Abstract
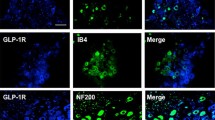
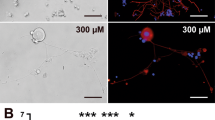
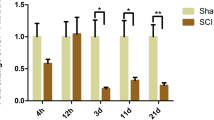
Upregulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokine tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) is involved in the development and progression of numerous neurological disorders. Recent reports have challenged the concept that TNF-α exhibits only deleterious effects of pro-inflammatory destruction, and have raised the awareness that it may play a beneficial role in neuronal growth and function in particular conditions, which prompts us to further investigate the role of this cytokine. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is a cytokine possessing powerful neuroprotective effects in promoting neuronal survival, neuronal differentiation, neurite elongation, and neurite regeneration. The association of IGF-1 with TNF-α and the biological effects, produced by interaction of IGF-1 and TNF-α, on neuronal outgrowth status of primary sensory neurons are still to be clarified. In the present study, using an in vitro model of primary cultured rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, we demonstrated that TNF-α challenge at different concentrations elicited diverse biological effects. Higher concentration of TNF-α (10 ng/mL) dampened neurite outgrowth, induced activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) expression, reduced growth-associated protein 43 (GAP-43) expression, and promoted GAP-43 and ATF3 coexpression, which could be reversed by IGF-1 treatment; while lower concentration of TNF-α (1 ng/mL) promoted neurite sprouting, decreased ATF3 expression, increased GAP-43 expression, and inhibited GAP-43 and ATF3 coexpression, which could be potentiated by IGF-1 supplement. Moreover, IGF-1 administration restored the activation of Akt and p70 S6 kinase (S6K) suppressed by higher concentration of TNF-α (10 ng/mL) challenge. In contrast, lower concentration of TNF-α (1 ng/mL) had no significant effect on Akt or S6K activation, and IGF-1 administration activated these two kinases. The effects of IGF-1 were abrogated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002. These data imply that IGF-1 counteracts the toxic effect of higher concentration of TNF-α, while potentiates the growth-promoting effect of lower concentration of TNF-α, with the node for TNF-α and IGF-1 interaction being the PI3K/Akt/S6K signaling pathway. This study is helpful for interpretation of the association of IGF-1 with TNF-α and the neurobiological effects elicited by interaction of IGF-1 and TNF-α in neurological disorders.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogawa N, Kawai H, Terashima T, Kojima H, Oka K, Chan L, Maegawa H (2014) Gene therapy for neuropathic pain by silencing of TNF-α expression with lentiviral vectors targeting the dorsal root ganglion in mice. PLoS One 9(3):e92073
Huang Y, Zang Y, Zhou L, Gui W, Liu X, Zhong Y (2014) The role of TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B pathway on the up-regulation of voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.7 in DRG neurons of rats with diabetic neuropathy. Neurochem Int 75:112–119
Zhang Q, Yu J, Wang J, Ding CP, Han SP, Zeng XY, Wang JY (2015) The Red nucleus TNF-α participates in the initiation and maintenance of neuropathic pain through different signaling pathways. Neurochem Res 40(7):1360–1371
Allison DJ, Thomas A, Beaudry K, Ditor DS (2016) Targeting inflammation as a treatment modality for neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury: a randomized clinical trial. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):152
Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR, Oliverio PJ, Sandberg G, Crayton H, Richert JR, Siegel JN (2001) Demyelination occurring during anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy for inflammatory arthritides. Arthritis Rheum 44(12):2862–2869
Shin IS, Baer AN, Kwon HJ, Papadopoulos EJ, Siegel JN (2006) Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes occurring with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist therapy. Arthritis Rheum 54(5):1429–1434
Fromont A, De Seze J, Fleury MC, Maillefert JF, Moreau T (2009) Inflammatory demyelinating events following treatment with anti-tumor necrosis factor. Cytokine 45(2):55–57
Cruz Fernández-Espartero M, Pérez-Zafrilla B, Naranjo A, Esteban C, Ortiz AM, Gómez-Reino JJ, Carmona L; BIOBADASER Study Group (2011) Demyelinating disease in patients treated with TNF antagonists in rheumatology: data from BIOBADASER, a pharmacovigilance database, and a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 41(3):524–533
Seror R, Richez C, Sordet C, Rist S, Gossec L, Direz G, Houvenagel E, Berthelot JM, Pagnoux C, Dernis E, Melac-Ducamp S, Bouvard B, Asquier C, Martin A, Puechal X, Mariette X; Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation Section of the SFR (2013) Pattern of demyelination occurring during anti-TNF-α therapy: a French national survey. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52(5):868–874
Kaltsonoudis E, Voulgari PV, Konitsiotis S, Drosos AA (2014) Demyelination and other neurological adverse events after anti-TNF therapy. Autoimmun Rev 13(1):54–58
Croci L, Barili V, Chia D, Massimino L, van Vugt R, Masserdotti G, Longhi R, Rotwein P, Consalez GG (2011) Local insulin-like growth factor I expression is essential for Purkinje neuron survival at birth. Cell Death Differ 18:48–59
Froehlich W, Bernstein JA, Hallmayer JF, Dolmetsch RE (2013) SHANK3 and IGF1 restore synaptic deficits in neurons from 22q13 deletion syndrome patients. Nature 503(7475):267–271
Lee W, Frank CW, Park J (2014) Directed axonal outgrowth using a propagating gradient of IGF-1. Adv Mater 26:4936–4940
Joshi Y, Sória MG, Quadrato G, Inak G, Zhou L, Hervera A, Rathore KI, Elnaggar M, Cucchiarini M, Marine JC, Puttagunta R, Di Giovanni S (2015) The MDM4/MDM2-p53-IGF1 axis controls axonal regeneration, sprouting and functional recovery after CNS injury. Brain 138:1843–1862
Mardinly AR, Spiegel I, Patrizi A, Centofante E, Bazinet JE, Tzeng CP, Mandel-Brehm C, Harmin DA, Adesnik H, Fagiolini M, Greenberg ME (2016) Sensory experience regulates cortical inhibition by inducing IGF1 in VIP neurons. Nature 531(7594):371–375
Kenchappa P, Yadav A, Singh G, Nandana S, Banerjee K (2004) Rescue of TNFalpha-inhibited neuronal cells by IGF-1 involves Akt and c-Jun N-terminal kinases. J Neurosci Res 76(4):466–474
Hunt D, Raivich G, Anderson PN (2012) Activating transcription factor 3 and the nervous system. Front Mol Neurosci 5:7
Tsujino H, Kondo E, Fukuoka T, Dai Y, Tokunaga A, Miki K, Yonenobu K, Ochi T, Noguchi K (2000) Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) induction by axotomy in sensory and motoneurons: a novel neuronal marker of nerve injury. Mol Cell Neurosci 15(2):170–182
Bráz JM, Basbaum AI (2010) Differential ATF3 expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons reveals the profile of primary afferents engaged by diverse noxious chemical stimuli. Pain 150(2):290–301
Teramoto K, Tsuboi Y, Shinoda M, Hitomi S, Abe K, Kaji K, Tamagawa T, Suzuki A, Noma N, Kobayashi M, Komiyama O, Urata K, Iwata K (2013) Changes in expression of growth-associated protein-43 in trigeminal ganglion neurons and of the jaw openingreflex following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats. Eur J Oral Sci 121:86–91
Ceber M, Sener U, Mihmanli A, Kilic U, Topcu B, Karakas M (2015) The relationship between changes in the expression of growth associated protein-43 and functional recovery of the injured inferior alveolar nerve following transection without repair in adult rats. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 43:1906–1913
Venters HD, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (2000) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces neuronal death by silencing survival signals generated by the type I insulin-like growth factor receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci 917:210–220
Gey M, Wanner R, Schilling C, Pedro MT, Sinske D, Knöll B. (2016) Atf3 mutant mice show reduced axon regeneration and impaired regeneration-associated gene induction after peripheral nerve injury. Open Biol 6(8):160091
Murata R, Ohtori S, Ochiai N, Takahashi N, Saisu T, Moriya H, Takahashi K, Wada Y (2006) Extracorporeal shockwaves induce the expression of ATF3 and GAP-43 in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Auton Neurosci 128(1–2):96–100
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3(9):745–756
Hong H, Kim BS, Im HI (2016) Pathophysiological role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders. Int Neurourol J 20(Suppl 1):S2–S7
Su F, Bai F, Zhang Z (2016) Inflammatory Cytokines and Alzheimer’s Disease: a review from the perspective of genetic polymorphisms. Neurosci Bull 32(5):469–480
Dexter DT, Jenner P (2013) Parkinson disease: from pathology to molecular disease mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 62:132–144
Zhang J, Su YM, Li D, Cui Y, Huang ZZ, Wei JY, Xue Z, Pang RP, Liu XG, Xin WJ (2014) TNF-α-mediated JNK activation in the dorsal root ganglion neurons contributes to Bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy. Brain Behav Immun 38:185–191
Saha RN, Ghosh A, Palencia CA, Fung YK, Dudek SM, Pahan K (2009) TNF-alpha preconditioning protects neurons via neuron-specific up-regulation of CREB-binding protein. J Immunol 183(3):2068–2078
Camara ML, Corrigan F, Jaehne EJ, Jawahar MC, Anscomb H, Koerner H, Baune BT (2013) TNF-α and its receptors modulate complex behaviours and neurotrophins in transgenic mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(12):3102–3114
Saleh A, Smith DR, Balakrishnan S, Dunn L, Martens C, Tweed CW, Fernyhough P (2011) Tumor necrosis factor-α elevates neurite outgrowth through an NF-κB-dependent pathway in cultured adult sensory neurons: diminished expression in diabetes may contribute to sensory neuropathy. Brain Res 1423:87–95
Kitiyanant N, Kitiyanant Y, Svendsen CN, Thangnipon W (2012) BDNF-, IGF-1- and GDNF-secreting human neural progenitor cells rescue amyloid β-induced toxicity in cultured rat septal neurons. Neurochem Res 37(1):143–152
Yamahara K, Yamamoto N, Nakagawa T, Ito J (2015) Insulin-like growth factor 1: a novel treatment for the protection or regeneration of cochlear hair cells. Hear Res 330(Pt A):2–9
Costales J, Kolevzon A (2016) The therapeutic potential of insulin-like growth factor-1 in central nervous system disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 63:207–222
Fontaine V, Mohand-Said S, Hanoteau N, Fuchs C, Pfizenmaier K, Eisel U (2002) Neurodegenerative and neuroprotective effects of tumor Necrosis factor (TNF) in retinal ischemia: opposite roles of TNF receptor 1 and TNF receptor 2. J Neurosci 22(7):RC216
Fischer R, Maier O, Siegemund M, Wajant H, Scheurich P, Pfizenmaier K (2011) A TNF receptor 2 selective agonist rescues human neurons from oxidative stress-induced cell death. PLoS One 6(11):e27621
Dong Y, Fischer R, Naudé PJ, Maier O, Nyakas C, Duffey M, Van der Zee EA, Dekens D, Douwenga W, Herrmann A, Guenzi E, Kontermann RE, Pfizenmaier K, Eisel UL (2016) Essential protective role of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 in neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(43):12304–12309
Leu B, Koch E, Schmidt JT (2010) GAP43 phosphorylation is critical for growth and branching of retinotectal arbors in zebrafish. Dev Neurobiol 70(13):897–911
Williams RR, Venkatesh I, Pearse DD, Udvadia AJ, Bunge MB (2015) MASH1/Ascl1a leads to GAP43 expression and axon regeneration in the adult CNS. PLoS One 10(3):e0118918
Hai T, Wolfgang CD, Marsee DK, Allen AE, Sivaprasad U (1999) ATF3 and stress responses. Gene Expr 7(4–6):321–335
Seijffers R, Allchorne AJ, Woolf CJ (2006) The transcription factor ATF-3 promotes neurite outgrowth. Mol Cell Neurosci 32(1–2):143–154
Wang L, Deng S, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Yang L, Guan Y, Jiang H, Li H (2012) Increased inflammation and brain injury after transient focal cerebral ischemia in activating transcription factor 3 knockout mice. Neuroscience 220:100–108
Seijffers R, Zhang J, Matthews JC, Chen A, Tamrazian E, Babaniyi O, Selig M, Hynynen M, Woolf CJ, Brown RH (2014) ATF3 expression improves motor function in the ALS mouse model by promoting motor neuron survival and retaining muscle innervation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(4):1622–1627
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81371929) and the National Science and Technology Innovation Project for College Students of China (201510422097).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Yue, Y., Ouyang, M. et al. The Effects of IGF-1 on TNF-α-Treated DRG Neurons by Modulating ATF3 and GAP-43 Expression via PI3K/Akt/S6K Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res 42, 1403–1421 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2192-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2192-1