Abstract
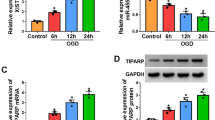
Background: Ischemic stroke is a very dangerous disease with high incidence, fatality and disability rate in human beings. Massive evidence has indicated that oxidative stress and inflammation are intimately correlated with progression of ischemic stroke. Additionally, LncRNAs were reported to be involved in ischemic stroke. Here, we aim to explore the effects and molecular mechanism of lncRNA OIP5-AS1 on oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemic stroke. Methods: HMC3 and SH-SY5Y cells were under the condition of oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) treatment to establish cell models of ischemic stroke. Commercial kits were employed to detect the indicators of oxidative stress including ROS, MDA and SOD. The expression of OIP5-AS1, miR-155-5p and IRF2BP2 mRNA was determined using RT-qPCR. The protein levels of inflammatory factors including TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 and IRF2BP2 were assessed by western blot and/or ELISA. Luciferase activity assay was employed to validate their correlations among OIP5-AS1, miR-155-5p and IRF2BP2. Results: In OGD/R-induced HMC3 and SH-SY5Y cells, the expression of OIP5-AS1 and IRF2BP2 was reduced while miR-155-5p was elevated. OGD/R induction promoted oxidative stress and inflammatory response in HMC3 and SH-SY5Y cells, while OIP5-AS1 or IRF2BP2 sufficiency as well as miR-155-5p inhibitor attenuated OGD/R-induced these influences. In addition, IRF2BP2 knockdown abolished the suppressive impacts of OIP5-AS1 overexpression on oxidative stress and inflammatory response in OGD/R-induced HMC3 and SH-SY5Y cells. Mechanistically, OIP5-AS1 enhanced IRF2BP2 expression via sponging miR-155-5p. Conclusion: OIP5-AS1 suppressed oxidative stress and inflammatory response to alleviate cell injury caused by OGD/R induction in HMC3 and SH-SY5Y cells through regulating miR-155-5p/IRF2BP2 axis, which might offer novel targeted molecules for ischemic stroke therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- OGD/R:
-
oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- IRF2BP2:
-
Interferon regulatory factor 2 binding protein2
- IRF-2:
-
Interferon regulatory factor-2
- IL4:
-
Interleukin-4
- MCAO/R:
-
middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion
- ox-LDL:
-
oxidative low-density lipoprotein
- HFD:
-
high fat diet
- EMEM:
-
Eagle’s minimum essential medium
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- CCK-8:
-
cell counting kit-8
References
Feske SK (2021) Ischemic stroke. Am J Med 134:1457–1464
Phipps MS et al (2020) Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ 368:l6983
Feigin VL et al (2018) Global, Regional, and Country-Specific Lifetime Risks of Stroke, 1990 and 2016. N Engl J Med 379:2429–2437
Turc G et al (2019) European Stroke Organisation (ESO) - european Society for minimally invasive neurological therapy (ESMINT) guidelines on mechanical thrombectomy in Acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg
Baron JC (2018) Protecting the ischaemic penumbra as an adjunct to thrombectomy for acute stroke. Nat Rev Neurol 14:325–337
Kapranov P et al (2007) RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316:1484–1488
Bao MH et al (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis 9:281
Wang SW et al (2018) Non-coding RNA in Acute ischemic stroke: mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Cell Transpl 27:1763–1777
Zhang X et al (2017) Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci 37:1797–1806
Chen Z et al (2021) Depleting SOX2 improves ischemic stroke via lncRNA PVT1/microRNA-24-3p/STAT3 axis. Mol Med 27:107
Chen Y et al (2021) Up-regulating lncRNA OIP5-AS1 protects neuron injury against cerebral hypoxia-ischemia induced inflammation and oxidative stress in microglia/macrophage through activating CTRP3 via sponging miR-186-5p. Int Immunopharmacol 92:107339
Niu X et al (2020) lncRNA Oip5-as1 attenuates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury by sponging miR-29a to activate the SIRT1/AMPK/PGC1α pathway. Cell Prolif 53:e12818
Sun H et al (2021) Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 overexpression promotes viability and inhibits high Glucose-Induced oxidative stress of cardiomyocytes by Targeting MicroRNA-34a/SIRT1 Axis in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 21:2017–2027
Chen ZJ et al (2020) Glycine improves ischemic stroke through miR-19a-3p/AMPK/GSK-3β/HO-1 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:2021–2031
Han B et al (2018) Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy 14:1164–1184
Zhang H et al (2020) Plasma endothelial microvesicles and their carrying miRNA-155 serve as biomarkers for ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res 98:2290–2301
Shi Y et al (2020) MiR-155-5p accelerates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via targeting DUSP14 by regulating NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24:1408–1419
Ramalho-Oliveira R et al (2019) IRF2BP2: a new player in the regulation of cell homeostasis. J Leukoc Biol 106:717–723
Kim I et al (2019) The IRF2BP2-KLF2 axis regulates osteoclast and osteoblast differentiation. BMB Rep 52:469–474
Ma YL et al (2018) Suppressing Irf2bp2 expressions accelerates metabolic syndrome-associated brain injury and hepatic dyslipidemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:1651–1658
Cruz SA et al (2017) Loss of IRF2BP2 in Microglia increases inflammation and functional deficits after focal ischemic brain Injury. Front Cell Neurosci 11:201
Huang Y (2018) The novel regulatory role of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med 22:5768–5775
Zhou RS et al (2019) Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer 19:779
Lu J et al (2020) LncRNA PVT1 regulates ferroptosis through miR-214-mediated TFR1 and p53. Life Sci 260:118305
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136:215–233
Chamorro Á et al (2016) Neuroprotection in acute stroke: targeting excitotoxicity, oxidative and nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol 15:869–881
Chen H et al (2020) Therapeutic targets of oxidative/nitrosative stress and neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke: applications for natural product efficacy with omics and systemic biology. Pharmacol Res 158:104877
Kanazawa M et al (2017) Microglia and Monocytes/Macrophages polarization reveal Novel Therapeutic mechanism against Stroke.Int J Mol Sci18
Zhao Y et al (2022) Neuronal injuries in cerebral infarction and ischemic stroke: from mechanisms to treatment (review).Int J Mol Med49
Agholme L et al (2010) An in vitro model for neuroscience: differentiation of SH-SY5Y cells into cells with morphological and biochemical characteristics of mature neurons. J Alzheimers Dis 20:1069–1082
Xu H et al (2021) Neuroprotective effect of cajaninstilbene acid against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion damages by activating AMPK/Nrf2 pathway. J Adv Res 34:199–210
Akella A et al (2019) Long noncoding RNAs in the pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. Neuromolecular Med 21:474–483
Stanzione R et al (2020) Pathogenesis of ischemic stroke: role of epigenetic mechanisms. Genes (Basel, p 11
Greither T et al (2020) MiR-155-5p and MiR-203a-3p are prognostic factors in soft tissue sarcoma. Cancers (Basel) 12
Wu M et al (2020) MiR-155-5p promotes oral cancer progression by targeting chromatin remodeling gene ARID2. Biomed Pharmacother 122:109696
Guo P et al (2020) MiR-155-5p plays as a “janus” in the expression of inflammatory cytokines induced by T-2 toxin. Food Chem Toxicol 140:111258
Huang LG et al (2018) Silencing rno-mir-155-5p in rat temporal lobe epilepsy model reduces pathophysiological features and cell apoptosis by activating Sestrin-3. Brain Res 1689:109–122
Jiang K et al (2020) miR-155-5p Promotes Oxalate- and Calcium-Induced Kidney Oxidative Stress Injury by Suppressing MGP Expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:5863617
Zhao L et al (2019) Mir-155-5p inhibits the viability of vascular smooth muscle cell via targeting FOS and ZIC3 to promote aneurysm formation. Eur J Pharmacol 853:145–152
Yu G et al (2019) MiR-142a-3p and mir-155-5p reduce methamphetamine-induced inflammation: role of the target protein Peli1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 370:145–153
Liu Y et al (2020) miRNA-mRNA network regulation in the skeletal muscle fiber phenotype of chickens revealed by integrated analysis of miRNAome and transcriptome. Sci Rep 10:10619
Chen HH et al (2015) IRF2BP2 reduces macrophage inflammation and susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Circ Res 117:671–683
Funding
This work was supported by Hainan Provincial Cerebrovascular Disease Clinical Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: Ying Xia; study concepts: Ji-Kun Zhang; study design: Ji-Kun Zhang; definition of intellectual content: Ying Xia; literature research: Ji-Kun Zhang, You Li; experimental studies: Ji-Kun Zhang, You Li, Zheng-Tao Yu, Jun-Wen Jiang; data acquisition: You Li, Hong Tang; data analysis: Ji-Kun Zhang, Guo-Long Tu; statistical analysis: Ji-Kun Zhang, Jun-Wen Jiang; manuscript preparation: Ji-Kun Zhang; manuscript editing: Ji-Kun Zhang; manuscript review: Ying Xia; All the authors approved for the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
These authors declared no competing interests in this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JK., Li, Y., Yu, ZT. et al. OIP5-AS1 Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Ischemic Stroke Through miR-155-5p/IRF2BP2 Axis. Neurochem Res 48, 1382–1394 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03830-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-022-03830-7