Abstract
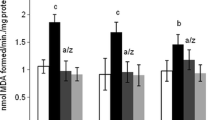
Alumina nanoparticles (ALNPs) are widely used causing neurobehavioral impairment in intoxicated animals and humans. Sesamol (SML) emerged as a natural phytochemical with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, no study has directly tested the potential of SML to protect against AlNP-induced detrimental effects on the brain. AlNPs (100 mg/kg) were orally administered to rats by gavage with or without oral sesamol (100 mg/kg) for 28 days. In AlNP-intoxicated group, the brain AChE activity was elevated. The concentrations of MDA and 8-OHdG were increased suggesting lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage. GSH depletion with inhibited activities of CAT and SOD were demonstrated. Serum levels of IL-1β and IL-6 were elevated. The expressions of GST, TNF-α, and caspase-3 genes in the brain were upregulated. Histopathologically, AlNPs induced hemorrhages, edema, neuronal necrosis, and/or apoptosis in medulla oblongata. The cerebellum showed loss of Purkinje cells, and the cerebrum showed perivascular edema, neuronal degeneration, necrosis, and neuronal apoptosis. However, concomitant administration of SML with AlNPs significantly ameliorated the toxic effects on the brain, reflecting antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects of SML. Considering these results, sesamol could be a promising phytochemical with neuroprotective activity against AlNP-induced neurotoxicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable
References
Abdel-Daim MM, Eissa IAM, Abdeen A, Abdel-Latif HMR, Ismail M, Dawood MAO, Hassan AM (2019) Lycopene and resveratrol ameliorate zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced oxidative stress in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 69:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.03.016
Aboelwafa HR, El-Kott AF, Abd-Ella EM, Yousef HN (2020) The possible neuroprotective effect of silymarin against aluminum chloride-prompted Alzheimer's-like disease in rats. Brain Sci 10:628. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10090628
Abou-Zeid SM, AbuBakr HO, Mohamed MA, El-Bahrawy A (2018) Ameliorative effect of pumpkin seed oil against emamectin induced toxicity in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 98:242–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.040
Abou-Zeid SM, Tahoun EA, AbuBakr HO (2021) Ameliorative effects of jojoba oil on fipronil-induced hepatorenal- and neuro-toxicity: the antioxidant status and apoptotic markers expression in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12083-2
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879
Arslanbaş E, COŞAR Z (2019) Toxic effects of cutaneous and oral exposure to aluminum and magnesium nanoparticles on brain tissue in rats. Ankara Üniversitesi Veteriner Fakültesi Dergisi. https://doi.org/10.33988/auvfd.569990
Arya A, Chahal R, Rao R, Rahman MH, Kaushik D, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Khalifa SMA, El-Seedi HR, Kamel M, Albadrani GM, Abdel-Daim MM, Mittal V (2021) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential of various sesquiterpene analogues for Alzheimer's disease therapy. Biomolecules 11:350. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030350
Auti ST, Kulkarni YA (2019) Neuroprotective effect of cardamom oil against aluminum induced neurotoxicity in rats. Front Neurol 10:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00399
Beutler E, Duron OBM, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bhattacharya T, Maishu SP, Akter R, Rahman MH, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Bin-Jumah M, Kamel M, Abdel-Latif MA, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) A review on natural sources derived protein nanoparticles as anticancer agents. Curr Top Med Chem 21. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026621666210412151700
Casetta I, Govoni V, Granieri E (2005) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Pharm Des 11:2033–2052. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612054065729
Chen L, Yokel RA, Hennig B, Toborek M (2008) Manufactured aluminum oxide nanoparticles decrease expression of tight junction proteins in brain vasculature. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 4:286–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-008-9131-5
Chopra K, Tiwari V, Arora V, Kuhad A (2010) Sesamol suppresses neuro-inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. J Pain 10:950–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2010.01.006
Chu PY, Chien SP, Hsu DZ, Liu MY (2010) Protective effect of sesamol on the pulmonary inflammatory response and lung injury in endotoxemic rats. Food Chem Toxicol 48:1821–1826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2010.04.014
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Zaineldin AI, Doan H, Moustafa E, Abdel Daim M, Esteban M, Hassaan MS (2019a) Dietary supplementation of selenium nanoparticles modulated systemic and mucosal immune status and stress resistance of red sea bream (Pagrus major). Fish Physiol Biochem 45:219–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-018-0556-3
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Zaineldin AI, Van Doan H, Ahmed HA, Elsabagh M, Abdel-Daim MM (2019b) An evaluation of dietary selenium nanoparticles for red sea bream (Pagrus major) aquaculture: growth, tissue bioaccumulation, and antioxidative responses. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:30876–30884. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06223-6
De A, Ghosh S, Chakrabarti M, Ghosh I, Banerjee R, Mukherjee A (2020) Effect of low-dose exposure of aluminium oxide nanoparticles in Swiss albino mice: Histopathological changes and oxidative damage. Toxicol Ind Health 36:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233720936828
Dey S, Bakthavatchalu V, Tseng MT, Wu P, Florence RL, Grulke EA, Yokel RA, Dhar SK, Yang HS, Chen Y, St Clair DK (2008) Interactions between SIRT1 and AP-1 reveal a mechanistic insight into the growth promoting properties of alumina (Al2O3) nanoparticles in mouse skin epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis 29:1920–1929. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgn175
Dong L, Tang S, Deng F, Gong Y, Zhao K, Zhou J, Liang D, Fang J, Hecker M, Giesy JP, Bai X, Zhang H (2019) Shape-dependent toxicity of alumina nanoparticles in rat astrocytes. Sci Total Environ 690:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.532
El-Sayed A, Kamel M (2020) Advances in nanomedical applications: diagnostic, therapeutic, immunization, and vaccine production. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:19200–19213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06459-2
El-Seedi HR, El-Shabasy RM, Khalifa SAM, Saeed A, Shah A, Shah R, Iftikhar FJ, Abdel-Daim MM, Omri A, Hajrahand NH, Sabir JSM, Zou X, Halabi MF, Sarhan W, Guo W (2019) Metal nanoparticles fabricated by green chemistry using natural extracts: biosynthesis, mechanisms, and applications. RSC Adv 9:24539–24559. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra02225b
Emmett SR, Greenfield SA (2004) A peptide derived from the C-terminal region of acetylcholinesterase modulates extracellular concentrations of acetylcholinesterase in the rat substantia nigra. Neurosci Lett 358:210–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2003.12.078
Farag MR, Mahmoud HK, El-Sayed SAA, Ahmed SYA, Alagawany M, Abou-Zeid SM (2021) Neurobehavioral, physiological and inflammatory impairments in response to bifenthrin intoxication in Oreochromis niloticus fish: Role of dietary supplementation with Petroselinum crispum essential oil. Aquat Toxicol 231:105715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105715
Gao XJ, Xie GN, Liu L, Fu ZJ, Zhang ZW, Teng LZ (2017) Sesamol attenuates oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation in focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med 14:841–847. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4550
Gibson-Corley KN, Olivier AK, Meyerholz DK (2013) Principles for valid histopathologic scoring in research. Vet Pathol 50:1007–1015
Guo JD, Zhao X, Li Y, Li GR, Liu XL (2018) Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease (Review). Int J Mol Med 41:1817–1825. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3406
Hassanzadeh P, Arbabi E, Rostami F (2014) The ameliorative effects of sesamol against seizures, cognitive impairment and oxidative stress in the experimental model of epilepsy. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17:100–107
Hemalatha G, Pugalendi KV, Saravanan R (2013) Modulatory effect of sesamol on DOCA-salt-induced oxidative stress in uninephrectomized hypertensive rats. Mol Cell Biochem 379:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1647-1
Hsin YH, Chen CF, Huang S, Shih TS, Lai PS, Chueh PJ (2008) The apoptotic effect of nanosilver is mediated by a ROS- and JNK-dependent mechanism involving the mitochondrial pathway in NIH3T3 cells. Toxicol Lett 179:130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.04.015
Jan KC, Ho CT, Hwang LS (2008) Bioavailability and tissue distribution of sesamol in rat. J Agric Food Chem 56:7032–7037. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf8012647
Ji JW, Zhang QL, Bai R, Gao FP, Ge CC, Wang ZW, Chen CY, Zhang C, Niu Q, Lao Z, Sheng DW, Bing ZY, Zhi Z (2011) Changes of brain oxidative stress induced by nano-alumina in ICR mice. 29:434–436
Jo E, Seo GB, Kim H, Choi K, Kwon JT, Kim P, Eom I (2016) Toxic effects of alumina nanoparticles in rat cerebrums and kidneys. Journal of Environmental Health Sciences 42:27–33. https://doi.org/10.5668/JEHS.2016.42.1.27
Kabir MT, Rahman MH, Akter R, Behl T, Kaushik D, Mittal V, Pandey P, Akhtar MF, Saleem A, Albadrani GM, Kamel M, Khalifa SAM, El-Seedi HR, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) Potential role of curcumin and its nanoformulations to treat various types of cancers. Biomolecules 11:392. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11030392
Kandeil MA, Mohammed ET, Hashem KS, Aleya L, Abdel-Daim MM (2020) Moringa seed extract alleviates titanium oxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs)-induced cerebral oxidative damage, and increases cerebral mitochondrial viability. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:19169–19184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05514-2
Kanimozhi P, Prasad NR (2009) Antioxidant potential of sesamol and its role on radiation-induced DNA damage in whole-body irradiated Swiss albino mice. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 28:192–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2009.04.003
Krause B, Kriegel F, Rosenkranz D, Dreiack N, Tentschert J, Jungnickel H, Jalili P, Fessard V, Laux P, Luch A (2020) Aluminum and aluminum oxide nanomaterials uptake after oral exposure - a comparative study. Sci Rep 10:2698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59710-z
Kuhad A, Chopra K (2008) Effect of sesamol on diabetes-associated cognitive decline in rats. Exp Brain Res 185:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1166-y
Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A (2010) Protective effect of sesamol against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced cognitive dysfunction and altered glutathione redox balance in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:577–582. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2010.00537.x
Kumar A, Choudhary S, Adhikari JS, Chaudhury NK (2018) Sesamol ameliorates radiation induced DNA damage in hematopoietic system of whole body γ-irradiated mice. Environ Mol Mutagen 59:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.22118
Li XB, Zheng H, Zhang ZR, Li M, Huang ZY, Schluesener HJ, Li YY, Xu SQ (2009) Glia activation induced by peripheral administration of aluminum oxide nanoparticles in rat brains. Nanomedicine 5:473–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2009.01.013
Li H, Huang T, Wang Y, Pan B, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Niu Q (2020) Toxicity of alumina nanoparticles in the immune system of mice. Nanomedicine (London) 15:927–946. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm-2020-0009
Liu Z, Chen Y, Qiao Q, Sun Y, Liu Q, Ren B, Liu X (2017) Sesamol supplementation prevents systemic inflammation-induced memory impairment and amyloidogenesis via inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB. Mol Nutr Food Res 61:5,1600734. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201600734
Liu H, Zhang W, Fang Y, Yang H, Tian L, Li K, Lai W, Bian L, Lin B, Liu X, Xi Z (2020a) Neurotoxicity of aluminum oxide nanoparticles and their mechanistic role in dopaminergic neuron injury involving p53-related pathways. J Hazard Mater 392:122312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122312
Liu L, Liu Y, Zhao J, Xing X, Zhang C, Meng H (2020b) Neuroprotective effects of D-(-)-quinic acid on aluminum chloride-induced dementia in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 11:5602597. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5602597
Livak KJ, Schmittgen HD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Majdalawieh AF, Mansour ZR (2019) Sesamol, a major lignan in sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum): anti-cancer properties and mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 855:75–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.05.008
Manke A, Wang L, Rojanasakul Y (2013) Mechanisms of nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress and toxicity. Biomed Res Int 2013:942916. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/942916
Mishra K, Srivastava PS, Chaudhury NK (2011) Sesamol as a potential radioprotective agent: in vitro studies. Radiat Res 176:613–623. https://doi.org/10.1667/rr2661.1
Misra S, Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Chopra K (2011) Modulation of nitrergic pathway by sesamol prevents cognitive deficits and associated biochemical alterations in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin administered rats. Eur J Pharmacol 659:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.03.026
Mohammed ET, Safwat GM (2013) Assessment of the ameliorative role of selenium nanoparticles on the oxidative stress of acetaminophen in some tissues of male albino rats. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences 2:80–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjbas.2013.01.003
Mohammed ET, Safwat GM (2020) grape seed proanthocyanidin extract mitigates titanium dioxide nanoparticle (TiO2-NPs)-induced hepatotoxicity through TLR-4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 196:579–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01955-5
Mohammed ET, Hashem KS, Abdelazem AZ, Foda FAMA (2020) Prospective protective effect of ellagic acid as a SIRT1 activator in iron oxide nanoparticle-induced renal damage in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 198:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02034-w
Morsy GM, Abou El-Ala KS, Ali AA (2016) Studies on fate and toxicity of nanoalumina in male albino rats: oxidative stress in the brain, liver and kidney. Toxicol Ind Health 32:200–214. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713498462
Mrad I, Sakly M, Amara S (2017) Aluminum oxide nanoparticles induced cognitive deficits and oxidative stress in frontal cortex and cerebellum of rat. Adv J Toxicol Curr Res 1:007–014
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80218-3
Nogueira D, Arl M, Köerich J, Zitta C, Ouriques L, Vicentini D, Matias W (2019) Comparison of cytotoxicity of α-Al2O3 and η-Al2O3 nanoparticles toward neuronal and bronchial cells. Toxicol in Vitro 61:104596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104596
Ohkawa H, Ohishi W, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Prabhakar PV, Reddy UA, Singh SP, Balasubramanyam A, Rahman MF, Indu Kumari S, Agawane SB, Murty US, Grover P, Mahboob M (2012) Oxidative stress induced by aluminum oxide nanomaterials after acute oral treatment in Wistar rats. J Appl Toxicol 32:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1775
Prasad NR, Menon VP, Vasudev V, Pugalendi KV (2005) Radioprotective effect of sesamol on gamma-radiation induced DNA damage, lipid peroxidation and antioxidants levels in cultured human lymphocytes. Toxicology. 209:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2004.12.009
Ren B, Yuan T, Diao Z, Zhang C, Liu Z, Xuebo L (2018) Protective effects of sesamol on systemic oxidative stress-induced cognitive impairments via regulating Nrf2/Keap1 pathway. Food Funct 9. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8FO01436A
Ren B, Yuan T, Zhang X, Wang L, Pan J, Liu Y, Zhao B, Zhao W, Liu Z, Liu X (2020) Protective effects of sesamol on systemic inflammation and cognitive impairment in aging mice. J Agric Food Chem 68:3099–3111. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07598
Ruankham W, Suwanjang W, Wongchitrat P, Prachayasittikul V, Prachayasittikul S, Phopin K (2021) Sesamin and sesamol attenuate H2O2-induced oxidative stress on human neuronal cells via the SIRT1-SIRT3-FOXO3a signaling pathway. Nutr Neurosci 24:90–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/1028415X.2019.1596613
Sachdeva AK, Misra S, Pal Kaur I, Chopra K (2015) Neuroprotective potential of sesamol and its loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in ICV-STZ-induced cognitive deficits: behavioral and biochemical evidence. Eur J Pharmacol 15(747):132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.014
Samak DH, El-Sayed YS, Shaheen HM, El-Far AH, Onoda A, Abdel-Daim MM, Umezawa M (2018) In-ovo exposed carbon black nanoparticles altered mRNA gene transcripts of antioxidants, proinflammatory and apoptotic pathways in the brain of chicken embryos. Chem Biol Interact 295:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.031
Sengul AB, Asmatulu E (2020) Toxicity of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1659–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01033-6
Serteser M, Ozben T, Gumuslu S, Balkan S, Balkan E (2002) Lipid peroxidation in rat brain during focal cerebral ischemia: prevention of malondialdehyde and lipid conjugated diene production by a novel antiepileptic, lamotrigine. Neurotoxicol 23:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0161-813x(02)00018-9
Shah SA, Yoon GH, Ahmad A, Ullah F, Ul Amin F, Kim MO (2015) Nanoscale-alumina induces oxidative stress and accelerates amyloid beta (Aβ) production in ICR female mice. Nanoscale 7:15225–15237. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr03598h
Sonia Angeline M, Sarkar A, Anand K, Ambasta RK, Kumar P (2013) Sesamol and naringenin reverse the effect of rotenone-induced PD rat model. Neuroscience 254:379–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.029
VanGilder RL, Kelly KA, Chua MD, Ptachcinski RL, Huber JD (2009) Administration of sesamol improved blood-brain barrier function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Brain Res 197:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-1866-6
Whyte KA, Greenfield SA (2003) Effects of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase on cell survival, neurite outgrowth, and voltage-dependent calcium currents of embryonic ventral mesencephalic neurons. Exp Neurol 184:496–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-4886(03)00386-8
Win-Shwe TT, Fujimaki H (2011) Nanoparticles and neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 12:6267–6280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12096267
Wu XL, Liou CJ, Li ZY, Lai XY, Fang LW, Huang WC (2015) Sesamol suppresses the inflammatory response by inhibiting NF-κB/MAPK activation and upregulating AMP kinase signaling in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Inflamm Res 64:577–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0836-7
Xiong S, Mu T, Wang G, Jiang X (2014) Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mammals. Protein Cell 5:737–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-014-0089-1
Yun J, Yang H, Li X, Sun H, Xu J, Meng Q, Wu S, Zhang X, Yang X, Li B, Chen R (2020) Up-regulation of miR-297 mediates aluminum oxide nanoparticle-induced lung inflammation through activation of Notch pathway. Environ Pollut 259:113839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113839
Zahin N, Anwar R, Tewari D, Kabir MT, Sajid A, Mathew B, Uddin MS, Aleya L, Abdel-Daim MM (2020) Nanoparticles and its biomedical applications in health and diseases: special focus on drug delivery. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:19151–19168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05211-0
Zatta P, Zambenedetti P, Bruna V, Filippi B (1994) Activation of acetylcholinesterase by aluminium(III): the relevance of the metal species. Neuroreport 5:1777–1780. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-199409080-00023
Zhang QL, Li MQ, Ji JW, Gao FP, Bai R, Chen CY, Wang ZW, Zhang C, Niu Q (2011) In vivo toxicity of nano-alumina on mice neurobehavioral profiles and the potential mechanisms. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24(1 Suppl):23S–29S
Zhang Q, Wang H, Ge C, Duncan J, He K, Adeosun SO, Xi H, Peng H, Niu Q (2017) Alumina at 50 and 13 nm nanoparticle sizes have potential genotoxicity. J Appl Toxicol 37:1053–1064. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3456
Zhang H, Wang P, Yu H, Yu K, Cao Z, Xu F, Yang X, Song M, Li Y (2018) Aluminum trichloride-induced hippocampal inflammatory lesions are associated with IL-1β-activated IL-1 signaling pathway in developing rats. Chemosphere 203:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.162
Zhang H, Jiao W, Cui H, Sun Q, Fan H (2021a) Combined exposure of alumina nanoparticles and chronic stress exacerbates hippocampal neuronal ferroptosis via activating IFN-γ/ASK1/JNK signaling pathway in rats. J Hazard Mater 411:125179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125179
Zhang P, Wang Y, Wang H, Cao J (2021b) Sesamol alleviates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits via inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in rats. Neuroreport 32:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000001564
Acknowledgements
We thank consult of Central Labs in both Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Sadat City, and Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, as we had bench space to work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shimaa Abou-Zeid: conceptualization, investigation, data analysis, writing original draft. Basma Elkhadrawey: methodology. Anis Anis: histopathological examination, writing original draft. Huda AbuBakr: gene expression study, writing original draft. Badr El-Bialy: methodology and revising the manuscript. Hesham Elsabbagh: conceived the idea and managed the study. Nermeen El-Borai: conceptualization, investigation, data analysis, writing original draft. All authors have contributed to writing this article, editing, and have critically read and revised the manuscript, and approved its submission for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval and consent to participate this study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) (Approval number: VUSC-007-1-20), Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Sadat City, Egypt.
Consent for publication
All the authors have given the consent to publish the paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou-Zeid, S., Elkhadrawey, B., Anis, A. et al. Neuroprotective effect of sesamol against aluminum nanoparticle-induced toxicity in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 53767–53780 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14587-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14587-x