Abstract
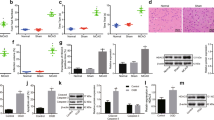
Inflammatory damage plays an important role in cerebral ischemic pathogenesis and may represent a target for treatment. Evodiamine (Evo) has been proved to elicit a variety of biological effects through its anti-inflammatory property in the treatment of infectious disease, Alzheimer’s disease and hypoxia-induced inflammatory response. Whether this protective effect applies to cerebral ischemic injury, we therefore investigated the potential neuroprotective role of Evo and the underlying mechanisms. Male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice were subjected to permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) and randomly divided into five groups: Sham (sham-operated + 1 % DMSO + 0.5 % tween80), pMCAO (pMCAO + 0.9 % saline), Vehicle (pMCAO + 1 % DMSO + 0.5 % tween80), Evo-L (Vehicle + Evo 50 mg/kg) and Evo-H (Vehicle + Evo 100 mg/kg) groups. Evo was administered intragastrically twice daily for 3 days, and once again 30 min before mouse brain ischemia was induced by pMCAO. Neurological deficit, brain water content and infarct size were measured at 24 h after stroke. The expression of pAkt, pGSK3β, NF-κB and claudin-5 in ischemic cerebral cortex was analyzed by western blot and qRT-PCR. Compared with Vehicle group, Evo significantly ameliorated neurological deficit, brain water content and infarct size, upregulated the expression of pAkt, pGSK3β and claudin-5, and downregulated the nuclear accumulation of NF-κB (P < 0.05). Evo protected the brain from ischemic damage caused by pMCAO; this effect may be through upregulation of pAkt, pGSK3β and claudin-5, and downregulation of NF-κB expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan H, Li L, Zhang X, Liu Y, Yang C, Yang Y, Yin J (2009) Oxymatrine downregulates TLR4, TLR2, MyD88, and NF-kappaB and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Mediat Inflamm 2009:704–706
Pluta R, Ułamek M, Jabłoński M (2009) Alzheimer’s mechanisms in ischemic brain degeneration. Anat Rec 292:1863–1881
Xing Y, Zhang X, Zhao K, Cui L, Wang L, Dong L, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang C, Zhang X, Zhu C, Qiao H, Ji Y, Cao X (2012) Beneficial effects of sulindac in focal cerebral ischemia: a positive role in Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Brain Res 1482:71–80
Cui L, Zhang X, Yang R, Wang L, Liu L, Li M, Du W (2011) Neuroprotection and underlying mechanisms of oxymatrine in cerebral ischemia of rats. Neurol Res 33:319–324
Li L, Zhang X, Cui L, Wang L, Liu H, Ji H, Du Y (2013) Ursolic acid promotes the neuroprotection by activating Nrf2 pathway after cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res 1497:32–39
Zhu C, Zhang X, Qiao H, Wang L, Zhang X, Xing Y, Wang C, Dong L, Ji Y, Cao X (2012) The intrinsic PEDF is regulated by PPARγ in permanent focal cerebral ischemia of rat. Neurochem Res 37:2099–2107
Collino M, Aragno M, Castiglia S, Tomasinelli C, Thiemermann C, Boccuzzi G, Fantozzi R (2009) Insulin reduces cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in the hippocampus of diabetic rats: a role for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Diabetes 58:235–242
Sen P, Mukherjee S, Ray D, Raha S (2003) Involvement of the Akt/PKB signaling pathway with disease processes. Mol Cell Biochem 253:241–246
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307:1098–1101
Kelly S, Zhao H, Hua Sun G, Cheng D, Qiao Y, Luo J, Martin K, Steinberg GK, Harrison SD, Yenari MA (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta inhibitor Chir025 reduces neuronal death resulting from oxygen-glucose deprivation, glutamate excitotoxicity, and cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol 188:378–386
Zhang X, Zhang X, Wang C, Li Y, Dong L, Cui L, Wang L, Liu Z, Qiao H, Zhu C, Xing Y, Cao X, Ji Y, Zhao K (2012) Neuroprotection of early and short-time applying berberine in the acute phase of cerebral ischemia: up-regulated pAkt, pGSK and pCREB, down-regulated NF-kappaB expression, ameliorated BBB permeability. Brain Res 1459:61–70
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Kong JS, Jeong SO, Cho GJ, Ryter SW, Chung HT (2013) Carbon monoxide protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via ROS-dependent Akt signaling and inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3β. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013:306421
Malek R, Borowicz KK, Jargiello M, Czuczwar SJ (2007) Role of nuclear factor kappaB in the central nervous system. Pharmacol Rep 59:25–33
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS, Michalek SM (2005) Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat Immunol 6:777–784
Ji H, Zhang X, Du Y, Liu H, Li S, Li L (2012) Polydatin modulates inflammation by decreasing NF-kappaB activation and oxidative stress by increasing Gli1, Ptch1, SOD1 expression and ameliorates blood-brain barrier permeability for its neuroprotective effect in pMCAO rat brain. Brain Res Bull 87:50–59
Pluta R, Jabłoński M, Ułamek-Kozioł M, Kocki J, Brzozowska J, Januszewski S, Furmaga-Jabłońska W, Bogucka-Kocka A, Maciejewski R, Czuczwar SJ (2013) Sporadic Alzheimer’s disease begins as episodes of brain ischemia and ischemically dysregulated Alzheimer’s disease genes. Mol Neurobiol 48:500–515
Yi JH, Park SW, Kapadia R, Vemuganti R (2007) Role of transcription factors in mediating post-ischemic cerebral inflammation and brain damage. Neurochem Int 50:1014–1027
Zheng Z, Yenari MA (2004) Post-ischemic inflammation: mole-cular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurol Res 26:884–992
Chen L, Wang L, Zhang X, Cui L, Xing Y, Dong L, Liu Z, Li Y, Zhang X, Wang C, Bai X, Zhang J, Zhang L, Zhao X (2012) The protection by Octreotide against experimental ischemic stroke: up-regulated transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 and down-regulated NF-kappaB expression. Brain Res 1475:80–87
Schneider A, Martin-Villalba A, Weih F, Vogel J, Wirth T, Schwaninger M (1999) NF-kappaB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat Med 5:554–559
Wang L, Zhang X, Liu L, Cui L, Yang R, Li M, Du W (2010) Tanshinone II A down-regulates HMGB1, RAGE, TLR4, NF-kappaB expression, ameliorates BBB permeability and endothelial cell function, and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1321:143–151
Liu Y, Zhang XJ, Yang CH, Fan HG (2009) Oxymatrine protects rat brains against permanent focal ischemia and downregulates NF-kappaB expression. Brain Res 1268:174–180
Yuan SM, Gao K, Wang DM, Quan XZ, Liu JN, Ma CM, Qin C, Zhang LF (2011) Evodiamine improves congnitive abilities in SAMP8 and APP(swe)/PS1(DeltaE9) transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 32:295–302
Chang CP, Chang JY, Wang FY, Tseng J, Chang JG (1995) The effect of Evodia rutaecarpa extract on cytokine secretion by human mononuclear cells in vitro. Am J Chin Med 23:173–180
Lee TJ, Kim EJ, Kim S, Jung EM, Park JW, Jeong SH, Park SE, Yoo YH, Kwon TK (2006) Caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis induced by evodiamine in human leukemic U937 cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2398–2407
Rasul A, Yu B, Zhong L, Khan M, Yang H, Ma T (2012) Cytotoxic effect of evodiamine in SGC-7901 human gastric adenocarcinoma cells via simultaneous induction of apoptosis and autophagy. Oncol Rep 27:1481–1487
Wei WT, Chen H, Wang ZH, Ni ZL, Liu HB, Tong HF, Guo HC, Liu DL, Lin SZ (2012) Enhanced antitumor efficacy of gemcitabine by evodiamine on pancreatic cancer via regulating PI3 K/Akt pathway. Int J Biol Sci 8:1–14
Heo SK, Yun HJ, Yi HS, Noh EK, Park SD (2009) Evodiamine and rutaecarpine inhibit migration by LIGHT via suppression of NADPH oxidase activation. J Cell Biochem 107:123–133
Wei J, Ching LC, Zhao JF, Shyue SK, Lee HF, Kou YR, Lee TS (2013) Essential role of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 in evodiamine-mediated protection against atherosclerosis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 207:299–307
Rang WQ, Du YH, Hu CP, Ye F, Xu KP, Peng J, Deng HW, Li YJ (2004) Protective effects of evodiamine on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Planta Med 70:1140–1143
Liu YN, Pan SL, Liao CH, Huang DY, Guh JH, Peng CY, Chang YL, Teng CM (2009) Evodiamine represses hypoxia-induced inflammatory proteins expression and hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha accumulation in RAW264.7. Shock 32:263–269
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral arteryocclusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Liu Z, He D, Zhang X, Li Y, Zhu C, Dong L, Zhang X, Xing Y, Wang C, Qiao H, Chen L (2012) Neuroprotective effect of early and short-time applying sophoridine in pMCAO rat brain: down-regulated TRAF6 and up-regulated p-ERK1/2 expression, ameliorated brain infaction and edema. Brain Res Bull 88:379–384
Wang C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang X, Dong L, Xing Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Chen L, Qiao H, Wang L, Zhu C (2012) Protection by silibinin against experimental ischemic stroke: up-regulated pAkt, pmTOR, HIF-1α and Bcl-2, down-regulated Bax, NF-κB expression. Neurosci Lett 529:45–50
Tatlisumak T, Carano RA, Takano K, Opgenorth TJ, Sotak CH, Fisher M (1998) A novel endothelin antagonist, A-127722, attenuates ischemic lesion size in rats with temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion: a diffusion and perfusion MRI study. Stroke 29:850–857
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
Yang C, Zhang X, Fan H, Liu Y (2009) Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1282:133–141
Ikeda K, Negishi H, Yamori Y (2003) Antioxidant nutrients and hypoxia/ischemia brain injury in rodents. Toxicology 189:55–61
Shi J, Yan J, Lei Q, Zhao J, Chen K, Yang D, Zhao X, Zhang Y (2009) Intragastric administration of evodiamine suppresses NPY and AgRP gene expression in the hypothalamus and decreases food intake in rats. Brain Res 1247:71–78
Song G, Ouyang G, Bao S (2005) The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med 9:59–71
Grimes CA, Jope RS (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Martinez A, Castro A, Dorronsoro I, Alonso M (2002) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitors as new promising drugs for diabetes, neurodegeneration, cancer, and inflammation. Med Res Rev 22:373–384
Cohen P, Frame S (2001) The renaissance of GSK3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:769–776
Steinbrecher KA, Wilson W 3rd, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS (2005) Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta functions to specify gene-specific, NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol 25:8444–8455
Duckworth EA, Butler T, Collier L, Collier S, Pennypacker KR (2006) NF-kappaB protects neurons from ischemic injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Brain Res 1088:167–175
Nurmi A, Lindsberg PJ, Koistinaho M, Zhang W, Juettler E, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Weih F, Frank N, Schwaninger M, Koistinaho J (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35:987–991
Pluta R, Lossinsky AS, Wiśniewski HM, Mossakowski MJ (1994) Early blood-brain barrier changes in the rat following transient complete cerebral ischemia induced by cardiac arrest. Brain Res 633:41–52
Pluta R, Tomida S, Ikeda J, Nowak TS Jr, Klatzo I (1989) Cerebral vascular volume after repeated ischemic insults in the gerbil: comparison with changes in CBF and brain edema. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9:163–170
Bi X, Yan B, Fang S, Yang Y, He J, Li XM, Kong J (2009) Quetiapine regulates neurogenesis in ischemic mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB p65/p50 expression. Neurol Res 31:159–166
Yang Y, Rosenberg GA (2011) MMP-mediated disruption of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier of rat brain after cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol Biol 762:333–345
Torii H, Kubota H, Ishihara H, Suzuki M (2007) Cilostazol inhibits the redistribution of the actin cytoskeleton and junctional proteins on the blood-brain barrier under hypoxia/reoxygenation. Pharmacol Res 55:104–110
Gloor SM, Wachtel M, Bolliger MF, Ishihara H, Landmann R, Frei K (2001) Molecular and cellular permeability control at the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 36:258–264
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147:185–194
Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Andjelkovic AV (2011) Tracing the endocytosis of claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells. Methods Mol Biol 762:303–320
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81371287) and Hebei Province (Grant No. C2010000564). We thank technicians Ruichun Liu and Hongran Wu for their technical assistance and Prof. Yansu Guo M.D. PhD. and Weisong Duan M.D. PhD. for providing valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Zhang, X., Zhao, Y. et al. Pretreatment by Evodiamine is Neuroprotective in Cerebral Ischemia: Up-Regulated pAkt, pGSK3β, Down-Regulated NF-κB Expression, and Ameliorated BBB Permeability. Neurochem Res 39, 1612–1620 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1356-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1356-5