Abstract
Purpose
To challenge the prevalent pessimism regarding the outcome of patients with metastases in the brainstem resulting in the use of whole brain radiation for palliation rather than stereotactic radiosurgery for definitive control and preservation of quality of life. We present our single institution review of the efficacy and safety of treating brainstem metastases aggressively with GKRS.
Methods
Forty-one patients with 45 total lesions treated with GKRS were included. Mean age was 58.7 years, ranging from 22 to 82. Tumor volumes were objectively calculated, treatment effects assessed on imaging and clinical data collected and correlated to the radiosurgical response.
Results
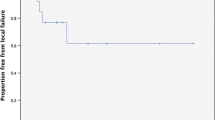
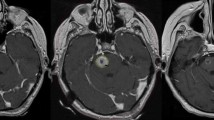
Mean survival after diagnosis of BSM was 11.6 months, ranging from 1.4 to 58.8 months. Margin dose ranged from 12 to 20 Gy. At first follow up, 11 (27%) patients had complete resolution of the treated lesion. At the second follow up 15 (37%) and third follow up 19 (46%) patients had a complete response. On average, there was a 64% decrease in tumor size at first follow up after treatment. 25 (61%) patients received WBRT in addition to radiosurgery; 16 (39%) received radiosurgery alone. There was no difference in overall survival between the two groups (p = 0.1324). ARE was seen in one patient who received 16 Gy to the margin of a 2.06 cm3 pontine tumor, but without correlative symptoms. One patient was treated with Bevacizumab® for progressive, but asymptomatic, edema following treatment that was not controlled by corticosteroids.
Conclusions
Location in brainstem should not be a deterrent to the use of radiosurgery for these patients. The addition or exclusion of WBRT should be based on the clinical progression of the patient and within the limits of this study does not seem to impact overall survival. With improved survival as a result of better systemic therapy, these patients can benefit from better preservation of cognitive function by this strategy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Adverse radiation effect(s)
- BM:
-
Brain metastasis
- BSM:
-
Brainstem metastasis
- GI:
-
Gradient Index
- GKRS:
-
Gamma Knife radio surgery
- Gy:
-
Gray
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- PCI:
-
Paddick Conformity Index
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- WBRT:
-
Whole brain radiation therapy
References
Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB (2005) Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 75(1):5–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-004-8093-6
Lin NU, Lee EQ, Aoyama H, Barani IJ, Barboriak DP, Baumert BG, Bendszus M, Brown PD, Camidge DR, Chang SM, Dancey J, de Vries EG, Gaspar LE, Harris GJ, Hodi FS, Kalkanis SN, Linskey ME, Macdonald DR, Margolin K, Mehta MP, Schiff D, Soffietti R, Suh JH, van den Bent MJ, Vogelbaum MA, Wen PY, Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology g (2015) Response assessment criteria for brain metastases: proposal from the RANO group. Lancet Oncol 16(6):e270–e278. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70057-4
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Mutani R (2002) Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 249(10):1357–1369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0870-6
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Trevisan E (2008) Brain metastases: current management and new developments. Curr Opin Oncol 20(6):676–684. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0b013e32831186fe
Cairncross JG, Kim JH, Posner JB (1980) Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Ann Neurol 7(6):529–541. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410070606
Da Silva AN, Nagayama K, Schlesinger D, Sheehan JP (2009) Early brain tumor metastasis reduction following Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg 110(3):547–552. https://doi.org/10.3171/2008.4.17537
Kim CH, Im YS, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH, Lee JI (2008) Gamma knife radiosurgery for ten or more brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 44(6):358–363. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2008.44.6.358
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB (1988) Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 45(7):741–744
Matsumoto K, Tada E, Tamesa N, Tomita S, Ohmoto T (1998) Stereotactic brachytherapy for a cystic metastatic brain tumor in the midbrain. Case report. J Neurosurg 88(1):141–144. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.88.1.0141
Baschnagel AM, Meyer KD, Chen PY, Krauss DJ, Olson RE, Pieper DR, Maitz AH, Ye H, Grills IS (2013) Tumor volume as a predictor of survival and local control in patients with brain metastases treated with Gamma Knife surgery. J Neurosurg 119(5):1139–1144. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.7.JNS13431
Patchell RA, Cirrincione C, Thaler HT, Galicich JH, Kim JH, Posner JB (1986) Single brain metastases: surgery plus radiation or radiation alone. Neurology 36(4):447–453
Patchell RA, Regine WF (2003) The rationale for adjuvant whole brain radiation therapy with radiosurgery in the treatment of single brain metastases. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2(2):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/153303460300200206
Serizawa T, Yamamoto M, Sato Y, Higuchi Y, Nagano O, Kawabe T, Matsuda S, Ono J, Saeki N, Hatano M, Hirai T (2010) Gamma Knife surgery as sole treatment for multiple brain metastases: 2-center retrospective review of 1508 cases meeting the inclusion criteria of the JLGK0901 multi-institutional prospective study. J Neurosurg 113(Suppl):48–52. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.8.GKS10838
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Sato Y, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Kenai H, Moriki A, Suzuki S, Kida Y, Iwai Y, Hayashi M, Onishi H, Gondo M, Sato M, Akimitsu T, Kubo K, Kikuchi Y, Shibasaki T, Goto T, Takanashi M, Mori Y, Takakura K, Saeki N, Kunieda E, Aoyama H, Momoshima S, Tsuchiya K (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15(4):387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70061-0
Joshi R, Johnson MD, Maitz A, Marvin KS, Olson RE, Grills IS (2016) Utility of graded prognostic assessment in evaluation of patients with brainstem metastases treated with radiosurgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 147:30–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.05.001
Jung EW, Rakowski JT, Delly F, Jagannathan J, Konski AA, Guthikonda M, Kim H, Mittal S (2013) Gamma Knife radiosurgery in the management of brainstem metastases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(10):2023–2028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2013.06.012
Kawabe T, Yamamoto M, Sato Y, Barfod BE, Urakawa Y, Kasuya H, Mineura K (2012) Gamma Knife surgery for patients with brainstem metastases. J Neurosurg 117(Suppl):23–30. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.GKS12977
Kilburn JM, Ellis TL, Lovato JF, Urbanic JJ, Bourland JD, Munley MT, Deguzman AF, McMullen KP, Shaw EG, Tatter SB, Chan MD (2014) Local control and toxicity outcomes in brainstem metastases treated with single fraction radiosurgery: is there a volume threshold for toxicity? J Neurooncol 117(1):167–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1373-x
Koyfman SA, Tendulkar RD, Chao ST, Vogelbaum MA, Barnett GH, Angelov L, Weil RJ, Neyman G, Reddy CA, Suh JH (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery for single brainstem metastases: the cleveland clinic experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 78(2):409–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.07.1750
Li Y, Xu D, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Liu D, Liu X, Wang G, Lin Y (2012) Gamma Knife surgery for brainstem metastases. J Neurosurg 117:13–16. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.GKS121020
Peterson HE, Larson EW, Fairbanks RK, MacKay AR, Lamoreaux WT, Call JA, Carlson JD, Ling BC, Demakas JJ, Cooke BS, Peressini B, Lee CM (2014) Gamma knife treatment of brainstem metastases. Int J Mol Sci 15(6):9748–9761. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15069748
Sengoz M, Kabalay IA, Tezcanli E, Peker S, Pamir N (2013) Treatment of brainstem metastases with gamma-knife radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 113(1):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1086-6
Trifiletti DM, Lee CC, Kano H, Cohen J, Janopaul-Naylor J, Alonso-Basanta M, Lee JY, Simonova G, Liscak R, Wolf A, Kvint S, Grills IS, Johnson M, Liu KD, Lin CJ, Mathieu D, Heroux F, Silva D, Sharma M, Cifarelli CP, Watson CN, Hack JD, Golfinos JG, Kondziolka D, Barnett G, Lunsford LD, Sheehan JP (2016) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: an international cooperative study to define response and toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 96(2):280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.06.009
Trifiletti DM, Lee CC, Winardi W, Patel NV, Yen CP, Larner JM, Sheehan JP (2015) Brainstem metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery: safety, efficacy, and dose response. J Neurooncol 125(2):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1927-6
Voong KR, Farnia B, Wang Q, Luo D, McAleer MF, Rao G, Guha-Thakurta N, Likhacheva A, Ghia AJ, Brown PD, Li J (2015) Gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brainstem metastases: the MD Anderson experience. Neurooncol Pract 2(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1093/nop/npu032
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J Neurosurg 93(Suppl 3):219–222. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.93.supplement
Paddick I, Lippitz B (2006) A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J Neurosurg 105:194–201. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.194
Hong T, Hayes L et al (2003) Radiosurgery: acute sequelae of stereotactic radiosurgery. Karger Publishers, Basel
Fuentes S, Delsanti C, Metellus P, Peragut JC, Grisoli F, Regis J (2006) Brainstem metastases: management using gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 58(1):37–42 (discussion 37–42)
Huang CF, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (1999) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases. J Neurosurg 91(4):563–568. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1999.91.4.0563
Hussain A, Brown PD, Stafford SL, Pollock BE (2007) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: survival, tumor control, and patient outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(2):521–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.081
Kased N, Huang K, Nakamura JL, Sahgal A, Larson DA, McDermott MW, Sneed PK (2008) Gamma knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastases: the UCSF experience. J Neurooncol 86(2):195–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-007-9458-4
Lorenzoni JG, Devriendt D, Massager N, Desmedt F, Simon S, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2009) Brain stem metastases treated with radiosurgery: prognostic factors of survival and life expectancy estimation. Surg Neurol 71(2):188–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2008.01.029 (discussion 195, 195–186)
Shuto T, Fujino H, Asada H, Inomori S, Nagano H (2003) Gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic tumours in the brain stem. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145(9):755–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-003-0034-1
Yen CP, Sheehan J, Patterson G, Steiner L (2006) Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brainstem tumors. J Neurosurg 105(2):213–219. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.105.2.213
Yoo TW, Park ES, Kwon DH, Kim CJ (2011) Gamma knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastasis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50(4):299–303. https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2011.50.4.299
Karampelas I, Podgorsak MB, Plunkett RJ, Fenstermaker RA (2008) Subthalamic nucleus metastasis causing hemichorea-hemiballism treated by gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery. Acta Neurochir 150(4):395–397
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10(11):1037–1044. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70263-3
Welzel G, Fleckenstein K, Schaefer J, Hermann B, Kraus-Tiefenbacher U, Mai SK, Wenz F (2008) Memory function before and after whole brain radiotherapy in patients with and without brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72(5):1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.03.009
Harrison G, Kano H, Lunsford LD, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D (2016) Quantitative tumor volumetric responses after Gamma Knife radiosurgery for meningiomas. J Neurosurg 124(1):146–154. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.12.JNS141341
Varma A, Nathoo N, Neyman G, Suh JH, Ross J, Park J, Barnett GH (2006) Gamma knife radiosurgery for glomus jugulare tumors: volumetric analysis in 17 patients. Neurosurgery 59(5):1030–1036. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000245596.46581.B2 (discussion 1036)
Pamir MN, Kilic T, Belirgen M, Abacioglu U, Karabekiroglu N (2007) Pituitary adenomas treated with gamma knife radiosurgery: volumetric analysis of 100 cases with minimum 3 year follow-up. Neurosurgery 61(2):270–280. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.NEU.0000255519.96837.C7 (discussion 280)
Prasad D, Steiner M, Steiner L (2000) Gamma surgery for vestibular schwannoma. J Neurosurg 92(5):745–759. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2000.92.5.0745
Feigl GC, Horstmann GA (2006) Volumetric follow up of brain metastases: a useful method to evaluate treatment outcome and predict survival after Gamma Knife surgery? J Neurosurg 105(Suppl):91–98. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.2006.105.7.91
Iyer A, Harrison G, Kano H, Weiner GM, Luther N, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D (2014) Volumetric response to radiosurgery for brain metastasis varies by cell of origin. J Neurosurg 121(3):564–569. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.4.JNS131502
Rivers C, Tranquilli M, Prasad S, Winograd E, Plunkett RJ, Fenstermaker RA, Fabiano AJ, Podgorsak MB, Prasad D (2017) Impact of the number of metastatic tumors treated by stereotactic radiosurgery on the dose to normal brain: implications for brain protection. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 95(5):352–358. https://doi.org/10.1159/000480666
Acknowledgements
The authors thank W. Fawn Dorr BA and Debra J. Zimmer for editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
DP serves as a consultant for Elekta AB, Sweden on matters unrelated to this work. All other authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers' bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required..
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winograd, E., Rivers, C.I., Fenstermaker, R. et al. The case for radiosurgery for brainstem metastases. J Neurooncol 143, 585–595 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03195-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03195-y