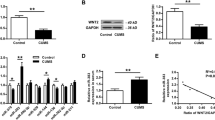
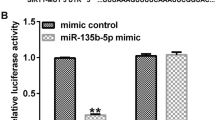
Abstract
Depression is a common, severe, and debilitating psychiatric disorder of unclear etiology. Our previous study has shown that protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent 1F (PPM1F) in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) displays significant regulatory effects in depression-related behaviors. miR-132-3p plays a potential role in the etiology of depression. This study explored the effect of miR-132-3p on the onset of depression and the possible underlying mechanism for modulating PPM1F expression during the pathology of depression. We found that miR-132-3p levels in the hippocampus of depressed mice subjected to chronic unpredictable stress (CUS) were dramatically reduced, which were correlated with depression-related behaviors. Knockdown of miR-132-3p in hippocampal DG resulted in depression-related phenotypes and increased susceptibility to stress. miR-132-3p overexpression in hippocampal DG alleviated CUS-induced depression-related performance. We then screened out the potential target genes of miR-132-3p, and we found that the expression profiles of sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (Srebf1) and forkhead box protein O3a (FOXO3a) were positively correlated with PPM1F under the condition of miR-132-3p knockdown. Finally, as anticipated, we revealed that the activities of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII) and adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) were reduced, which underlies the target signaling pathway of PPM1F. In conclusion, our study suggests that miR-132-3p was designed to regulate depression-related behaviors by indirectly regulating PPM1F and targeting Srebf1 and FOXO3a, which have been linked to the pathogenesis and treatment of depression.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
McCarron RM, Shapiro B, Rawles J, Luo J (2021) Depression. Ann Intern Med 174:ITC65–ITC80
Rosenblat JD, Kurdyak P, Cosci F, Berk M, Maes M, Brunoni AR, Li M, Rodin G, McIntyre RS, Carvalho AF (2020) Depression in the medically ill. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 54:346–366
Fox ME, Lobo MK (2019) The molecular and cellular mechanisms of depression: a focus on reward circuitry. Mol Psychiatry 24:1798–1815
Malhi GS, Mann JJ (2018) Depress Lancet 392:2299–2312
Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E (2011) Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet 12:99–110
Kocerha J, Dwivedi Y, Brennand KJ (2015) Noncoding RNAs and neurobehavioral mechanisms in psychiatric disease. Mol Psychiatry 20:677–684
Allen L, Dwivedi Y (2020) MicroRNA mediators of early life stress vulnerability to depression and suicidal behavior. Mol Psychiatry 25:308–320
Nguyen HD (2023) Resveratrol, Endocrine disrupting chemicals, neurodegenerative Diseases and Depression: genes, transcription factors, microRNAs, and sponges involved. Neurochem Res 48:604–624
Qian Y, Song J, Ouyang Y, Han Q, Chen W, Zhao X, Xie Y, Chen Y, Yuan W, Fan C (2017) Advances in roles of miR-132 in the nervous system. Front Pharmacol 8:770
Fu X, Liu J, Xie J, Chen G, Zhang H, Meng F, Wu M, Li Q, Liu Y, Wang W, Dai J, Wang D, Zhao D, Li C, Wang X (2022) Identification of potential therapeutic and diagnostic characteristics of Alzheimer disease by targeting the miR-132-3p/FOXO3a-PPM1F axis in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Res 1790:147983
Fang Y, Qiu Q, Zhang S, Sun L, Li G, Xiao S, Li X (2018) Changes in miRNA-132 and miR-124 levels in non-treated and citalopram-treated patients with depression. J Affect Disord 227:745–751
Qi S, Yang X, Zhao L, Calhoun VD, Perrone-Bizzozero N, Liu S, Jiang R, Jiang T, Sui J, Ma X (2018) MicroRNA132 associated multimodal neuroimaging patterns in unmedicated major depressive disorder. Brain 141:916–926
Amaral DG, Scharfman HE, Lavenex P (2007) The dentate gyrus: fundamental neuroanatomical organization (dentate gyrus for dummies). Prog Brain Res 163:3–22
Hsu D (2007) The dentate gyrus as a filter or gate: a look back and a look ahead. Prog Brain Res 163:601–613
Danzer SC (2012) Depression, stress, epilepsy and adult neurogenesis. Exp Neurol 233:22–32
Umschweif G, Greengard P, Sagi Y (2021) The dentate gyrus in depression. Eur J Neurosci 53:39–64
Su M, Hong J, Zhao Y, Liu S, Xue X (2015) MeCP2 controls hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression via homeostatic interactions with microRNA132 in rats with depression. Mol Med Rep 12:5399–5406
Ishida A, Sueyoshi N, Kameshita I (2018) Functions and dysfunctions of ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase phosphatase (CaMKP/PPM1F) and CaMKP-N/PPM1E. Arch Biochem Biophys 640:83–92
Liu J, Meng F, Wang W, Cui M, Wu M, Jiang S, Dai J, Lian H, Li Q, Xu Z, Wang Y, Zhang J, Li C (2021) PPM1F in hippocampal dentate gyrus regulates the depression-related behaviors by modulating neuronal excitability. Exp Neurol 340:113657
Meng F, Liu J, Dai J, Wu M, Wang W, Liu C, Zhao D, Wang H, Zhang J, Li M, Li C (2020) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in 5-HT neurons regulates susceptibility to depression-related behaviors induced by subchronic unpredictable stress. J Psychiatr Res 126:55–66
Li C, Meng F, Garza JC, Liu J, Lei Y, Kirov SA, Guo M, Lu XY (2021) Modulation of depression-related behaviors by adiponectin AdipoR1 receptors in 5-HT neurons. Mol Psychiatry 26:4205–4220
Malkesman O, Scattoni ML, Paredes D, Tragon T, Pearson B, Shaltiel G, Chen G, Crawley JN, Manji HK (2010) The female urine sniffing test: a novel approach for assessing reward-seeking behavior in rodents. Biol Psychiatry 67:864–871
Fogaca MV, Fukumoto K, Franklin T, Liu RJ, Duman CH, Vitolo OV, Duman RS (2019) N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist d-methadone produces rapid, mTORC1-dependent antidepressant effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 44:2230–2238
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301:805–809
Li C, Meng F, Lei Y, Liu J, Liu J, Zhang J, Liu F, Liu C, Guo M, Lu XY (2021) Leptin regulates exon-specific transcription of the Bdnf gene via epigenetic modifications mediated by an AKT/p300 HAT cascade. Mol Psychiatry 26:3701–3722
Liu J, Meng F, Dai J, Wu M, Wang W, Liu C, Zhao D, Wang H, Zhang J, Li C (2020) The BDNF-FoxO1 Axis in the medial prefrontal cortex modulates depressive-like behaviors induced by chronic unpredictable stress in postpartum female mice. Mol Brain 13:91
Zhao D, Wang D, Wang W, Dai J, Cui M, Wu M, Liu C, Liu J, Meng F, Wang K, Hu F, Liu D, Qiu C, Li W, Li C (2022) The altered sensitivity of acute stress induced anxiety-related behaviors by modulating insular cortex-paraventricular thalamus-bed nucleus of the stria terminalis neural circuit. Neurobiol Dis 174:105890
Trick AY, Chen FE, Schares JA, Freml BE, Lor P, Yun Y, Wang TH (2021) High resolution estimates of relative gene abundance with quantitative ratiometric regression PCR (qRR-PCR). Analyst 146:6463–6469
Vo N, Klein ME, Varlamova O, Keller DM, Yamamoto T, Goodman RH, Impey S (2005) A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16426–16431
Remenyi J, Hunter CJ, Cole C, Ando H, Impey S, Monk CE, Martin KJ, Barton GJ, Hutvagner G, Arthur JS (2010) Regulation of the miR-212/132 locus by MSK1 and CREB in response to neurotrophins. Biochem J 428:281–291
Troubat R, Barone P, Leman S, Desmidt T, Cressant A, Atanasova B, Brizard B, El Hage W, Surget A, Belzung C, Camus V (2021) Neuroinflammation and depression: a review. Eur J Neurosci 53:151–171
Rao JS, Kellom M, Kim HW, Rapoport SI, Reese EA (2012) Neuroinflammation and synaptic loss. Neurochem Res 37:903–910
Wayman GA, Davare M, Ando H, Fortin D, Varlamova O, Cheng HY, Marks D, Obrietan K, Soderling TR, Goodman RH, Impey S (2008) An activity-regulated microRNA controls dendritic plasticity by down-regulating p250GAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:9093–9098
Ronovsky M, Zambon A, Cicvaric A, Boehm V, Hoesel B, Moser BA, Yang J, Schmid JA, Haubensak WE, Monje FJ, Pollak DD (2019) A role for miR-132 in learned safety. Sci Rep 9:528
Su Q, Liu Y, Lv XW, Dai RX, Yang XH, Kong BH (2020) LncRNA TUG1 mediates ischemic myocardial injury by targeting miR-132-3p/HDAC3 axis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 318:H332–H344
Kariba Y, Yoshizawa T, Sato Y, Tsuyama T, Araki E, Yamagata K (2020) Brown adipocyte-derived exosomal mir-132-3p suppress hepatic Srebf1 expression and thereby attenuate expression of lipogenic genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 530:500–507
Cai Y, Wang W, Guo H, Li H, Xiao Y, Zhang Y (2018) miR-9-5p, miR-124-3p, and mir-132-3p regulate BCL2L11 in tuberous sclerosis complex angiomyolipoma. Lab Invest 98:856–870
Chen X, Li M, Zhou H, Zhang L (2019) miR-132 targets FOXA1 and exerts tumor-suppressing functions in thyroid Cancer. Oncol Res 27:431–437
Wong HK, Veremeyko T, Patel N, Lemere CA, Walsh DM, Esau C, Vanderburg C, Krichevsky AM (2013) De-repression of FOXO3a death axis by microRNA-132 and – 212 causes neuronal apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 22:3077–3092
Harvey BP, Banga SS, Ozer HL (2004) Regulation of the multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by the PP2C phosphatase PPM1F in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 279:24889–24898
Liu J, Stevens PD, Eshleman NE, Gao T (2013) Protein phosphatase PPM1G regulates protein translation and cell growth by dephosphorylating 4E binding protein 1 (4E-BP1). J Biol Chem 288:23225–23233
Voss M, Paterson J, Kelsall IR, Martin-Granados C, Hastie CJ, Peggie MW, Cohen PT (2011) Ppm1E is an in cellulo AMP-activated protein kinase phosphatase. Cell Signal 23:114–124
Hansen KF, Obrietan K (2013) MicroRNA as therapeutic targets for treatment of depression. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:1011–1021
Duman RS (2002) Synaptic plasticity and mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry 7(Suppl 1):S29–34
Klein ME, Lioy DT, Ma L, Impey S, Mandel G, Goodman RH (2007) Homeostatic regulation of MeCP2 expression by a CREB-induced microRNA. Nat Neurosci 10:1513–1514
Numakawa T, Richards M, Adachi N, Kishi S, Kunugi H, Hashido K (2011) MicroRNA function and neurotrophin BDNF. Neurochem Int 59:551–558
Meng F, Liu J, Dai J, Lian H, Jiang S, Li Q, Wu M, Wang W, Wang D, Zhao D, Liu C, Qiu C, Li C (2021) PPM1F in Dentate Gyrus modulates anxiety-related behaviors by regulating BDNF expression via AKT/JNK/p-H3S10 pathway. Mol Neurobiol 58:3529–3544
Cheng HY, Papp JW, Varlamova O, Dziema H, Russell B, Curfman JP, Nakazawa T, Shimizu K, Okamura H, Impey S, Obrietan K (2007) microRNA modulation of circadian-clock period and entrainment. Neuron 54:813–829
Furtado M, Katzman MA (2015) Examining the role of neuroinflammation in major depression. Psychiatry Res 229:27–36
Gaudet AD, Fonken LK, Watkins LR, Nelson RJ, Popovich PG (2018) MicroRNAs: roles in regulating Neuroinflammation. Neuroscientist 24:221–245
Thounaojam MC, Kaushik DK, Basu A (2013) MicroRNAs in the brain: it’s regulatory role in neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 47:1034–1044
Gong X, Huang M, Chen L (2022) Mechanism of mir-132-3p promoting neuroinflammation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease. eNeuro 9
Liu F, Li Y, Jiang R, Nie C, Zeng Z, Zhao N, Huang C, Shao Q, Ding C, Qing C, Xia L, Zeng E, Qian K (2015) miR-132 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in alveolar macrophages by the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Exp Lung Res 41:261–269
Kong H, Yin F, He F, Omran A, Li L, Wu T, Wang Y, Peng J (2015) The effect of miR-132, miR-146a, and miR-155 on MRP8/TLR4-Induced astrocyte-related inflammation. J Mol Neurosci 57:28–37
Skinner MK, Rawls A, Wilson-Rawls J, Roalson EH (2010) Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family phylogenetics and nomenclature. Differentiation 80:1–8
Toledo EM, Yang S, Gyllborg D, van Wijk KE, Sinha I, Varas-Godoy M, Grigsby CL, Lonnerberg P, Islam S, Steffensen KR, Linnarsson S, Arenas E (2020) Srebf1 controls midbrain dopaminergic neurogenesis. Cell Rep 31:107601
Swarup V, Morabito S, Miyoshi E, Michael N, Shahin S, Martini AC, Head E, Silva J, Leavy K, Perez-Rosendahl M (2021) Single-cell multi-omics analysis identifies dynamic regulation of SREBF1 in Alzheimer’s disease. In: 2021 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference. ALZ
Anderson MJ, Viars CS, Czekay S, Cavenee WK, Arden KC (1998) Cloning and characterization of three human forkhead genes that comprise an FKHR-like gene subfamily. Genomics 47:187–199
Rana T, Behl T, Sehgal A, Mehta V, Singh S, Sharma N, Bungau S (2021) Elucidating the possible role of FoxO in Depression. Neurochem Res 46:2761–2775
Ebert MS, Neilson JR, Sharp PA (2007) MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat Methods 4:721–726
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350–355
Huang Y, Shen XJ, Zou Q, Wang SP, Tang SM, Zhang GZ (2011) Biological functions of microRNAs: a review. J Physiol Biochem 67:129–139
Du J, Li M, Huang Q, Liu W, Li WQ, Li YJ, Gong ZC (2019) The critical role of microRNAs in stress response: therapeutic prospect and limitation. Pharmacol Res 142:294–302
Fries GR, Zhang W, Benevenuto D, Quevedo J (2019) MicroRNAs in major depressive disorder. Adv Exp Med Biol 1118:175–190
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171521 to CL) and Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2022YQ65; ZR2021MH073; ZR2019PH109). The Special Funds of Taishan Scholars Project of Shandong Province (NO.tsqn202211368 to CL). Innovation and entrepreneurship training program for College Students (202110440141; 202110440042). The Projects of Medical and Health Technology Development Program in Shandong Province, China (202003090720, 202003070728, 2019WS329). Scientific Research Foundation of Binzhou Medical University (BY2020KJ03 and BY2020KJ02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL and MHC contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by XXM, QYL and CL with assistance from GHC, JJX, MW, FTM, JL YL, DZ, WTW, DW, CLL and JJD. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XXM and MHC, and CL modified and approved the manuscript accordingly. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical Approval
This study was conducted per the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of the Binzhou Medical University Hospital approved the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, X., Li, Q., Chen, G. et al. Role of Hippocampal miR-132-3p in Modifying the Function of Protein Phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+-dependent 1 F in Depression. Neurochem Res 48, 2514–2530 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03926-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-023-03926-8