Abstract
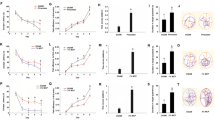
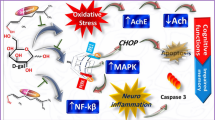
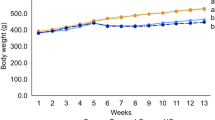
Cerebralcare granule® (CG) is a preparation of Traditional Chinese Medicine that widely used in China. It was approved by the China State Food and Drug Administration for treatment of headache and dizziness associated with cerebrovascular diseases. In the present study, we aimed to investigate whether CG had protective effect against d-galactose (gal)-induced memory impairment and to explore the mechanism of its action. d-gal was administered (100 mg/kg, subcutaneously) once daily for 8 weeks to induced memory deficit and neurotoxicity in the brain of aging mouse and CG (7.5, 15, and 30 g/kg) were simultaneously administered orally. The present study demonstrates that CG can alleviate aging in the mouse brain induced by d-gal through improving behavioral performance and reducing brain cell damage in the hippocampus. CG prevents aging mainly via suppression of oxidative stress response, such as decreasing NO and MDA levels, renewing activities of SOD, CAT, and GPx, as well as decreasing AChE activity in the brain of d-gal-treated mice. In addition, CG prevents aging through inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response and caspase-3-medicated neurodegeneration in the brain of d-gal treated mice. Taken together, these data clearly demonstrates that subcutaneous injection of d-gal produced memory deficit, meanwhile CG can protect neuron from d-gal insults and improve memory ability.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu JH, Mu XY, Zeng J, Xu CY, Liu J, Zhang MS, Li CP, Chen J, Li TY, Wang Y (2014) Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents cognitive impairment and hippocampus senescence in a rat model of d-galactose-induced aging. PLoS One 9:e101291
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Cheng W, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF, Ye Q, Fan SH, Shan Q, Wang YJ (2010) Chronic administration of troxerutin protects mouse brain against d-galactose-induced impairment of cholinergic system. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:157–164
Ali T, Badshah H, Kim TH, Kim MO (2015) Melatonin attenuates d-galactose-induced memory impairment, neuroinflmmation and neurodegeneration via RAGE/NF-K B/JNK signaling pathway in aging mouse model. J Pineal Res 58:71–85
Gao J, He H, Jiang W, Chang X, Zhu L, Luo F, Zhou R, Ma C, Yan T (2015) Salidroside ameliorates cognitive impairment in a d-galactose-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res 293:27–33
Lu J, Wu DM, Zheng YL, Hu B, Zhang ZF (2009) Purple sweet potato color alleviates d-galactose-induced brain aging in old mice by promoting survival of neurons via PI3 K pathway and inhibiting cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Brain Pathol 20:598–612
Sun K, Hu Q, Zhou CM, Xu XS, Wang F, Hu BH, Zhao XY, Chang X, Chen CH, Huang P, An LH, Liu YY, Fan JY, Wang CS, Yang L, Han JY (2010) Cerebralcare granule®, a Chinese herb compound preparation, improves cerebral microcirculatory disorder and hippocampal CA1 neuron injury in gerbils after ischemia–reperfusion. J Ethnopharmacol 130:398–406
Xu XS, Ma ZZ, Wang F, Hu BH, Wang CS, Liu YY, Zhao XR, An LH, Chang X, Liao FL, Fan JY, Niimi H, Han JY (2009) The antioxidant cerebralcare granule attenuates cerebral microcirculatory disturbance during ischemia-reperfusion injury. Shock 32:201–209
Xiong L, Zhang JJ, Sun D, Hui L (2011) Therapeutic benefit of Yangxue Qingnao granule on cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Chin J Integr Med 17:134–140
Qu Z, Zhang JZ, Gao WY, Chen H, Guo HM, Wang TT, Li HF, Liu CX (2014) Vasorelaxant effects of Cerebralcare granules are mediated by NO/cGMP pathway, potassium channel opening and calcium channel blockade in isolated rat thoracic aorta. J Ethnopharmacol 155:572–579
Li JJ, Zhu Q, Lu YP, Zhao P, Feng ZB, Qian ZM, Zhu L (2015) Ligustilide prevents cognitive impairment and attenuates neurotoxicity in d-galactose induced aging mice brain. Brain Res 1595:19–28
Hasanein P, Mahtaj AK (2015) Ameliorative effect of rosmarinic acid on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Neurosci Lett 585:23–27
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Li Q, Qu R, Ma SP (2009) Peoniflorin attenuates Abeta (1–42)-mediated neurotoxicity by regulating calcium homeostasis and ameliorating oxidative stress in hippocampus of rats. J Neurol Sci 280:71–78
Qu Z, Zhang JZ, Yang HG, Huo LQ, Gao J, Chen H, Gao WY (2016) Protective effect of tetrahydropalmatine against d-galactose induced memory impairment in rat. Physiol Behav 154:114–125
Li F, Gong QH, Wu Q, Lu YF, Shi JS (2010) Icariin isolated from epimedium brevicornum maxim attenuates learning and memory deficits induced by d-galactose in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96:301–305
Zhang PY, Peng CX, Zhang LH (2014) Berberine rescues d-galactose-induced synaptic/memory impairment by regulating the levels of arc. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 117:47–51
Qu Z, Zhang JZ, Gao WY, Chen H, Huang HH, Huo LQ, Li HF (2016) Antihypertensive and cardioprotective effects of cerebralcare granule® on spontaneously hypertensive rats from the perspective of the gaseous triumvirate NO–CO–H2S system. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 41:22–31
Zhao L, Gong N, Liu M, Pan XL, Sang SM, Sun XJ, Yu Z, Fang Q, Zhao N, Fei GQ, Jin LR, Zhong CJ, Xu TL (2014) Beneficial synergistic effects of microdose lithium with pyrroloquinoline quinone in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neurobiol Aging 35:2736–2745
Coban J, Betül-Kalaz E, Küçükgergin C, Aydın AF, Doğan-Ekici I, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Uysal M (2014) Blueberry treatment attenuates d-galactose-induced oxidative stress and tissue damage in rat liver. Geriatr Gerontol Int 14:490–497
Yoo DY, Kim W, Lee CH, Shin BN, Nam SM, Choi JH, Won MH, Yoon YS, Hwang IK (2012) Melatonin improves d-galactose-induced aging effects on behavior, neurogenesis, and lipid peroxidation in the mouse dentate gyrus via increasing pCREB expression. J Pineal Res 52:21–28
Çoban J, Doğan-Ekici I, Aydın AF, Betül-Kalaz E, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Uysal M (2015) Blueberry treatment decreased d-galactose-induced oxidative stress and brain damage in rats. Metab Brain Dis 30:793–802
Wang XY, Ma XH, Li W, Chu Y, Guo JH, Li SM, Wang JM, Zhang HC, Zhou SP, Zhu YH (2013) Simultaneous determination of five phenolic components and paeoniflorin in rat plasma by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry and pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Cerebralcare granule®. J Pharm Biomed Anal 86:82–91
Li XW, Tong L, Li YF, Sun GX, Yang DL, Sun H (2016) Simultaneous determination of seven alkaloids in rat plasma by UFLC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Cerebralcare granule. J Chromatogr B 1017:28–35
Cheng CY, Su SY, Tang NY, Ho TY, Chiang SY, Hsieh CL (2008) Ferulic acid provides neuroprotection against oxidative stress-related apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ICAM-1 mRNA expression in rats. Brain Res 1209:136–150
Lan Z, Chen LY, Fu Q, Ji WW, Wang SY, Liang ZH, Qu R, Kong LY, Ma SP (2013) Paeoniflorin attenuates amyloid-beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress and regulating the ngf-mediated signaling in rats. Brain Res 1498:9–19
Sul D, Kim HS, Lee D, Joo SS, Hwang KW, Park SY (2009) Protective effect of caffeic acid against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity by the inhibition of calcium influx and tau phosphorylation. Life Sci 84:257–262
Teresa I, Daniele DF, Giuseppe E, Alessandra D, Izzo AA (2006) The spice sage and its active ingredient rosmarinic acid protect PC12 cells from amyloid-beta peptide-induced neurotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1143–1149
Lu J, Wu DM, Hu B, Cheng W, Zheng YL, Zhang ZF, Ye Q, Fan SH, Shan Q, Wang YJ (2010) Chronic administration of troxerutin protects mouse brain against d-galactose-induced impairment of cholinergic system. Neurobiol Learn Mem 93:157–164
Yu YH, Bai FL, Wang WF, Liu YN, Yuan QY, Qu SS, Zhang T, Tian GY, Li SM, Li DH, Ren GP (2015) Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects mouse brain against d-galactose induced aging via suppression of oxidative stress response and advanced glycation end products formation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 133:122–131
Haider S, Liaquat L, Shahzad S, Sadir S, Madiha S, Batool Z, Tabassum S, Saleem S, Naqvi F, Perveen T (2015) A high dose of short term exogenous d-galactose administration in young male rats produces symptoms simulating the natural aging process. Life Sci 124:110–119
Reiter RJ, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Tan DX, Burkhardt S (2001) Free radical-mediated molecular damage. Ann N Y Acad Sci 939:200–215
Yu YH, Bai FL, Liu Y, Yang Y, Yuan Q, Zou D, Li S (2015) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF21) protects mouse liver against d-galactose-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via activating Nrf2 and PI3 K/Akt pathways. Mol Cell Biochem 403:287–299
Ullah F, Ali T, Ullah N, Kim MO (2015) Caffeine prevents d-galactose-induced cognitive deficits, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in the adult rat brain. Neurochem Int 90:114–124
Lei M, Hua XD, Xiao M, Ding J, Han QY, Hu G (2008) Impairments of astrocytes are involved in the d-galactose-induced brain aging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 369:1082–1087
Cho JY, Kim HS, Kim DH, Yan JJ, Suh HW, Song DK (2005) Inhibitory effects of long-term administration of ferulic acid on astrocyte activation induced by intracerebroventricular injection of beta-amyloid peptide (1-42) in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:901–907
Kumar A, Prakash A, Dogra S (2011) Centella asiatica attenuates d-galactose-induced cognitive impairment, oxidative and mitochondrial dysfunction in mice. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011:347569
Kumagai N, Chiba Y, Hosono M, Fujii M, Kawamura N, Keino H, Yoshikaw K, Ishii S, Saitoh Y, Satoh M, Shimad A, Hosokaw M (2007) Involvement of pro-inflammatory cytokines and microglia in an age-associated neurodegeneration model, the SAMP10 mouse. Brain Res 1185:75–85
Wang J, Lei H, Hou J, Liu JX (2015) Involvement of oxidative stress in SAMP10 mice with age-related neurodegeneration. Neurol Sci 36:743–750
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, China (Grant No. 2014M562675).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no conflict of interest in this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Z., Yang, H., Zhang, J. et al. Cerebralcare Granule®, a Chinese Herb Compound Preparation, Attenuates d-Galactose Induced Memory Impairment in Mice. Neurochem Res 41, 2199–2214 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1934-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1934-9