: common but often misdiagnosed conditions. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2010.0684.
Mrak, R. E., & Griffin, W. S. T. (2007). Dementia with Lewy bodies: definition, diagnosis, and pathogenic relationship to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 3, 619–625.
Mungas, D., Beckett, L., Harvey, D., Tomaszewski Farias, S., Reed, B., Carmichael, O., et al. (2010). Heterogeneity of cognitive trajectories in diverse older persons. Psychology and Aging. doi:10.1037/a0019502.
Newell, K. L., Hyman, B. T., Growdon, J. H., & Hedley-Whyte, E. T. (1999). Application of the National Institute on Aging (NIA)-Reagan institute criteria for the neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Journal of Neuropathology & Experimental Neurology. doi:10.1097/00005072-199911000-00004.
Palmer, K., Bäckman, L., Winblad, B., & Fratiglioni, L. (2003). Detection of Alzheimer's disease and dementia in the preclinical phase: population based cohort study. British Medical Journal. doi:10.1136/bmj.326.7383.245.
Pinhiero, J. C., & Bates, D. M. (2000). Mixed-effects models in S and S-PLUS. New York: Springer.
Price, D. L., Tanzi, R. E., Borchelt, D. R., & Sisodia, S. S. (1998). Alzheimer’s disease: genetic studies and transgenic models. Annual Review of Genetics. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.32.1.461.
Price, J. L., McKeel, D. W., Buckles, V. D., Roe, C. M., Xiong, C., Grundman, M., et al. (2009). Neuropathology of nondemented aging: presumptive evidence for preclinical Alzheimer disease. Neurobiology of Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.04.002.
Reed, B. R., Mungas, D. M., Kramer, J. H., Ellis, W., Vinters, H. V., Zarow, C., et al. (2007). Profiles of neuropsychological impairment in autopsy-defined Alzheimer’s disease and cerebrovascular disease. Brain. doi:10.1093/brain/awl385.
* Riley, K. P., Jicha, G. A., Davis, D., Abner, E. L., Cooper, G. E., Stiles, N., et al. (2011). Prediction of preclinical Alzheimer's disease: longitudinal rates of change of cognition. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-102133.
Rosenthal, R. (1979). The file drawer problem and tolerance for null results. Psychological Bulletin. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.86.3.638.
Rosenthal, R., & DiMatteo, M. R. (2001). Meta-analysis: recent developments in quantitative methods for literature reviews. Annual Review of Psychology. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.59.
Ruscio, J. (2008). A probability-based measure of effect size: robustness to base rates and other factors. Psychological Methods, 13, 19–30. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.13.1.19.
Salmon, D. P. (2000). Disorders of memory in Alzheimer’s disease. In L. S. Cermak (2nd Ed.), Handbook of neuropsychology, Vol. 2: Memory and its disorders (pp.155–195). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Salmon, D. P., & Bondi, M. W. (2009). Neuropsychological assessment of dementia. Annual Review of Psychology. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.57.102904.190024.
* Scheff, S. W., Price, D. A., Schmitt, F. A., Scheff, M. A., & Mufson, E. J. (2011). Synaptic loss in the inferior temporal gyrus in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. doi:10.3233/JAD-2011-101782.
* Schmitt, F. A., Davis, D. G., Wekstein, D. R., Smith, C. D., Ashford, J. W., & Markesbery, W. R. (2000). Preclinical. AD revisited: Neuropathology of Cognitively Normal Older Adults. Neurology. doi:10.1212/WNL.55.3.370.
Sloane, P. D., Zimmerman, S., Suchindran, C., Reed, P., Wang, L., Boustani, M., & Sudha, S. (2002). The public health impact of Alzheimer’s disease, 2000-2050: potential implication of treatment advances. Annual Review of Public Health. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.23.100901.140525.
Storandt, M., Botwinick, J., Danziger, W. L., Berg, L., & Hughes, C. P. (1984). Psychometric differentiation of mild senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.1984.04050170043013.
Strauss, E., Sherman, E. M. S., & Spreen, O. (2006). A compendium of neuropsychological tests: Administration, norms, and commentary (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Tabert, M. H., Manly, J. J., Liu, X., Pelton, G. H., Rosenblum, S., Jacobs, M., et al. (2006). Neuropsychological prediction of conversion to Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Archives of General Psychiatry. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.8.916.
Tierney, M. C., Snow, W. G., Reid, D. W., Zorzitto, M. L., & Fisher, R. H. (1987). Psychometric differentiation of dementia: replication and extension of the findings of Storandt and coworkers. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.1987.00520190032013.
Tierney, M. C., Szalai, J. P., Snow, W. G., Fisher, R. H., Nores, A., Nadon, G., et al. (1996). Prediction of probable Alzheimer's disease in memory-impaired patients: A prospective longitudinal study. Neurology. doi:10.1212/WNL.46.3.661.
* Tiraboschi, P., & Guerra, U. P. (2010). How to distinguish dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer’s disease? The Open Nuclear Medicine Journal. doi:10.2174/1876388X01002020058.
Tiraboschi, P., Salmon, D. P., Hansen, L. A., Hofstetter, R. C., Thal, L. J., & Corey-Bloom, J. (2006). What best differentiates Lewy body from Alzheimer's disease in early-stage dementia? Brain. doi:10.1093/brain/awh725.
Tombaugh, T. N., & McIntyre, N. J. (1992). The mini-mental state examination: a comprehensive review. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb01992.x.
Varma, A. R., Snowden, J. S., Lloyd, J. J., Talbot, P. R., Mann, D. M. A., & Neary, D. (1999). Evaluation of the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria in the differentiation of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp.66.2.184.
Viechtbauer, W. (2010). Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. Journal of Statistical Software, 36, 1–48 Retrieved from http://www.jstatsoft.org/v36/i03.
Walker, Z., McKeith, I., Rodda, J., Qassem, T., Tatsch, K., Booij, J., et al. (2012). Comparison of cognitive decline between dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease: a cohort study. British Medical Journal Open. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000380.
Wang, B. W., Lu, E., Mackenzie, I. R. A., Assaly, M., Jacova, C., Lee, P. E., et al. (2012). Multiple pathologies are common in Alzheimer patients in clinical trials. The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. doi:10.1017/S0317167100015316.
Welsh, K., Butters, N., Hughes, J., Mohs, R., & Heyman, A. (1991). Detection of abnormal memory decline in mild cases of Alzheimer's disease using CERAD neuropsychological measures. Archives of Neurology. doi:10.1001/archneur.1991.00530150046016.
* Yoshizawa, H., Vonsattel, J. P. G., & Honig, L. S. (2013). Early neuropsychological discriminants for Lewy body disease: an autopsy series. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-304381.
Zakzanis, K. K. (2001). Statistics to tell the truth, the whole truth, and nothing but the truth: formulae, illustrative numerical examples, and heuristic interpretation of effect size analyses for neuropsychological researchers. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology. doi:10.1016/S0887-6177(00)00076-7.
Acknowledgments
The data from this manuscript were presented at the annual conferences of the International Neuropsychological Society (2014, 2015) and the American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology (2014). This manuscript was based on the first author’s Master’s thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurnani, A.S., Gavett, B.E. The Differential Effects of Alzheimer's Disease and Lewy Body Pathology on Cognitive Performance: a Meta-analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 27, 1–17 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-016-9334-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-016-9334-0