Abstract
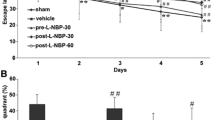
S-oxiracetam (S-ORC), a nootropic drug, was used to protect against ischemic stroke by lessening the blood brain barrier dysfunction and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis. However, the potential effects of S-ORC in the recovery of cognitive functions after ischemic stroke and the underlying mechanisms remains unclear. In this study, middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R) in rats was used as the animal model. By using Y-maze test, Morris water maze, triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated 2'-deoxyuridine 5'-triphosphate (dUTp) nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay, hematoxylin and eosin, immunohistochemical staining and western blot to evaluate the protective effect of S-ORC on cognitive recovery, we were able to confirm that S-ORC ameliorated spatial learning impairment, tissue loss, and hippocampal neuronal apoptosis and injury induced by MCAO/R in rats. These cognitive effects were achieved by restoring the normal function of synaptophysin and increasing PSD95 expression in the hippocampus. Furthermore, we found that methyllycaconitine, the antagonist of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7nAChR), and LY294002, the inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), were able to block the cognitive effects of S-ORC after MCAO/R in rats. In conclusion, α7nAChR and PI3K are key molecules that mediated the signaling pathway leading to S-ORC-induced cognitive restoration after MCAO/R.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Pasi M, Poggesi A, Salvadori E, Pantoni L (2012) Post-Stroke dementia and cognitive impairment. Front Neurol Neurosci 30:65
Béjot Y, Jacquin A, Rouaud O, Durier J, Aboa-Eboulé C, Hervieu M, Osseby GV, Giroud M (2012) One-year survival of demented stroke patients: data from the Dijon Stroke Registry, France (1985–2008). Eur J Neurol 19:712–717
Bombi L, Eu-Jung C, Eun-Jung L, Han SM, Dae-Hyun H, Hye-Jung L, Insop S (2011) The neuroprotective effect of methanol extract ofgagamjungjihwanand fructus euodiae on ischemia-induced neuronal and cognitive impairment in the rat. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med eCAM 2011:685254
Peng T, Britton GL, Kim H, Cattano D, Aronowski J, Grotta J, Mcpherson DD, Huang SL (2013) Therapeutic time window and dose dependence of xenon delivered via echogenic liposomes for neuroprotection in Stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 19:773–784
Liu AF, Zhao FB, Jing W, Lu YF, Jian T, Yin Z, Yan G, Hu XJ, Liu XY, Jie T (2016) Effects of vagus nerve stimulation on cognitive functioning in rats with cerebral ischemia reperfusion. J Transl Med 14:1–12
Li F, Yan CQ, Lin LT, Li H, Zeng XH, Liu Y, Du SQ, Zhu W, Liu CZ (2015) Acupuncture attenuates cognitive deficits and increases pyramidal neuron number in hippocampal CA1 area of vascular dementia rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:133
Counts SE, Alldred MJ, Che S, Ginsberg SD, Mufson EJ (2014) Synaptic gene dysregulation within hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in mild cognitive impairment. Neuropharmacology 79:172
Sopala M, Danysz W (2001) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat enhances age-related deficits in spatial memory. J Neural Transm 108:1445–1456
Olsen GM, Scheelkrüger J, Møller A, Jensen LH (1994) Relation of spatial learning of rats in the Morris water maze task to the number of viable CA1 neurons following four-vessel occlusion. Behav Neurosci 108:681
Murthy VN, De CP (2003) Cell biology of the presynaptic terminal. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:701–728
Buffington SA, Wei H, Costamattioli M (2014) Translational control in synaptic plasticity and cognitive dysfunction. Annu Rev Neurosci 37:17
Ali T, Kim MO (2015) Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3β pathway in the mouse hippocampus. J Pineal Res 59:47–59
Pan W, Han S, Lin K, Sha L, Du J, Cui H (2016) Effects of dihydrotestosterone on synaptic plasticity of the hippocampus in mild cognitive impairment male SAMP8 mice. Exp Ther Med 12:1455–1463
Ma KG, Qian YH (2019) Alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and its effects on Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropeptides 73:96–106
From the American Association of Neurological Surgeons ASoNC, Interventional Radiology Society of Europe CIRACoNSESoMINTESoNESOSfCA, Interventions SoIRSoNS, World Stroke O, Sacks D, Baxter B, BCV C, Carpenter JS, Cognard C, Dippel D, Eesa M, Fischer U, Hausegger K, Hirsch JA, Shazam Hussain M, Jansen O, Jayaraman MV, Khalessi AA, Kluck BW, Lavine S, Meyers PM, Ramee S, Rufenacht DA, Schirmer CM, Vorwerk D (2018) Multisociety consensus quality improvement revised consensus statement for endovascular therapy of acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 13:612–632
Bertrand D, Lee CH, Flood D, Marger F, Donnelly-Roberts D (2015) Therapeutic potential of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol Rev 67:1025–1073
Corradi J, Bouzat C (2016) Understanding the bases of function and modulation of alpha7 nicotinic receptors: implications for drug discovery. Mol Pharmacol 90:288–299
Vulfius CA, Lebedev DS, Kryukova EV, Kudryavtsev DS, Kolbaev SN, Utkin YN, Tsetlin VI (2020) PNU-120596, a positive allosteric modulator of mammalian alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, is a negative modulator of ligand-gated chloride-selective channels of the gastropod Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurochem 155:274–284
Sadigh-Eteghad S, Vatandoust SM, Mahmoudi J, Rahigh Aghsan S, Majdi A (2020) Cotinine ameliorates memory and learning impairment in senescent mice. Brain Res Bull 164:65–74
Samakova A, Gazova A, Sabova N, Valaskova S, Jurikova M, Kyselovic J (2019) The PI3k/Akt pathway is associated with angiogenesis, oxidative stress and survival of mesenchymal stem cells in pathophysiologic condition in ischemia. Physiol Res 68:S131–S138
Sun Z, Sun L, Tu L (2020) GABAB receptor-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling pathway alleviates oxidative stress and neuronal cell injury in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 76:1513–1526
Wang Y, Lin Y, Wang L, Zhan H, Luo X, Zeng Y, Wu W, Zhang X, Wang F (2020) TREM2 ameliorates neuroinflammatory response and cognitive impairment via PI3K/AKT/FoxO3a signaling pathway in Alzheimer's disease mice. Aging (Albany NY) 12:20862–20879
Gouliaev AH, Senning A (1994) Piracetam and other structurally related nootropics. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 19:180–222
Zhang Q, Yang W, Yang Y, Xing H, Zhang Q, Li J, Lu Y, He J, Yang S, Zhao D, Chen X (2015) Comparative pharmacokinetic studies of racemic oxiracetam and its pure enantiomers after oral administration in rats by a stereoselective HPLC method. J Pharm Biomed Anal 111:153–158
Fan W, Li X, Huang L, He S, Xie Z, Fu Y, Fang W, Li Y (2018) S-oxiracetam ameliorates ischemic stroke induced neuronal apoptosis through up-regulating alpha7 nAChR and PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta signal pathway in rats. Neurochem Int 115:50–60
Huang L, Shang E, Fan W, Li X, Li B, He S, Fu Y, Zhang Y, Li Y, Fang W (2017) S-oxiracetam protect against ischemic stroke via alleviating blood brain barrier dysfunction in rats. Eur J Pharm Sci 109:40–47
Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Atkins KD, Bazan NG (2009) Robust docosahexaenoic acid-mediated neuroprotection in a rat model of transient, focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:3121–3126
Ortolano F, Maffia P, Dever G, Rodolico G, Millington OR, De Simoni MG, Brewer JM, Bushell TJ, Garside P, Carswell HV (2010) Advances in imaging of new targets for pharmacological intervention in stroke: real-time tracking of T-cells in the ischaemic brain. Br J Pharmacol 159:808–811
Huang J, Kodithuwakku ND, He W, Zhou Y, Fan W, Fang W, He G, Wu Q, Chu S, Li Y (2015) The neuroprotective effect of a novel agent N2 on rat cerebral ischemia associated with the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology 95:12–21
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Zhou Y, Huang J, He W, Fan W, Fang W, He G, Wu Q, Chu S, Li Y (2014) N2 ameliorates neural injury during experimental ischemic stroke via the regulation of thromboxane A2 production. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:458–465
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Shen CC, Yang YC, Chiao MT, Cheng WY, Tsuei YS, Ko JL (2010) Characterization of endogenous neural progenitor cells after experimental ischemic stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res 7:6
Holmbom B, Naslund U, Eriksson A, Virtanen I, Thornell LE (1993) Comparison of triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining versus detection of fibronectin in experimental myocardial infarction. Histochemistry 99:265–275
Lee JY, Lee HE, Kang SR, Choi HY, Ryu JH, Yune TY (2014) Fluoxetine inhibits transient global ischemia-induced hippocampal neuronal death and memory impairment by preventing blood-brain barrier disruption. Neuropharmacology 79:161–171
Li D, Wang C, Yao Y, Chen L, Liu G, Zhang R, Liu Q, Shi FD, Hao J (2016) mTORC1 pathway disruption ameliorates brain inflammation following stroke via a shift in microglia phenotype from M1 type to M2 type. FASEB J 30:3388
Li J, Han B, Ma X, Qi S (2010) The effects of propofol on hippocampal caspase-3 and Bcl-2 expression following forebrain ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Res 1356:11–23
Cheng Q, Yakel JL (2015) Activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors increases intracellular cAMP levels via activation of AC1 in hippocampal neurons. Neuropharmacology 95:405–414
Kita Y, Ago Y, Higashino K, Asada K, Takano E, Takuma K, Matsuda T (2014) Galantamine promotes adult hippocampal neurogenesis via M(1) muscarinic and alpha7 nicotinic receptors in mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17:1957–1968
Wang C, Chen T, Li G, Zhou L, Sha S, Chen L (2015) Simvastatin prevents beta-amyloid(25-35)-impaired neurogenesis in hippocampal dentate gyrus through alpha7nAChR-dependent cascading PI3K-Akt and increasing BDNF via reduction of farnesyl pyrophosphate. Neuropharmacology 97:122–132
Sugawara T, Lewén A, Noshita N, Gasche Y, Chan PH (2002) Effects of global ischemia duration on neuronal, astroglial, oligodendroglial, and microglial reactions in the vulnerable hippocampal CA1 subregion in rats. J Neurotrauma 19:85–98
Kaewkaen P, Tong-Un T, Wattanathorn J, Muchimapura S, Kaewrueng W, Wongcharoenwanakit S (2012) Mulberry fruit extract protects against memory impairment and hippocampal damage in animal model of vascular dementia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:263520
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
Wu P, Luo Y, Zhen L, Hu X, Shang Y, Liao Y, Xue H, Huang F, Xiao W (2016) Rannasangpei is a therapeutic agent in the treatment of vascular dementia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:1–10
Lee B, Choi EJ, Lee EJ, Han SM, Hahm DH, Lee HJ, Shim I (2010) The neuroprotective effect of methanol extract of gagamjungjihwan and fructus euodiae on ischemia-induced neuronal and cognitive impairment in the rat. Evidence-Based Complementray Altern Med 2011:685254
Han L, Ji Z, Chen W, Yin D, Xu F, Li S, Chen F, Zhu G, Peng D (2015) Protective effects of tao-hong-si-wu decoction on memory impairment and hippocampal damage in animal model of vascular dementia. Evidence-Based Complementary Altern Med eCAM 2015:195835
Wan X, Wang H, Ma P, Xi L, Sun J, He Z, Zhang X, Liu X (2014) Simultaneous determination of oxiracetam and its degraded substance in rat plasma by HPLC-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetic study after a single high-dose intravenous administration. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 969:95–100
Wan D, Xue L, Zhu H, Luo Y (2013) Catalpol induces neuroprotection and prevents memory dysfunction through the cholinergic system and BDNF. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:134852
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the technical support from the Public Platform of Medical Research Center, Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81701313), and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2242020K40175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, W., Zhang, Y., Li, X. et al. S-oxiracetam Facilitates Cognitive Restoration after Ischemic Stroke by Activating α7nAChR and the PI3K-Mediated Pathway. Neurochem Res 46, 888–904 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03233-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03233-0