Abstract
Purpose
LncRNAs play essential roles in the cellular and molecular biology of glioma. Some LncRNAs exert their role through sponging miRNAs and regulating multiple signaling pathways. LINC02381 is involved in several cancer types as either oncogene or tumor suppressor. Here, we intended to find the molecular mechanisms of the LINC02381 effect during the glioma progression in related cell lines.
Methods and results
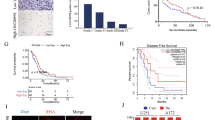
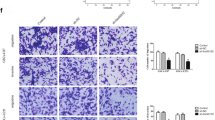
RNA-seq data analysis indicated the oncogenic characteristics of LINC02381, and RT-qPCR results confirmed its upregulation compared to normal tissues. Besides its expression was relatively stronger in invasive glioma cell lines. Furthermore, in silico analysis revealed LINC02381 is concentrated in the cytoplasm and predicted its sponging effect against miR-128 and miR-150, which was verified through dual luciferase assay. When LINC02381 was overexpressed in 1321N1, U87, and A172 cell lines, IGF1R and TrkC receptors as well as their downstream pathways (PI3K and RAS/MAPK), were upregulated, detected by RT-qPCR, and verified by western analysis. Consistently, LINC02381 overexpression was followed by an increased proliferation rate of transfected glioma cell lines, detected by flow cytometry and MTT assay, and RT-qPCR. It also resulted in elevated EMT and stemness markers expression level, increased migration rate, and reduced apoptosis rate, detected by RT-qPCR, western analysis, scratch test, and Annexin/PI flow cytometry analysis, respectively.
Conclusion
The overall results indicated that LINC02381 exerts its oncogenic effect in glioma cells through sponging miR-128 and miR-150 to upregulate the IGF1R signaling pathway. Our results introduce LINC02381 and miR-128, and miR-150 as potential prognosis and therapy targets for the treatment of glioma.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
“The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Louis DN et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131(6):803–820
Ma Q et al (2018) Cancer stem cells and immunosuppressive microenvironment in glioma. Front Immunol 9:2924
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359(5):492–507
DeSouza PA et al (2021) Long, noncoding RNA dysregulation in glioblastoma. Cancers 13(7):1604
Gao Y-F et al (2016) A critical overview of long non-coding RNA in glioma etiology 2016: an update. Tumor Biology 37(11):14403–14413
Jiang M-C et al (2019) Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic opportunities. Am J Cancer Res 9(7):1354
Yeh M et al (2021) MicroRNA-138 suppresses glioblastoma proliferation through downregulation of CD44. Sci Rep 11(1):1–11
Shan Z-N et al (2016) miR128-1 inhibits the growth of glioblastoma multiforme and glioma stem-like cells via targeting BMI1 and E2F3. Oncotarget 7(48):78813
Peng Y, Croce CM (2016) The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 1(1):1–9
Li Q et al (2016) LncRNA and mRNA expression profiles of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) reveal the potential roles of lncRNAs in GBM pathogenesis. Tumor Biol 37(11):14537–14552
Kazimierczyk M et al (2020) Human long noncoding RNA interactome: detection, characterization and function. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1027
Mu M et al (2020) LncRNA BCYRN1 inhibits glioma tumorigenesis by competitively binding with miR-619-5p to regulate CUEDC2 expression and the PTEN/AKT/p21 pathway. Oncogene 39(45):6879–6892
Li Z et al (2017) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis of glioma cells through derepressing Rap1B by sponging miR-101. J Neurooncol 134(1):19–28
Wang P et al (2015) Long non-coding RNA CASC2 suppresses malignancy in human gliomas by miR-21. Cell Signal 27(2):275–282
Kim S-H et al (2021) Long non-coding RNAs in brain tumors: roles and potential as therapeutic targets. J Hematol Oncol 14(1):1–17
Shi T et al (2020) HOTAIRM1, an enhancer lncRNA, promotes glioma proliferation by regulating long-range chromatin interactions within HOXA cluster genes. Mol Biol Rep 47(4):2723–2733
Feng W et al (2017) Up-regulation of the long non-coding RNA RMRP contributes to glioma progression and promotes glioma cell proliferation and invasion. Arch Med Sci 13(6):1315
Cai H et al (2020) LncRNA LINC00998 inhibits the malignant glioma phenotype via the CBX3-mediated c-Met/Akt/mTOR axis. Cell Death Dis 11(12):1–17
Ke J et al (2015) Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits malignant biological behaviors of human glioma cells via modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget 6(26):21934
Li Y et al (2021) LncRNA NEAT1 promotes glioma cancer progression via regulation of miR-98-5p/BZW1. Biosci Rep
Liu Z et al (2020) LncRNA H19 promotes glioma angiogenesis through miR-138/HIF-1α/VEGF axis. Neoplasma 67(1):111–118
Jia P et al (2016) Long non-coding RNA H19 regulates glioma angiogenesis and the biological behavior of glioma-associated endothelial cells by inhibiting microRNA-29a. Cancer Lett 381(2):359–369
Jafarzadeh M et al (2020) Epigenetically silenced LINC02381 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Biochimie 171:63–71
Jafarzadeh M, Soltani BM (2020) Long noncoding RNA LOC400043 (LINC02381) inhibits gastric cancer progression through regulating Wnt signaling pathway. Front Oncol 10:2189
Bian X et al (2021) ELK1-induced upregulation lncRNA LINC02381 accelerates the osteosarcoma tumorigenesis through targeting CDCA4 via sponging miR-503–5p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 548:112–119
Chen X et al (2020) LINC02381 promoted Cell viability and migration via targeting miR-133b in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Manag Res 12:3971
Sun Y, Wang X, Bu X (2021) LINC02381 contributes to cell proliferation and hinders cell apoptosis in glioma by transcriptionally enhancing CBX5. Brain Res Bull 176:121–129
Shan Y et al (2018) LncRNA SNHG7 sponges miR-216b to promote proliferation and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer through upregulating GALNT1. Cell Death Dis 9(7):1–13
Xu M et al (2019) lncRNA SNHG6 regulates EZH2 expression by sponging miR-26a/b and miR-214 in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):1–17
Salmena L et al (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146(3):353–358
Du Z, Lovly CM (2018) Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol Cancer 17(1):1–13
Zhang Q et al (2021) FoxP3-miR-150-5p/3p suppresses ovarian tumorigenesis via an IGF1R/IRS1 pathway feedback loop. Cell Death Dis 12(3):1–16
Chen P-H et al (2016) The inhibition of microRNA-128 on IGF-1-activating mTOR signaling involves in temozolomide-induced glioma cell apoptotic death. PLoS ONE 11(11):e0167096
Peruzzi F et al (1999) Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19(10):7203–7215
Guidi M et al (2010) Overexpression of miR-128 specifically inhibits the truncated isoform of NTRK3 and upregulates BCL2 in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. BMC Mol Biol 11(1):1–17
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE (2004) Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer 4(7):505–518
Huo L et al (2019) miR-128-3p inhibits glioma cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting NPTX1 through IRS-1/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 17(4):2921–2930
Huang C-Y et al (2015) miR-128-3p suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by regulating PIK3R1 and is correlated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Oncol Rep 33(6):2889–2898
Zhuang M et al (2021) LncRNA Bmp1 promotes the healing of intestinal mucosal lesions via the miR-128-3p/PHF6/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell Death Dis 12(6):1–16
Liu X et al (2020) Nanocomplexes loaded with miR-128-3p for enhancing chemotherapy effect of colorectal cancer through dual-targeting silence the activity of PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK pathway. Drug Deliv 27(1):323–333
Wu SJ et al (2018) MicroRNA-150 enhances radiosensitivity by inhibiting the AKT pathway in NK/T cell lymphoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):1–10
Zhao J, Li D, Fang L (2019) MiR-128-3p suppresses breast cancer cellular progression via targeting LIMK1. Biomed Pharmacother 115:108947
Cao X-Z, Bin H, Zang Z-N (2019) MiR-128 suppresses the growth of thyroid carcinoma by negatively regulating SPHK1. Biomed Pharmacother 109:1960–1966
Shi Z-M et al (2012) MiR-128 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting p70S6K1. PLoS ONE 7(3):e32709
Tan Z, Jia J, Jiang Y (2018) MiR-150-3p targets SP1 and suppresses the growth of glioma cells. Biosci Rep 38(3)
Lian B et al (2018) miR-128 targets the SIRT1/ROS/DR5 pathway to sensitize colorectal cancer to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 49(6):2151–2162
Han H et al (2018) miR-128 induces pancreas cancer cell apoptosis by targeting MDM4. Exp Ther Med 15(6):5017–5022
Ye Y et al (2018) MiR-128 promotes the apoptosis of glioma cells via binding to NEK2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(24):8781–8788
Shang C et al (2016) miR-128 regulates the apoptosis and proliferation of glioma cells by targeting RhoE. Oncol Lett 11(1):904–908
Gugnoni M, Ciarrocchi A (2019) Long noncoding RNA and epithelial mesenchymal transition in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 20(8):1924
Liu X et al (2016) MicroRNA-128 inhibits EMT of human osteosarcoma cells by directly targeting integrin α2. Tumor Biol 37(6):7951–7957
Zhao C et al (2020) MicroRNA-128-3p enhances the chemosensitivity of temozolomide in glioblastoma by targeting c-Met and EMT. Sci Rep 10(1):1–12
Cao D et al (2020) MiR-128 suppresses metastatic capacity by targeting metadherin in breast cancer cells. Biol Res 53(1):1–13
Hong X, Yu J-J (2019) MicroRNA-150 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion, and metastasis in prostate cancer through the TRPM4-mediated β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 316(4):C463–C480
Dai F-Q et al (2019) miR-150-5p inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis and recurrence by targeting HMGA2 and β-catenin signaling. Mol Ther-Nucleic Acids 16:675–685
Zhang PF et al (2019) LncRNA SNHG3 induces EMT and sorafenib resistance by modulating the miR-128/CD151 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Physiol 234(3):2788–2794
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the help and advice of the 4402-laboratory members at the Department of Genetics, TMU. Tehran-Iran.
Funding
This study was supported by Tarbiat Modares University and NIGEB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HN performed the experiments. HN and BMS designed the experiments. BMS and MFT supervised the study. ARJ has helped with lab work. AJ provided the tissues and pathology information. SJM advised the research.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Ethical/Scientific Committee of Tarbiat Modares University under; IR.MODARES.REC.1400.129.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nemati, H., Fakhre-Taha, M., Javanmard, AR. et al. LINC02381-ceRNA exerts its oncogenic effect through regulation of IGF1R signaling pathway in glioma. J Neurooncol 158, 1–13 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-03992-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-022-03992-y