Abstract
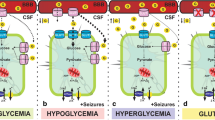
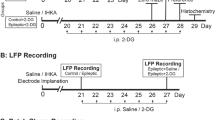
Epilepsy is a disorder of the brain characterized by an enduring predisposition to generate epileptic seizures. The glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2-DG) has been reported to exert antiepileptic effects by upregulating KATP subunits (kir6.1 and kir6.2). We evaluated whether 2-DG exhibits anti-seizure effect by mediating the netrin-G1-KATP signaling pathway in epilepsy. In a mouse epilepsy model induced by lithium chloride-pilocarpine, 2-DG intervention increased the mRNA and protein expression levels of kir6.1 and kir6.2, and these increases were significantly reversed after knocking down netrin-G1 expression. Similarly, in cultured neurons with a magnesium-free medium, we found that the frequency of spontaneous postsynaptic potentials (SP) was increased, and in the meanwhile, expression levels of kir6.1 and kir6.2 were increased after pretreatment with 2DG. These effects were remarkably reversed after knocking down netrin-G1. Thus, our findings show that 2DG exhibits anti-seizure effects through the netrin-G1-KATP signaling pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, Bogacz A, Cross JH, Elger CE et al (2014) ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. EPILEPSIA 55:475–482
Tanywe A, Matchawe C, Fernandez R (2016) The experiences of people living with epilepsy in developing countries: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep 14:136–192
Nadler JV (2003) The recurrent mossy fiber pathway of the epileptic brain. Neurochem Res 28:1649–1658
Pan Y, Liu G, Fang M, Shen L, Wang L, Han Y et al (2010) Abnormal expression of netrin-G2 in temporal lobe epilepsy neurons in humans and a rat model. Exp Neurol 224:340–346
Yin Y, Miner JH, Sanes JR (2002) Laminets: laminin- and netrin-related genes expressed in distinct neuronal subsets. Mol Cell Neurosci 19:344–358
Moore SW, Tessier-Lavigne M, Kennedy TE (2007) Netrins and their receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol 621:17–31
Meerabux JM, Ohba H, Fukasawa M, Suto Y, Aoki-Suzuki M, Nakashiba T et al (2005) Human netrin-G1 isoforms show evidence of differential expression. GENOMICS 86:112–116
Nakashiba T, Ikeda T, Nishimura S, Tashiro K, Honjo T, Culotti JG et al (2000) Netrin-G1: a novel glycosyl phosphatidylinositol-linked mammalian netrin that is functionally divergent from classical netrins. J Neurosci 20:6540–6550
Lin JC, Ho WH, Gurney A, Rosenthal A (2003) The netrin-G1 ligand NGL-1 promotes the outgrowth of thalamocortical axons. Nat Neurosci 6:1270–1276
Kim S, Burette A, Chung HS, Kwon SK, Woo J, Lee HW et al (2006) NGL family PSD-95-interacting adhesion molecules regulate excitatory synapse formation. Nat Neurosci 9:1294–1301
Aoki-Suzuki M, Yamada K, Meerabux J, Iwayama-Shigeno Y, Ohba H, Iwamoto K et al (2005) A family-based association study and gene expression analyses of netrin-G1 and -G2 genes in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 57:382–393
Medina-Ceja L, Pardo-Pena K, Ventura-Mejia C (2014) Evaluation of behavioral parameters and mortality in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy induced by intracerebroventricular pilocarpine administration. Neuroreport. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNR.0000000000000207
Woo J, Kwon SK, Kim E (2009) The NGL family of leucine-rich repeat-containing synaptic adhesion molecules. Mol Cell Neurosci 42:1–10
Ohtsuki T, Horiuchi Y, Koga M, Ishiguro H, Inada T, Iwata N et al (2008) Association of polymorphisms in the haplotype block spanning the alternatively spliced exons of the NTNG1 gene at 1p13.3 with schizophrenia in Japanese populations. Neurosci Lett 435:194–197
Eastwood SL, Harrison PJ (2008) Decreased mRNA expression of netrin-G1 and netrin-G2 in the temporal lobe in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol 33:933–945
Zakharyan R, Boyajyan A, Arakelyan A, Gevorgyan A, Mrazek F, Petrek M (2011) Functional variants of the genes involved in neurodevelopment and susceptibility to schizophrenia in an Armenian population. Hum Immunol 72:746–748
Zhu Y, Yang H, Bi Y, Zhang Y, Zhen C, Xie S et al (2011) Positive association between NTNG1 and schizophrenia in Chinese Han population. J Genet 90:499–502
Stepanyan A, Zakharyan R, Boyajyan A (2013) The netrin G1 gene rs628117 polymorphism is associated with ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett 549:74–77
Foster MN, Coetzee WA (2016) KATP channels in the cardiovascular system. Physiol Rev 96:177–252
Zhou M, Tanaka O, Suzuki M, Sekiguchi M, Takata K, Kawahara K et al (2002) Localization of pore-forming subunit of the ATP-sensitive K(+)-channel, Kir6.2, in rat brain neurons and glial cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 101:23–32
Wickenden AD (2002) Potassium channels as anti-epileptic drug targets. Neuropharmacology 43:1055–1060
Yang H, Guo R, Wu J, Peng Y, Xie D, Zheng W et al (2013) The antiepileptic effect of the glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-D-glucose is mediated by upregulation of K(ATP) channel subunits Kir6.1 and Kir6.2. Neurochem Res 38:677–685
McIntyre DC, Poulter MO, Gilby K (2002) Kindling: some old and some new. Epilepsy Res 50:79–92
Raedt R, Van Dycke A, Van Melkebeke D, De Smedt T, Claeys P, Wyckhuys T et al (2009) Seizures in the intrahippocampal kainic acid epilepsy model: characterization using long-term video-EEG monitoring in the rat. Acta Neurol Scand 119:293–303
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Rutecki PA, Lebeda FJ, Johnston D (1985) Epileptiform activity induced by changes in extracellular potassium in hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 54:1363–1374
Traynelis SF, Dingledine R (1988) Potassium-induced spontaneous electrographic seizures in the rat hippocampal slice. J Neurophysiol 59:259–276
Traynelis SF, Dingledine R, McNamara JO, Butler L, Rigsbee L (1989) Effect of kindling on potassium-induced electrographic seizures in vitro. Neurosci Lett 105:326–332
Tancredi V, Hwa GG, Zona C, Brancati A, Avoli M (1990) Low magnesium epileptogenesis in the rat hippocampal slice: electrophysiological and pharmacological features. Brain Res 511:280–290
Sombati S, Delorenzo RJ (1995) Recurrent spontaneous seizure activity in hippocampal neuronal networks in culture. J Neurophysiol 73:1706–1711
Clark S, Wilson WA (1999) Mechanisms of epileptogenesis. Adv Neurol 79:607–630
Gasior M, Yankura J, Hartman AL, French A, Rogawski MA (2010) Anticonvulsant and proconvulsant actions of 2-deoxy-d-glucose. Epilepsia 51:1385–1394
Matsukawa H, Akiyoshi-Nishimura S, Zhang Q, Lujan R, Yamaguchi K, Goto H et al (2014) Netrin-G/NGL complexes encode functional synaptic diversification. J Neurosci 34:15779–15792
Jiang K, Shui Q, Xia Z, Yu Z (2004) Changes in the gene and protein expression of K(ATP) channel subunits in the hippocampus of rats subjected to picrotoxin-induced kindling. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 128:83–89
Jiang KW, Gao F, Shui QX, Yu ZS, Xia ZZ (2004) Effect of diazoxide on regulation of vesicular and plasma membrane GABA transporter genes and proteins in hippocampus of rats subjected to picrotoxin-induced kindling. Neurosci Res 50:319–329
Gimenez-Cassina A, Martinez-Francois JR, Fisher JK, Szlyk B, Polak K, Wiwczar J et al (2012) BAD-dependent regulation of fuel metabolism and K(ATP) channel activity confers resistance to epileptic seizures. Neuron 74:719–730
He XP, Pan E, Sciarretta C, Minichiello L, McNamara JO (2010) Disruption of TrkB-mediated phospholipase Cgamma signaling inhibits limbic epileptogenesis. J Neurosci 30:6188–6196
Aziz Q, Thomas AM, Khambra T, Tinker A (2012) Regulation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel subunit, Kir6.2, by a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 287:6196–6207
Shi Y, Cui N, Shi W, Jiang C (2008) A short motif in Kir6.1 consisting of four phosphorylation repeats underlies the vascular KATP channel inhibition by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 283:2488–2494
Park WS, Ko EA, Han J, Kim N, Earm YE (2005) Endothelin-1 acts via protein kinase C to block KATP channels in rabbit coronary and pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 45:99–108
Wierda KD, Toonen RF, de Wit H, Brussaard AB, Verhage M (2007) Interdependence of PKC-dependent and PKC-independent pathways for presynaptic plasticity. Neuron 54:275–290
Forte N, Medrihan L, Cappetti B, Baldelli P, Benfenati F. 2-Deoxy-d-glucose enhances tonic inhibition through the neurosteroid-mediated activation of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. Epilepsia 2016
Garriga-Canut M, Schoenike B, Qazi R, Bergendahl K, Daley TJ, Pfender RM et al (2006) 2-Deoxy-D-glucose reduces epilepsy progression by NRSF-CtBP-dependent metabolic regulation of chromatin structure. Nat Neurosci 9:1382–1387
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501128) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81671296). The Jiyizhupao of Third Xiangya Hospital (JY201520). Thanks to the Experimental Animal Center of the Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University for affording animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuming Long and Kai Zhuang were both the first author to this article. Heng Yang and Zhi Song were both the corresponding author to this article. Yuming Long and Kai Zhuang conducted all the experiments and drafed the main manuscript text. Zhonghai Ji, Yaru Han, Yanqing Fei and Wen Zheng made statistical analysis and prepared all the figures in this article. Heng Yang and Zhi Song designed the whole experiment procedure and supervised the research.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, Y., Zhuang, K., Ji, Z. et al. 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose Exhibits Anti-seizure Effects by Mediating the Netrin-G1-KATP Signaling Pathway in Epilepsy. Neurochem Res 44, 994–1004 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02734-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02734-3