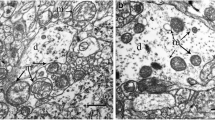
We studied correlations between the intensity of accumulation of oxidatively modified proteins and the state of the system of proteolysis in the basal nuclei (nucl. caudatus, pallidum, nucl. accumbens of the septum, and amygdala) of the rat brain after an episode of intense acute hypobaric hypoxia. We demonstrated that, the processes of protein peroxidation in the basal ganglia are intensified under the action of hypoxia in a parallel manner with increase in proteolytic activity. Accumulation of oxidized proteins is considered a factor influencing the activity of proteolysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. E. Dubinina and A. V. Pustygina, “Oxidative modification of proteins, its role in pathological states,” Ukr. Biokhim. Zh., 80, No. 6, 5-18 (2008).
L. V. Patushenkov, “Main techniques for estimate of protective action of antihypoxants in experiment and peculiarities of their influence on metabolic processes in cell,” in: Pharmacological Correction of Hypoxic States [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1989), pp. 118-124.
R. D. Sinel’nikov and Ya. R. Sinel’nikov, Atlas of Human Anatomy [in Russian], Meditsina, Moscow (1994).
V. M. Magalyas, A. O. Mikheyev, Yu. Ye. Rogovyi, et al., Modern Techniques for Experimental and Clinical Studies of the Central Scientific-Research Laboratory of the Bukovina State Medical Academy [in Ukrainian], BDMA, Chernovtsy (2001).
O. V. Goiko, Practical Use of the Software STATISTICA for the Analysis of Medico-Biological Data [in Ukrainian], Vyshcha Shkola, Kyiv (2004).
A. L. Dafre, N. S. Arteni, I. R. Siqueira, et al., “Perturbations in the thiol homeostasis following nеоnatal cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in rats,” Neurosci. Lett., 345, No. 1, 65-68 (2003).
T. Zitnanova, K. Sumegova, and M. Simko, “Protein carbonyls as a biomarker of hypoxic stress,” Clin. Biochem., 40, No. 8, 567-570 (2007).
K. N. Veremeenko, Proteolysis in the Norm and Pathology [in Russian], Zdorov’ya, Kyiv (1998).
A. I. Arakov and I. M. Mosokhoyev, “Modification of proteins by active oxygen and their dissociation,” Biokhimiya, 54, No. 2, 179-186 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sopova, I.Y. Correlations between the Amount of Oxidatively Modified Proteins and Proteolytic Activity in the Rat Basal Nuclei after Acute Hypoxia. Neurophysiology 46, 373–375 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-014-9457-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-014-9457-y