Abstract
Aim
Accumulating evidence suggests that lncRNAs are potential biomarkers and key regulators of tumor development and progression. However, the precise function of most lncRNAs in glioma remains unknown. In this study, we explored the role of long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1018 (LINC01018) in human glioma.
Methods
Expression levels of LINC01018 and miR-182-5p in clinical glioma tissues and cell lines were detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay and Transwell assay. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) related proteins were measured by Western blotting. Direct relationship between LINC01018 and miR-182-5p was tested by dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation assay (RIP), and rescue assays. Lastly, bioinformatics analyses were conducted to predict the downstream factors of LINC01018/miR-182-5p axis in glioma.
Results
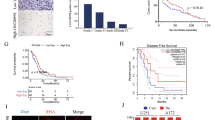
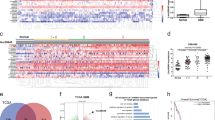
LINC01018 was significantly down-regulated in glioma tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of LINC01018 dramatically inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and reverse EMT process in glioma. LINC01018 directly target to miR-182-5p. Forced up-regulation of miR-182-5p reversed the inhibitory effects on proliferative and metastatic abilities of glioma cells with LINC01018 overexpression. Lastly, the bioinformatics analyses revealed that LINC01018/miR-182-5p axis mediated a cluster of downstream genes (ADRA2C, RAB6B, RAB27B, RAPGEF5, STEAP2, TAGLN3, and UNC13C), which were potential key factors in the development of glioma.
Conclusion
LINC01018 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in human glioma by targeting miR-182-5p, and should be considered as a potential therapeutic target in this cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Omuro A, DeAngelis LM (2013) Glioblastoma and other malignant gliomas: a clinical review. JAMA 310(17):1842–1850
Chhabda S et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumours of the Central Nervous System: what the paediatric neuroradiologist needs to know. Quant Imaging Med Surg 6(5):486–489
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507
Ahluwalia MS, Chang SM (2014) Medical therapy of gliomas. J Neurooncol 119(3):503–512
Alifieris C, Trafalis DT (2015) Glioblastoma multiforme: pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther 152:63–82
Stupp R et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136(4):629–641
Ulitsky I, Bartel DP (2013) lincRNAs: genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell 154(1):26–46
Wu H, Yang L, Chen LL (2017) The Diversity of long noncoding RNAs and their generation. Trends Genet 33(8):540–552
Gibb EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL (2011) The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer 10:38
Yang G, Lu X, Yuan L (2014) LncRNA: a link between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1839(11):1097–1109
Yan Y et al (2017) An insight into the increasing role of LncRNAs in the pathogenesis of gliomas. Front Mol Neurosci 10:53
Chandra Gupta S, Nandan Tripathi Y (2017) Potential of long non-coding RNAs in cancer patients: from biomarkers to therapeutic targets. Int J Cancer 140(9):1955–1967
Wang W et al (2020) Non-coding RNAs shuttled via exosomes reshape the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):67
Sun Z et al (2018) Emerging role of exosome-derived long non-coding RNAs in tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer 17(1):82
Wang S et al (2019) LINC01018 confers a novel tumor suppressor role in hepatocellular carcinoma through sponging microRNA-182-5p. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 317(2):G116–G126
Miao Y et al (2017) Comprehensive analysis of a novel four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for human gastric cancer. Oncotarget 8(43):75007–75024
Cerami E et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2(5):401–404
Gao J et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 6(269):pl1
Tang Z et al (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102
Li JH et al (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42(D1):D92–D97
Cavaliere R, Wen PY, Schiff D (2007) Novel therapies for malignant gliomas. Neurol Clin 25(4):1141–1171
Juratli TA, Schackert G, Krex D (2013) Current status of local therapy in malignant gliomas–a clinical review of three selected approaches. Pharmacol Ther 139(3):341–358
Zottel A et al (1842) (2020) Coding of glioblastoma progression and therapy resistance through long noncoding RNAs. Cancers 12(7):1842
Liang Q et al (2020) Profiling pro-neural to mesenchymal transition identifies a lncRNA signature in glioma. J Transl Med 18(1):378
Lee JM et al (2006) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol 172(7):973–981
Dhamija S, Diederichs S (2016) From junk to master regulators of invasion: lncRNA functions in migration EMT and metastasis. Int J Cancer 139(2):269–280
Huber MA, Kraut N, Beug H (2005) Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17(5):548–558
Lee JT (2012) Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Science 338(6113):1435–1439
Pandey RR, Kanduri C (2011) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional programming by long noncoding RNAs. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 51:1–27
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505(7483):344–352
Jiang L et al (2020) LINC01018 and SMIM25 sponged miR-182-5p in endometriosis revealed by the ceRNA network construction. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 34:2058738420976309
Zhang S et al (2020) Circular RNA SFMBT2 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of glioma cells through Mir-182-5p/Mtss1 pathway. Technol Cancer Res Treat 19:1533033820945799
Xue J et al (2016) miR-182-5p induced by STAT3 activation promotes glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 76(14):4293–4304
Wang H et al (2015) Hypomethylated Rab27b is a progression-associated prognostic biomarker of glioma regulating MMP-9 to promote invasion. Oncol Rep 34(3):1503–1509
Prasad B, Tian Y, Li X (2020) Large-scale analysis reveals gene signature for survival prediction in primary glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol 57(12):5235–5246
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
The authors thank for the financial supports from Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81902846) and Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (Grant No. 201707010380).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hu Su, Zhao Hailin and Luo Dongdong wrote the paper; Yin Jiang, Huang Shuncheng and Zhang Shun conceived the experiments; Li Dan and Peng Biao analyzed the data; Hu Su, Zhao Hailin and Luo Dongdong collected and provided the sample for this study. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.


Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Hailin, Z., Dongdong, L. et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC01018 inhibits human glioma cell proliferation and metastasis by directly targeting miRNA-182-5p. J Neurooncol 160, 67–78 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04113-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-04113-5