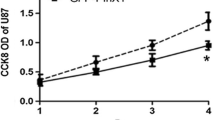
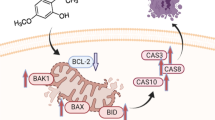
Abstract
Plumbagin, a natural quinonoid constituent isolated from the root of medicinal plant Plumbago zeylanica L, has exhibited anti-tumor and anti-proliferative activities in various tumor cell lines as well as in animal tumor models. However, its anticancer effects and the mechanisms underlying its suppression of glioma cell growth have not been elucidated. Oncogenic transcription factor Forkhead Box M1 (FOXM1) has garnered particular interest in recent years as a potential target for the prevention and/or therapeutic intervention in glioma, nevertheless, less information is currently available regarding FOXM1 inhibitor. Here, we reported that plumbagin could effectively inhibit cell proliferation, migration and invasion and induce apoptosis of glioma cells. Cell cycle assay showed that plumbagin induced G2/M arrest. Interestingly, we found that plumbagin decreased the expression of FOXM1 both at mRNA level and protein level. Plumbagin also inhibited the transactivation ability of FOXM1, resulting in down-regulating the expression of FOXM1 downstream target genes, such as cyclin D1, Cdc25B, survivin, and increasing the expression of p21CIP1 and p27KIP1. Most importantly, down-regulation of FOXM1 by siFOXM1 transfection enhanced plumbagin-induced change in viability. On the contrary, over-expression of FOXM1 by cDNA transfection reduced plumbagin-induced glioma cell growth inhibition. These results suggest that plumbagin exhibits its anticancer activity partially by inactivation of FOXM1 signaling pathway in glioma cells. Our findings indicate that plumbagin may be considered as a potential natural FOXM1 inhibitor, which could contribute to the development of new anticancer agent for therapy of gliomas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Onishi M, Ichikawa T, Kurozumi K, Date I (2011) Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain tumor pathology 28(1):13–24
Kim CS, Jung S, Jung TY, Jang WY, Sun HS, Ryu HH (2011) Characterization of invading glioma cells using molecular analysis of leading-edge tissue. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 50(3):157–165
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes DE, Ackerson T, Major ML, Kalinichenko VV, Costa RH, Raychaudhuri P, Tyner AL, Lau LF (2008) FoxM1 regulates transcription of JNK1 to promote the G(1)/S transition and tumor cell invasiveness. J Biol Chem 283(30):20770–20778
Wang XH, Krupczak-Hollis K, Tan YJ, Dennewitz MB, Adami GR, Costa RH (2002) Increased hepatic forkhead box M1B (FoxM1B) levels in old-aged mice stimulated liver regeneration through diminished p27(KiP1) protein levels and increased Cdc25B expression. J Biol Chem 277(46):44310–44316
Liu MG, Dai BB, Kang SH, Ban KC, Huang FJ, Lang FF, Aldape KD, Xie TX, Pelloski CE, Xie KP, Sawaya R, Huang SY (2006) FoxM1B is overexpressed in human glioblastomas and critically regulates the tumorigenicity of glioma cells. Cancer Res 66(7):3593–3602
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT, Colman H, Huang H, Xue J, Liu M, Wang Y, Sawaya R, Xie K, Yung WK, Medema RH, He X, Huang S (2011) FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 20(4):427–442
Zhang N, Wu XJ, Yang LX, Xiao FZ, Zhang H, Zhou AD, Huang ZS, Huang SY (2012) FoxM1 inhibition sensitizes resistant glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by downregulating the expression of DNA-repair gene Rad51. Clin Cancer Res 18(21):5961–5971
Bhattacharya A, Jindal B, Singh P, Datta A, Panda D (2013) Plumbagin inhibits cytokinesis in bacillus subtilis by inhibiting FtsZ assembly–a mechanistic study of its antibacterial activity. FEBS J 280(18):4585–4599
Checker R, Sharma D, Sandur SK, Subrahmanyam G, Krishnan S, Poduval TB, Sainis KB (2010) Plumbagin inhibits proliferative and inflammatory responses of T cells independent of ROS generation but by modulating intracellular thiols. J Cell Biochem 110(5):1082–1093
Kawiak A, Zawacka-Pankau J, Lojkowska E (2012) Plumbagin induces apoptosis in Her2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through the mitochondrial-mediated pathway. J Nat Prod 75(4):747–751
Li J, Shen L, Lu FR, Qin Y, Chen R, Li J, Li Y, Zhan HZ, He YQ (2012) Plumbagin inhibits cell growth and potentiates apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells in vitro through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 33(2):242–249
Sinha S, Pal K, Elkhanany A, Dutta S, Cao Y, Mondal G, Iyer S, Somasundaram V, Couch FJ, Shridhar V, Bhattacharya R, Mukhopadhyay D, Srinivas P (2013) Plumbagin inhibits tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer cells in vivo. Int j cancer J int du cancer 132(5):1201–1212
Kuo PL, Hsu YL, Cho CY (2006) Plumbagin induces G2-M arrest and autophagy by inhibiting the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in breast cancer cells. Mole cancer ther 5(12):3209–3221
Shih YW, Lee YC, Wu PF, Lee YB, Chiang TA (2009) Plumbagin inhibits invasion and migration of liver cancer HepG2 cells by decreasing productions of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and urokinase- plasminogen activator. Hepato res: off j Jpn Soc Hepatol 39(10):998–1009
Manu KA, Shanmugam MK, Rajendran P, Li F, Ramachandran L, Hay HS, Kannaiyan R, Swamy SN, Vali S, Kapoor S, Ramesh B, Bist P, Koay ES, Lim LH, Ahn KS, Kumar AP, Sethi G (2011) Plumbagin inhibits invasion and migration of breast and gastric cancer cells by downregulating the expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4. Mole cancer 10:107
Xu KH, Lu DP (2010) Plumbagin induces ROS-mediated apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia cells in vivo. Leuk Res 34(5):658–665
Sullivan C, Liu YH, Shen JJ, Curtis A, Newman C, Hock JM, Li X (2012) Novel interactions between FOXM1 and CDC25A regulate the cell cycle. PLoS ONE 7(12):e51277
Zhou X, Hua L, Zhang W, Zhu M, Shi Q, Li F, Zhang L, Song C, Yu R (2012) FRK controls migration and invasion of human glioma cells by regulating JNK/c-Jun signaling. J neuro-oncol 110(1):9–19
Zhou X, Zhan W, Bian W, Hua L, Shi Q, Xie S, Yang D, Li Y, Zhang X, Liu G, Yu R (2013) GOLPH3 regulates the migration and invasion of glioma cells though RhoA. Biochem biophys res commun 433(3):338–344
Zhou XP, Xu XB, Meng QM, Hu JX, Zhi TL, Shi Q, Yu RT (2013) Bex2 is critical for migration and invasion in malignant glioma cells. J Mol Neurosci 50(1):78–87
Lam (2009) FoxM1 is a downstream target and marker of HER2 overexpression in breast cancer. Int J Oncol 35(01):57
Wang CC, Chiang YM, Sung SC, Hsu YL, Chang JK, Kuo PL (2008) Plumbagin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through reactive oxygen species/c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathways in human melanoma A375.S2 cells. Cancer Lett 259(1):82–98
Qiu JX, He YQ, Wang Y, Xu RL, Qin Y, Shen X, Zhou SF, Mao ZF (2013) Plumbagin induces the apoptosis of human tongue carcinoma cells through the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Med sci monit basic res 19:228–236
Xu TP, Shen H, Liu LX, Shu YQ (2013) Plumbagin from plumbago Zeylanica L induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines through NF-kappa B inactivation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(4):2325–2331
Dai B, Kang SH, Gong W, Liu M, Aldape KD, Sawaya R, Huang S (2007) Aberrant FoxM1B expression increases matrix metalloproteinase-2 transcription and enhances the invasion of glioma cells. Oncogene 26(42):6212–6219
Down CF, Millour J, Lam EWF, Watson RJ (2012) Binding of FoxM1 to G2/M gene promoters is dependent upon B-Myb. Bba Gene Regul Mech 1819:855–862
Schuller U, Zhao Q, Godinho SA, Heine VM, Medema RH, Pellman D, Rowitch DH (2007) Forkhead transcription factor FoxM1 regulates mitotic entry and prevents spindle defects in cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Mol Cell Biol 27(23):8259–8270
Chen X, Muller GA, Quaas M, Fischer M, Han N, Stutchbury B, Sharrocks AD, Engeland K (2013) The forkhead transcription factor FOXM1 controls cell cycle-dependent gene expression through an atypical chromatin binding mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 33(2):227–236
Pilarsky C, Wenzig M, Specht T, Saeger HD, Grutzmann R (2004) Identification and validation of commonly overexpressed genes in solid tumors by comparison of microarray data. Neoplasia 6(6):744–750
McGovern UB, Francis RE, Peck B, Guest SK, Wang J, Myatt SS, Krol J, Kwok JMM, Polychronis A, Coombes RC, Lam EWF (2009) Gefitinib (Iressa) represses FOXM1 expression via FOXO3a in breast cancer. Mol cancer therapeutics 8(3):582–591
Radhakrishnan SK, Rhat UG, Hughes DE, Wang IC, Costa RH, Gartel AL (2006) Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box M1. Cancer Res 66(19):9731–9735
Bhat UG, Halasi M, Gartel AL (2009) FoxM1 is a general target for proteasome inhibitors. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6593
Zhou BBS, Bartek J (2004) Targeting the checkpoint kinases: chemosensitization versus chemoprotection. Nat Rev Cancer 4(3):216–225
Lian FR, Sarkar FH (1998) Genistein-induced G2-M arrest, P21(WAF1) up-regulation and apoptosis in a non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line. FASEB J 12(8):A1340–A1340
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81402074; 81472345; 81400167);Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu province (No. BK20140224; No. BK20140227);Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 14KJB320022).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xuejiao Liu and Wei Cai have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Cai, W., Niu, M. et al. Plumbagin induces growth inhibition of human glioma cells by downregulating the expression and activity of FOXM1. J Neurooncol 121, 469–477 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1664-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1664-2