Abstract
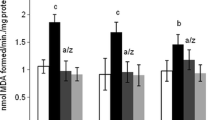
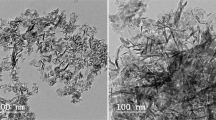
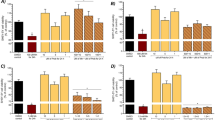
Brain contains the highest lipid content involved in various structural and physiological activities such as structural development, neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, signal transduction and myelin sheath formation. Lipids bilayer is essential to maintain the structural integrity for the physiological functions of protein. Impairments in lipid metabolism and its composition can lead to the progression of various brain ailments such as neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. Aluminium (Al), the potent neurotoxin has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) like pathology. Al can bind to biomembrane and influence oligomerization and conformational changes of proteins by acting as cross-linkers. The present study evaluated the influence of Ginkgo biloba (GBE) on the lipid profile alterations induced by Al lactate in hippocampal and cortical regions using FTIR spectroscopy. Rats were exposed with 10 mg/kg b.w. (intraperitoneal) of Al lactate for 6 weeks. This was followed by a treatment protocol of GBE (100 mg/kg b.w.) both preexposure (2 weeks) and conjunctive (6 weeks) exposure. A self recovery group was also included, where Al withdrawal was done for 2 weeks post Al exposure. A significant decrease in peak areas of cholesterol, sphingolipids and phospholipids was observed in Al treated groups. Further, polyunsaturated fatty acids and membrane fluidity has also decreased, as revealed by olefinic and methyl asymmetric stretching bands. Al treatment significantly increased the fluorescence polarization, anisotropy and order parameter, which however were normalized following GBE supplementation. Results also showed that pretreatment with GBE provided more beneficial effects on the adverse changes following Al in membrane composition and behavioral outcome.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Al:
-
Aluminium
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid beta
- BBB:
-
Blood Brain Barrier
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- Fig:
-
Figure
- i.p:
-
Intra-peritoneal
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxidation
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- kg:
-
Kilogram
- mg:
-
Milligram
- Tris HCl:
-
Tris Hydrochloride
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances
- TCA:
-
Tricholro acetic acid
- GBE:
-
Ginkgo biloba Extract
References
Cermenati G, Mitro N, Audano M, Melcangi RC, Crestani M, De Fabiani E, Caruso D (2015) Lipids in the nervous system: from biochemistry and molecular biology to patho-physiology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851(1):51–60
Schmitt F, Hussain G, Dupuis L, Loeffler JP, Henriques A (2014) A plural role for lipids in motor neuron diseases: energy, signaling and structure. Front Cell Neurosci 8:25
Hussain G, Anwar H, Rasul A, Imran A, Qasim M, Zafar S et al (2020) Lipids as biomarkers of brain disorders. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60(3):351–374
Dreissig I, Machill S, Salzer R, Krafft C (2009) Quantification of brain lipids by FTIR spectroscopy and partial least squares regression. Spectrochim Acta Part A 71(5):2069–2075
Aureli M, Grassi S, Prioni S, Sonnino S, Prinetti A (2015) Lipid membrane domains in the brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851(8):1006–1016
Olsen AS, Færgeman NJ (2017) Sphingolipids: membrane microdomains in brain development, function and neurological diseases. Open Biol 7(5):170069
Brown HA, Murphy RC (2009) Working towards an exegesis for lipids in biology. Nat Chem Biol 5(9):602–606
Bozek K, Wei Y, Yan Z, Liu X, Xiong J, Sugimoto M et al (2015) Organization and evolution of brain lipidome revealed by large-scale analysis of human, chimpanzee, macaque, and mouse tissues. Neuron 85(4):695–702
Müller CP, Reichel M, Mühle C, Rhein C, Gulbins E, Kornhuber J (2015) Brain membrane lipids in major depression and anxiety disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851(8):1052–1065
Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327(5961):46–50
Vetrivel KS, Meckler X, Chen Y, Nguyen PD, Seidah NG, Vassar R et al (2009) Alzheimer disease Aβ production in the absence of S-palmitoylation-dependent targeting of BACE1 to lipid rafts. J Biol Chem 284(6):3793–3803
Parsons RB, Austen BM (2007) Protein–protein interactions in the assembly and subcellular trafficking of the BACE (β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme) complex of Alzheimer's disease
Marin R, Fabelo N, Fernández-Echevarría C, Canerina-Amaro A, Rodríguez-Barreto D, Quinto-Alemany D et al (2016) Lipid raft alterations in aged-associated neuropathologies. Curr Alzheimer Res 13(9):973–984
Marin R, Diaz M (2018) Estrogen interactions with lipid rafts related to neuroprotection. Impact of brain ageing and menopause. Front Neurosci 12:128
Verma S, Sharma S, Ranawat P, Nehru B (2020) Modulatory effects of Ginkgo biloba against amyloid aggregation through induction of heat shock proteins in aluminium induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 45:465
Pandya JD, Dave KR, Katyare SS (2004) Effect of long-term aluminum feeding on lipid/phospholipid profiles of rat brain myelin. Lipids Health Dis 3(1):13
Bhalla P, Nair P, Garg ML, Dhawan DK (2009) Effects of lithium on membrane fluidity and lipid profile in brain membranes of aluminum-treated rats. Toxicol Environ Chem 91(4):723–733
Kneipp J, Lasch P, Baldauf E, Beekes M, Naumann D (2000) Detection of pathological molecular alterations in scrapie-infected hamster brain by Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1501(2–3):189–199
Çakmak G, Togan I, Uğuz C, Severcan F (2003) FT-IR spectroscopic analysis of rainbow trout liver exposed to nonylphenol. Appl Spectrosc 57(7):835–841
Mourant JR, Yamada YR, Carpenter S, Dominique LR, Freyer JP (2003) FTIR spectroscopy demonstrates biochemical differences in mammalian cell cultures at different growth stages. Biophys J 85(3):1938–1947
Severcan F, Toyran N, Kaptan N, Turan B (2000) Fourier transform infrared study of the effect of diabetes on rat liver and heart tissues in the C–H region. Talanta 53(1):55–59
Verma S, Ranawat P, Sharma N, Nehru B (2019) Ginkgo biloba attenuates aluminum lactate-induced neurotoxicity in reproductive senescent female rats: behavioral, biochemical, and histopathological study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):27148–27167
Ali T, Yoon GH, Shah SA, Lee HY, Kim MO (2015) Osmotin attenuates amyloid beta-induced memory impairment, tau phosphorylation and neurodegeneration in the mouse hippocampus. Sci Rep 5(1):1–17
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T (1991) Utility of an elevated plus-maze for dissociation of amnesic and behavioral effects of drugs in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 194(1):71–76
Nehru B, Verma R, Khanna P, Sharma SK (2008) Behavioral alterations in rotenone model of Parkinson's disease: attenuation by co-treatment of centrophenoxine. Brain Res 1201:122–127
Kulkarni SK (1999) Handbook of experimental pharmacology, 3rdrd rev edn. Vallabh Prakashan, New Delhi, pp 123–125
Kalonia H, Mishra J, Kumar A (2012) Targeting neuro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress by minocycline attenuates quinolinic-acid-induced Huntington’s disease-like symptoms in rats. Neurotox Res 22(4):310–320
Sivakumar S, Sivasubramanian J, Raja B (2012) Aluminium induced structural, metabolic alterations and protective effects of desferrioxamine in the brain tissue of mice: an FTIR study. Spectrochim Acta Part A 99:252–258
Sivakumar S, Khatiwada CP, Sivasubramanian J, Raja B (2014) Protective effects of deferiprone and desferrioxamine in brain tissue of aluminum intoxicated mice: an FTIR study. Biomed Prev Nutr 4(1):53–61
Trush MA, Mimnaugh EG, Ginsburg E, Gram TE (1981) In vitro stimulation by paraquat of reactive oxygen-mediated lipid peroxidation in rat lung microsomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 60(2):279–286
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Pearse AGE (1968) Histochemistry, theoretical and applied: theoretical and applied. Churchill Livingstone, London
Humanson GL (1961) Basic procedures-animal tissue technique. Part I. WH Freeman and Company, San Francisco, pp 130–132
Lin SCC, Way EL (1982) A high affinity Ca2+-ATPase in enriched nerve-ending plasma membranes. Brain Res 235(2):387–392
Lin SCC, Way EL (1984) Characterization of calcium-activated and magnesium-activated ATPases of brain nerve endings. J Neurochem 42(6):1697–1706
Swapna I, Kumar KSS, Murthy CR, Senthilkumaran B (2006) Membrane alterations and fluidity changes in cerebral cortex during acute ammonia intoxication. Neurotoxicology 27(3):402–408
Shinitzky M, Barenholz Y (1974) Dynamics of the hydrocarbon layer in liposomes of lecithin and sphingomyelin containing dicetylphosphate. J Biol Chem 249(8):2652–2657
Pottel H, van der Meer W, Herreman W (1983) Correlation between the order parameter and the steady-state fluorescence anisotropy of 1, 6-diphenyl-1, 3, 5-hexatriene and an evaluation of membrane fluidity. Biochim Biophys Acta 730(2):181–186
Massey V, Williams CH (1965) On the reaction mechanism of yeast glutathione reductase. J Biol Chem 240(11):4470–4480
Vanderkooi JM, Callis JB (1974) Pyrene. Probe of lateral diffusion in the hydrophobic region of membranes. Biochemistry 13(19):4000–4006
Akkas SB, Inci S, Zorlu F, Severcan F (2007) Melatonin affects the order, dynamics and hydration of brain membrane lipids. J Mol Struct 834:207–215
Liu KZ, Bose R, Mantsch HH (2002) Infrared spectroscopic study of diabetic platelets. Vib Spectrosc 28(1):131–136
Sharma AC, Kulkarni SK (1992) Evaluation of learning and memory mechanisms employing elevated plus-maze in rats and mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16(1):117–125
Shiotsuki H, Yoshimi K, Shimo Y, Funayama M, Takamatsu Y, Ikeda K et al (2010) A rotarod test for evaluation of motor skill learning. J Neurosci Methods 189(2):180–185
Sumathi T, Shobana C, Kumari BR, Nandhini DN (2011) Protective role of Cynodon dactylon in ameliorating the aluminium-induced neurotoxicity in rat brain regions. Biol Trace Elem Res 144(1–3):843–853
Pogue AI, Lukiw WJ (2016) Aluminum, the genetic apparatus of the human CNS and Alzheimer's disease (AD). Morphologie 100(329):56–64
Lukiw WJ (2013) Alzheimer's disease (AD) as a disorder of the plasma membrane. Front Physiol 4:24
Mesa-Herrera F, Taoro-González L, Valdés-Baizabal C, Diaz M, Marín R (2019) Lipid and lipid raft alteration in aging and neurodegenerative diseases: a window for the development of new biomarkers. Int J Mol Sci 20(15):3810
Sood PK, Verma S, Nahar U, Nehru B (2015) Neuroprotective role of lazaroids against aluminium chloride poisoning. Neurochem Res 40(8):1699–1708
Lee HJ, Korshavn KJ, Kochi A, Derrick JS, Lim MH (2014) Cholesterol and metal ions in Alzheimer's disease. Chem Soc Rev 43(19):6672–6682
Petrov AM, Kasimov MR, Zefirov AL (2016) Brain cholesterol metabolism and its defects: linkage to neurodegenerative diseases and synaptic dysfunction. Acta Naturae 8(1):58–73
Sood PK, Nahar U, Nehru B (2011) Curcumin attenuates aluminum-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in rat brain. Neurotox Res 20(4):351
Marcheggiani F, Cirilli I, Orlando P, Silvestri S, Vogelsang A, Knott A, Blatt T, Weise JM, Tiano L (2019) Modulation of Coenzyme Q10 content and oxidative status in human dermal fibroblasts using HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor over a broad range of concentrations. From mitohormesis to mitochondrial dysfunction and accelerated aging. Aging (Albany NY) 11(9):2565
Cakmak G, Zorlu F, Severcan M, Severcan F (2011) Screening of protective effect of amifostine on radiation-induced structural and functional variations in rat liver microsomal membranes by FT-IR spectroscopy. Anal Chem 83(7):2438–2444
Garip S, Bozoglu F, Severcan F (2007) Differentiation of mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl Spectrosc 61(2):186–192
Swegert CV, Dave KR, Katyare SS (1999) Effect of aluminium-induced Alzheimer like condition on oxidative energy metabolism in rat liver, brain and heart mitochondria. Mech Ageing Dev 112(1):27–42
Verstraeten SV, Oteiza PI (2000) Effects of Al3+ and related metals on membrane phase state and hydration: correlation with lipid oxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 375(2):340–346
Verstraeten SV, Oteiza PI (2002) Al3+-mediated changes in membrane physical properties participate in the inhibition of polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis. Arch Biochem Biophys 408(2):263–271
Mulder C, Wahlund LO, Teerlink T, Blomberg M, Veerhuis R, Van Kamp GJ et al (2003) Decreased lysophosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylcholine ratio in cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 110(8):949–955
Zamir O, Charlton MP (2006) Cholesterol and synaptic transmitter release at crayfish neuromuscular junctions. J Physiol 571(1):83–99
Ugalde CL, Finkelstein DI, Lawson VA, Hill AF (2016) Pathogenic mechanisms of prion protein, amyloid-β and α-synuclein misfolding: the prion concept and neurotoxicity of protein oligomers. J Neurochem 139(2):162–180
Smith JV, Luo Y (2004) Studies on molecular mechanisms of Ginkgo biloba extract. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(4):465–472
Toyran N, Zorlu F, Dönmez G, Öğe K, Severcan F (2004) Chronic hypoperfusion alters the content and structure of proteins and lipids of rat brain homogenates: a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study. Eur Biophys J 33(6):549–554
Diaz M, Fabelo N, Martín V, Ferrer I, Gomez T, Marin R (2015) Biophysical alterations in lipid rafts from human cerebral cortex associate with increased BACE1/AβPP interaction in early stages of Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimer's Dis 43(4):1185–1198
Marin R, Fabelo N, Martín V, Garcia-Esparcia P, Ferrer I, Quinto-Alemany D, Díaz M (2017) Anomalies occurring in lipid profiles and protein distribution in frontal cortex lipid rafts in dementia with Lewy bodies disclose neurochemical traits partially shared by Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Neurobiol Aging 49:52–59
Piccinini M, Scandroglio F, Prioni S, Buccinnà B, Loberto N, Aureli M et al (2010) Deregulated sphingolipid metabolism and membrane organization in neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurobiol 41(2–3):314–340
Derenne A, Vandersleyen O, Goormaghtigh E (2014) Lipid quantification method using FTIR spectroscopy applied on cancer cell extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1841(8):1200–1209
Ribes D, Colomina MT, Vicens P, Domingo JL (2010) Impaired spatial learning and unaltered neurogenesis in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease after oral aluminum exposure. Curr Alzheimer Res 7(5):401–408
Kaur A, Joshi K, Minz RW, Gill KD (2006) Neurofilament phosphorylation and disruption: a possible mechanism of chronic aluminium toxicity in Wistar rats. Toxicology 219(1–3):1–10
Hu H, Yang YJ, Li XP, Chen GH (2005) Effect of aluminum chloride on motor activity and species-typical behaviors in mice. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi 23(2):132–135
Abd-Elhady RM, Elsheikh AM, Khalifa AE (2013) Anti-amnestic properties of Ginkgo biloba extract on impaired memory function induced by aluminum in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 31(7):598–607
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Prof. Bimla Nehru for her invaluable advice and support in the preparation of this work.
Funding
The study was carried out by the funds received by University grants commission-Basic Scientific research (UGC-BSR) to Ms Sonia Verma and DST-PURSE 2017–18, New Delhi to Department of Biophysics, Panjab University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sonia Verma has carried out all the research work presented in this article. She has analysed all the results. She has written and edited the scientific article. All the coauthors has helped the author with their valuable suggestions in the research work and writing the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All the protocols performed were approved by Animal Ethical Committee (IAEC) of Panjab University, Chandigarh, India with approval no. PU/45/99/CPCSEA/IAEC/2018/153. Every effort was made to minimize the number of animals and the distress caused throughout the experiment.
Informed Consent
All authors have agreed to submit the article in its current form.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Ranawat, P. & Nehru, B. Studies on the Neuromodulatory Effects of Ginkgo biloba on Alterations in Lipid Composition and Membrane Integrity of Rat Brain Following Aluminium Neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res 45, 2143–2160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03075-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-020-03075-2