Abstract
Purpose
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been increasingly used for elderly patients with brain metastases (BMs). However, no studies based on a large sample size have been reported. To compare SRS treatment results between elderly and non-elderly patients, we performed a subset study of elderly patients using our prospectively-accumulated multi-institution study database (JLGK0901 Study, Lancet Oncol 15:387–395, 2014).
Methods
During the 2009–2011 period, 1194 eligible patients undergoing gamma knife SRS alone for newly diagnosed BMs were enrolled in this study from 23 gamma knife facilities in Japan. Observation was discontinued at the end of 2013. The 1194 patients were divided into the two age groups, 693 elderly ( ≥ 65 years) and 501 non-elderly ( < 65 years) patients. Our study protocol neither set an upper age limit nor required dose de-escalation.
Results
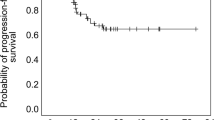
Median post-SRS survival time was significantly shorter in the elderly than in the non-elderly patient group (10.3 vs 14.3 months, HR 1.380, 95% CI 1.218–1.563, p < 0.0001). However, regarding all secondary endpoints including neurological death, neurological deterioration, SRS-related complications, leukoencephalopathy, local recurrence, newly-developed tumors, meningeal dissemination, salvage SRS, whole brain radiotherapy and surgery and decreased mini-mental state examination scores, the elderly patient group was not inferior to the non-elderly patient group. In the 693 elderly patients, there was no post-SRS median survival time difference between those with 5–10 versus 2–4 tumors (10.8 vs 8.9 months, HR 0.936, 95% CI 0.744–1.167, p = 0.5601).
Conclusions
We conclude that elderly BM patients are not unfavorable candidates for SRS alone treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, “Population Census”; Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, “Vital Statistics”; National Institute of Population and Social Security Research. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/social_security/dl/social_security6-g.pdf. Accessed 05 May 2019
Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, United Nations. https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/. Accessed 05 May 2019
Noel G, Bollet MA, Noel S et al (2005) Linac stereotactic radiosurgery: an effective and safe treatment for elderly patients with brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63:1555–1561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.04.037
Kim SH, Weil RJ, Chao ST et al (2008) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases in older patients. Cancer 113:834–840. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23625
Rades D, Pluemer A, Veninga T, Schild SE (2008) Comparison of different treatment approaches for one to two brain metastases in elderly patients. Strahlenther Onkol 184(11):565–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1908-1
Minniti G, Esposito V, Clarke E et al (2013) Stereotactic radiosurgery in elderly patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 111:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-1016-z
Watanabe S, Yamamoto M, Sato Y et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: a case-matched study comparing treatment results for patients 80 years of age versus patients 65–79 years of age. J Neurosurg 121:1148–1157. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.6.JNS132790
Park JY, Moon KS, Lee KH et al (2015) Gamma knife radiosurgery for elderly patients with brain metastases: evaluation of scoring systems that predict survival. BMC Cancer 15:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1070-y
Yomo S, Hayashi M (2016) Is upfront stereotactic radiosurgery a rational treatment option for very elderly patients with brain metastases? A retrospective analysis of 106 consecutive patients age 80 years and older. BMC Cancer 16:948. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-016-2983-9
Chen L, Shen C, Redmond KJ et al (2017) Use of stereotactic radiosurgery in elderly and very elderly patients with brain metastases to limit toxicity associated with whole brain radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98:939–947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.02.031
Randolph DM, McTyre E, Klepin H, Peiffer AM, Ayala-Peacock D, Lester S et al (2017) Impact of radiosurgical management of geriatric patients with brain metastases: Clinical and quality of life outcomes. J Radiosurg SBRT 5:35–42
Roh TH, Choi MS, You N et al (2018) Identifying candidates for gamma knife radiosurgery among elderly patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 137:559–565. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-018-2745-4
Gregucci F, Fiorentino A, Corradini S, Figlia V, Mazzola R, Ricchetti F et al (2019) Linac-based radiosurgery or fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy with flattening filter-free volumetric modulated arc therapy in elderly patients: A mono-institutional experience on 110 brain metastases. Strahlenther Onkol. 195:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-018-1405-0
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Higuchi Y et al (2017) a multi-institutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901 study update): Irradiation-related complications and long-term maintenance of mini-mental state examination scores. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 99:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.04.037
Serizawa T, Yamamoto M, Higuchi Y et al (2019) Local tumor progression treated with Gamma Knife radiosurgery: differences between patients with 2–4 versus 5–10 brain metastases based on an update of a multi-institutional prospective observational study (JLGK0901). J Neurosurg 26:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3171/2019.1.JNS183085
Shuto T, Akabane A, Yamamoto M et al (2018) Multiinstitutional prospective observational study of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer (JLGK0901 study-NSCLC). J Neurosurg 113(129):86–94. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.GKS181378
Serizawa T, Yamamoto M, Sato Y et al (2010) Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional prospective study. J Neurosurg 113(Suppl):48–52. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.8.GKS10838
Gooley TA, Leisenring W, Crowley J, Storer BE (1999) Estimation of failure probabilities in the presence of competing risks: New representations of old estimators. Stat Med 18:695–706
Fine JP, Gray RJ (1999) A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J Am Stat Assoc 94:496–509
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases. JAMA 295:2483–2491. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.1145
Lutterbach J, Bartelt S, Momm F, Becker G, Frommhold H, Ostertag C (2005) Is older age associated with a worse prognosis due to different patterns of care? A long-term study of 1346 patients with glioblastomas or brain metastases. Cancer 103:1234–1244. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.20895
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Higuchi Y et al (2018) Prognostic grading system specifically for elderly patients with brain metastases after stereotactic radiosurgery: A two-institute study. J Neurosurg 129(Suppl1):95–102. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.7.GKS181458
Nolte SM, Venugopal C, McFarlane N et al (2016) A cancer stem cell model for studying brain metastases from primary lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 105:551–562. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djt022
Chang JC. (2016) Cancer stem cells: Role in tumor growth, recurrence, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Medicine 95: e4766. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004766
Knisely JP, Yu JB, Flanigan J, Sznol M, Kluger HM, Chiang VL (2012) Radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in the ipilimumab era and the possibility of longer survival. J Neurosurg 117:227–233. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.5.JNS111929
Cohen-Inbar O, Shih HH, Xu Z, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2017) The effect of timing of stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of melanoma brain metastases treated with ipilimumab. J Neurosurg 127:1007–1014. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.9.JNS161585
Diao K, Bian SX, Routman DM et al (2018) Combination ipilimumab and radiosurgery for brain metastases: tumor, edema, and adverse radiation effects. J Neurosurg 129:1397–1406. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.7.JNS171286
Miller JA, Bennett EE, Xiao R et al (2016) Association Between radiation necrosis and tumor biology after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastasis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96:1060–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.08.039
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to all investigators of the JLGK Study Group who are not included as co-authors, as well as Ms. Yukiko Hanawa, Tokyo Gamma Unit Center, Tsukiji Neurological Clinic, for her meticulous work in managing the database. We thank Bierta E. Barfod, Katsuta Hospital Mito GammaHouse, for her help with English editing.
Funding
JPY11,000,000 the Japanese Brain Foundation (Non-governmental organization).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11060_2019_3242_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Post-stereotactic radiosurgery survival according to two age groups in the six original cancer categories; non-small cell lung cancer (upper, left), small cell lung cancer (upper, right), breast cancer (middle, left), gastro-intestinal tract cancer (middle, right), kidney cancer (lower, left) and others (lower, right). X-axis; survival fraction, Y-axis; months after stereotactic radiosurgery. Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 2855 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higuchi, Y., Yamamoto, M., Serizawa, T. et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery in elderly patients with brain metastases: comparison with non-elderly patients using database of a multi-institutional prospective observational study (JLGK0901-Elderly). J Neurooncol 144, 393–402 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03242-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03242-8