Abstract
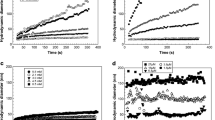
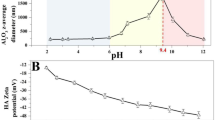
SiO2-engineered nanoparticles (SiO2-ENPs) are one of the most commonly employed nanomaterials. There was a lack of research on the comprehensive effects of environmental factors on the stability of SiO2-ENPs. In the present work, the aggregation size, surface charge, and percentage of nanoparticles have been studied under the presence of monovalent/divalent cations combined with natural organic matter (NOM), in an effort to provide a comprehensive investigation of the stability of SiO2-ENPs in complex environmental conditions. Results show that NOM adsorbed to the particles and made their zeta potential more negative, hence stabilizing them by electrostatic repulsion, and the stability of nano-SiO2 in NOM solutions follows the order of pH 9 > pH 7 > pH 5. In addition, SiO2-ENPs size in solutions with humic acid (HA) was larger than that with fulvic acid (FA). The aggregation of SiO2-ENPs enhanced with the increase of cation concentrations, and divalent cations (Ca2+) show stronger influence on SiO2-ENPs aggregate than monovalent cations. Divalent cations partially neutralized the adsorbed organic matter, and aggregation was enhanced with Ca2+, suggesting the presence of specific Ca2+-NOM bridges. The aggregation of SiO2-ENPs in electrolyte (CaCl2 or NaCl) and CaCl2 + NOM solutions follows in the order of pH 5~pH 9 > pH 7, showing that weakly acidic or alkaline conditions are not favorable for the stability of SiO2-ENPs in complex environmental systems.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sari Erkan H, Bakaraki Turan N, Onkal Engin G, Bilgili MS (2021) A review of advantages and challenges of using engineered nanoparticles for waste and wastewater treatments. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18(10):3295–3306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03054-8
Liu HQ, Hu DC, Chen XJ, Ma WS (2021) Surface engineering of nanoparticles for highly efficient UV-shielding composites. Polym Adv Technol 32(1):6–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5081
Alhumaidi MS, Arshad F, Aubry C, Ravaux F, McElhinney J, Hasan A, Zou L (2020) Electrostatically coupled SiO2 nanoparticles/poly (L-DOPA) antifouling coating on a nanofiltration membrane. Nanotechnol 31(27):275602. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ab8085
Anjum M, Miandad R, Waqas M, Gehany F, Barakat M (2019) Remediation of wastewater using various nano-materials. Arabian J Chem 12(8):4897–4919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.10.004
Cerbu C, Kah M, White JC, Astete CE, Sabliov CM (2021) Fate of biodegradable engineered nanoparticles used in veterinary medicine as delivery systems from a one health perspective. Molecules 26(523):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030523
Besha AT, Liu Y, Bekele DN, Dong Z, Naidu R, Gebremariam GN (2020) Sustainability and environmental ethics for the application of engineered nanoparticles. Environ Sci Policy 103:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2019.10.013
Xia H, Zhang WJ, Yang ZJ, Dai ZX (2021) Yang YS (2021) Spectrophotometric determination of p-nitrophenol under ENP interference. J Anal Methods Chem 1:6682722. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6682722
Abbas Q, Yousaf B, Amina AMU, Munir MAM, El-Naggar A, Rinklebe J, Naushad M (2020) Transformation pathways and fate of engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) in distinct interactive environmental compartments: a review. Environ Int 138:105646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105646
Arshad A, Iqbal J, Mansoor Q, Ahmed I (2017) Graphene/SiO2 nanocomposites: The enhancement of photocatalytic and biomedical activity of SiO2 nanoparticles by graphene. J Appl Phys 121:244901. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4979968
Xin XC, Wang YX, Meng ZJ, Yan FY (2021) SiO2 modified graphene oxide hybrids for improving fretting wear performance of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Ind Lubr Tribol 73(2):201–206. https://doi.org/10.1108/ILT-10-2020-0383
Sivakumar R, Gopalakrishnan P, Abdul Razak MS (2022) Comparative analysis of anti-reflection coatings on solar PV cells through TiO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles. Pigm Resin Technol 51(2):171–177. https://doi.org/10.1108/PRT-08-2020-0084
Kaushik S, Djiwanti SR, Skotti E (2019) Single-particle inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for characterization of engineered nanoparticles. Microb Nanobio 13–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16534-5_2
Zuin S, Gaiani M, Ferrari A, Golanski L (2013) Leaching of nanoparticles from experimental water-borne paints under laboratory test conditions. J Nanopart Res 16(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2185-1
Al-Kattan A, Wichser A, Vonbank R, Brunner S, Ulrich A, Zuin S, Arroyo Y, Golanski L, Nowack B (2015) Characterization of materials released into water from paint containing nano-SiO2. Chemosphere 119:1314–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.005
Arvidsson R, Hansen SF, Baun A (2020) Influence of natural organic matter on the aquatic ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles: recommendations for environmental risk assessment. NanoImpact 100263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.impact.2020.100263
Huangfu XL, Xu YH, Liu CH, He Q, Ma J, Ma CX, Huang RX (2019) A review on the interactions between engineered nanoparticles with extracellular and intracellular polymeric substances from wastewater treatment aggregates. Chemosphere 766–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.044
Liang L, Luo L, Zhang SZ (2011) Adsorption and desorption of humic and fulvic acids on SiO2 particles at nano and micro-scales. Colloids Surf, A 384:126–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.03.045
Singh R, Patel K, Tripathi I (2021) Interaction of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with plants in agro-ecosystems. Plant Microbes Eng Nanopart Nexus Agroecosyst 49–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66956-0_4
Yamakata A, Junie Jhon MV (2019) Curious behaviors of photogenerated electrons and holes at the defects on anatase, rutile, and brookite TiO2 powders: a review. J Photochem Photobiol, C 40:234–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2018.12.001
Jonathan SH, Erwin K, Nicolás AM, Patricia PG, Alejandra J, Roland B, Mora MdLL (2021) Describing phosphorus sorption processes on volcanic soil in the presence of copper or silver engineered nanoparticles. Minerals 11(4):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/min11040373
Ma R, Zhang S, Wen T, Gu P, Li L, Zhao G, Niu F, Huang Q, Tang Z, Wang X (2019) A critical review on visible-light-response CeO2-based photocatalysts with enhanced photooxidation of organic pollutants. Catal Today 335:20–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.11.016
Choi J, Zhang Q, Reipa V, Wang NS, Stratmeyer ME, Hitchins VM, Goering PL (2009) Comparison of cytotoxic and inflammatory responses of photoluminescent silicon nanoparticles with silicon micron-sized particles in RAW 2647 macrophages. J Appl Toxicol 29(1):52–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.1382
Fujioka K, Hiruoka M, Sato K, Manabe N, Hoshino A, Hirakuri K, Yamamoto K (2008) Evidence-based toxicity of probes. Colloidal quantum dots for biomedical applications III, Proc SPIE 6866:686613
O’Farrell N, Houlton A, Horrocks BR (2006) Silicon nanoparticles: applications in cell biology and medicine. Int J Nanomed 1(4):451–472. https://doi.org/10.2147/nano.2006.1.4.451
Vakurov A, Drummond-Brydson R, Ugwumsinachi O, Nelson A (2016) Significance of particle size and charge capacity in TiO2 nanoparticle-lipid interactions. J Colloid Interface Sci 473:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.03.045
Liu X, Wazne M, Chou T, Xiao R, Xu S (2011) Influence of Ca(2+) and Suwannee River humic acid on aggregation of silicon nanoparticles in aqueous media. Water Res 45(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.022
Xue N, Wang X, Zhang F, Wang Y, Chu Y, Zheng Y (2016) Effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on the removal of natural organic matter (NOM) by coagulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(12):11835–11844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6299-8
Jin Y, Jin X, Yang D, Mao X (2019) Controlling factors of surface water ionic composition characteristics in the lake genggahai catchment, NE Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. China Water 11(7):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11071329
Zeng C, Nguyen C, Boitano S, Field JA, Shadman F, Sierra-Alvarez R (2021) Toxicity of abrasive nanoparticles (SiO2, CeO2, and Al2O3) on Aliivibrio fischeri and human bronchial epithelial cells (16HBE14o-). J Nanopart Res 23(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05163-y
Ghoto K, Simon M, Shen ZJ, Gao GF, Li PF, Li H, Zheng HL (2020) Physiological and root exudation response of maize seedlings to TiO2 and SiO2 nanoparticles exposure. BioNanoSci 10(2):473–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-020-00724-2
Zhu M, Wang HT, Keller AA, Wang T, Li FT (2014) The effect of humic acid on the aggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles under different pH and ionic strengths. Sci Total Environ 487:375–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.04.036
Bhatnagar A, Sillanpaa M (2017) Removal of natural organic matter (NOM) and its constituents from water by adsorption – a review. Chemosphere 166:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.098
Hu XJ, Liu YG, Zeng GM, You SH, Wang H, Hu X (2014) Effects of background electrolytes and ionic strength on enrichment of Cd(ii) ions with magnetic graphene oxide-supported sulfanilic acid. J Colloid Interface Sci 435(435C):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.08.054
Thio BJ, Zhou D, Keller AA (2011) Influence of natural organic matter on the aggregation and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 189(1–2):556–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.02.072
Besha AT, Liu Y, Fang C, Bekele DN, Naidu R (2020) Assessing the interactions between micropollutants and nanoparticles in engineered and natural aquatic environments. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50(2):135–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1629799
Godinez IG, Darnault CJ (2011) Aggregation and transport of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: effects of pH, surfactants and flow velocity. Water Res 45(2):839–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.09.013
Lee J, Bartelt-Hunt SL, Li Y, Gilrein EJ (2016) The influence of ionic strength and organic compounds on nanoparticle TiO2 (n-TiO2) aggregation. Chemosphere 154:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.059
Weng L, Van Riemsdijk WH, Koopal LK, Hiemstra T (2006) Adsorption of humic substances on goethite: comparison between humic acids and fulvic acids. Environ Sci Technol 40(24):7494–7500. https://doi.org/10.1021/es060777d
De Wit JCM, Van Riemsdijk WH, Koopal LK (1993) Proton binding to humic substances. 1 Electrostatic effects. Environ Sci Technol 27:2005–2014. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00047a004
Praetorius A, Labille J, Scheringer M, Thill A, Hungerbühler K, Bottero JY (2014) Heteroaggregation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles with model natural colloids under environmentally relevant conditions. Environ Sci Technol 48(18):10690–10698. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5016555v
Stankus DP, Lohse SE, Hutchison JE, Nason JA (2010) Interactions between natural organic matter and gold nanoparticles stabilized with different organic capping agents. Environ Sci Technol 45(8):3238–3244. https://doi.org/10.1021/es102603p
Baalousha M, Nur Y, Romer I, Tejamaya M, Lead JR (2013) Effect of monovalent and divalent cations, anions and fulvic acid on aggregation of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles. Sci Total Environ 454–455:119–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.02.093
Loosli F, Le CP, Stoll S (2015) Effect of electrolyte valency, alginate concentration and pH on engineered TiO2 nanoparticle stability in aqueous solution. Sci Total Environ 535:28–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.037
Romanello MB, Fidalgo de Cortalezzi MM (2013) An experimental study on the aggregation of TiO2 nanoparticles under environmentally relevant conditions. Water Res 47(12):3887–3898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.061
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Westerhoff P, Crittenden J (2009) Impact of natural organic matter and divalent cations on the stability of aqueous nanoparticles. Water Res 43(17):4249–4257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.005
Ottofuelling S, Von der Kammer F, Hofmann T (2011) Commercial titanium dioxide nanoparticles in both natural and synthetic water: comprehensive multidimensional testing and prediction of aggregation behavior. Environ Sci Technol 45(23):10045–10052. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2023225
Baalousha M (2009) Aggregation and disaggregation of iron oxide nanoparticles: influence of particle concentration, pH and natural organic matter. Sci Total Environ 407(6):2093–2101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.022
Erhayem M, Sohn M (2014) Stability studies for titanium dioxide nanoparticles upon adsorption of Suwannee River humic and fulvic acids and natural organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 468–469:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.038
Yang K, Lin D, Xing B (2009) Interactions of humic acid with nanosized inorganic oxides. Langmuir 25(6):3571–3576. https://doi.org/10.1021/la803701b
Funding
This work was supported by Construction of High Level Teaching Teams in Universities of Beijing-the Youth Top-Notch Talent Cultivation Program (CIT&TCD201804051), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51508017), and the Youth Beijing Scholars program (NO.024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Du, X., Wang, M. et al. Stability of SiO2 nanoparticles with complex environmental conditions with the presence of electrolyte and NOM. J Nanopart Res 24, 187 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05555-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-022-05555-8