Abstract
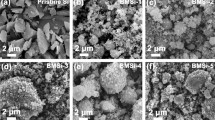
Silicon waste from industrial cutting silicon rod process is assessed as an anode for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) to expand utilization of silicon waste and effectively reduce the cost. However, it is still a big challenge to achieve a large-scale and green-effective manufacture. Hence, it is important to propose a facile, low-cost, and scalable method which prepares porous silicon as an anode by chemical etching of silicon waste using acid and alkaline solution. The silicon etched by HF solution possesses porous structure, which exhibits higher capacity than unetched samples. Comparatively, the silicon etched by NaOH solution has the flaky shape with about 110 nm and shows superior cycling performance and stability (600.7 mAh g−1 after 200 cycles at 420 mA g−1), which can be ascribed to its abundant porous structure, as well as the amorphous SiOx layer accommodating the volume expansion of embedded Si. The silicon waste modified by scalable etching reveals greatly enhanced electrochemical properties for LIB anodes. It is a promising method of improving the electrochemical properties of porous Si anode materials for commercial LIBs.
Graphical abstract
The two kinds of porous silicon were cleverly fabricated using KL-Si through facile ball-milling and chemical etching. H-Si owns the high initial coulombic efficiency and reversible capacity at lower current density. However, N-Si exhibits the superior cycling stability, which can be attributed to larger specific area and the SiOx layer to buffer enormous volume expansion of Si during discharge/charge process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen XH, Tian ZY, Fan RJ, Shao L, Zhang DP, Cao GL, Kou L, Bai YZ (2018) Research progress on silicon/carbon composite anode materials for lithium-ion battery. J Energy Chem 27:1067–1090
Kwak H, Park KH, Han D, Nam KW, Kim H, Jung YS (2020) Li+ conduction in air-stable Sb-substituted Li4SnS4 for all-solid-state Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 446:227338
Ao LY, Wu C, Xu YN, Wang X, Jiang K, Shang LY, Li YW, Zhang JZ, Hu ZG, Chu JH (2020) A novel Sn particles coated composite of SnOx/ZnO and N-doped carbon nanofibers as high-capacity and cycle-stable anode for lithium-ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 819:153036
Park MG, Lee DH, Jung H, Choi JH, Park CM (2018) Sn-based nanocomposite for Li-ion battery anode with high energy density, rate capability, and reversibility. ACS Nano 12:2955–2967
Mu TS, Shen BC, Lou SF, Zhang ZG, Ren Y, Zhou XM, Zuo PJ, Du CY, Ma YL, Huo H, Yin GP (2019) Scalable mesoporous silicon microparticles composed of interconnected nanoplates for superior lithium storage. Chem Eng J 375:121923
Guo WL, Yan X, Hou F, Wen L, Dai YJ, Yang DM, Jiang XT, Liu J, Liang J, Dou SX (2019) Flexible and free-standing SiOx/CNT composite films for high capacity and durable lithium ion batteries. Carbon 152:888–897
Liu N, Wu H, McDowell MT, Yao Y, Wang CM, Cui Y (2012) A yolk-shell design for stabilized and scalable Li-ion battery alloy anodes. Nano Lett 12:3315–3321
Choi SJ, Kim MC, Moon SH, Lee JE, Shin YK, Kim ES, Park KW (2018) 3D yolk–shell Si@void@CNF nanostructured electrodes with improved electrochemical performance for lithium-ion batteries. J Ind Eng Chem 64:344–351
Liang K, Yang HL, Guo WX, Du JL, Tian LY, Wen XF (2018) Facile preparation of nanoscale silicon as an anode material for lithium ion batteries by a mild temperature metathesis route. J Alloys Compd 735:441–444
Pan L, Wang HB, Gao DC, Chen SY, Tan L, Li L (2014) Facile synthesis of yolk–shell structured Si–C nanocomposites as anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Commun 50:5878–5880
Wu J, Anderson C, Beaupre P, Xu SW, Jin CR, Sharma A (2019a) Co-axial fibrous silicon asymmetric membranes for high-capacity lithium-ion battery anode. J Appl Electrochem 49:1013–1025
Han X, Zhang ZQ, Chen HX, You R, Zheng GR, Zhang QB, Wang JY, Li C, Chen SY, Yang Y (2019) Double-shelled microscale porous Si anodes for stable lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 436:226794
Sohna M, Kima D, Parka H, Kimb J, Kim H (2016) Porous silicon-carbon composite materials engineered by simultaneous alkaline etching for high-capacity lithium storage anodes. Electrochim Acta 196:197–205
Wang K, Pei SE, He ZS, Huang LA, Zhu SS, Guo JF, Shao HB, Wang JM (2019a) Synthesis of a novel porous silicon microsphere@carbon core-shell composite via in situ MOF coating for lithium ion battery anodes. Chem Eng J 356:272–281
Wang F, Sun L, Zi WW, Zhao BX, Du HB (2019b) Solution synthesis of porous silicon particles as an anode material for lithium ion batteries. Chem Eur J 25:9071–9077
Kong XZ, Zheng YC, Wang YP, Liang SQ, Cao GZ, Pan AQ (2019) Necklace-like Si@C nanofibers as robust anode materials for high performance lithium ion batteries. Sci Bull 64:261–269
Hua QQ, Dai DY, Zhang CZ, Han F, Lv TZ, Li XS, Wang SJ, Zhu R, Liao HJ, Zhang SG (2018) Transformation of sludge Si to nano-Si/SiOx structure by oxygen inward diffusion as precursor for high performance anodes in lithium ion batteries. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:134
Wang K, Xue B, Tan Y, Sun JM, Li QL, Shi S, Li PT (2019) Recycling of micron-sized Si powder waste from diamond wire cutting and its application in Li-ion battery anodes. J. Clean. Prod. 239:117997
He Q, Yu J, Wang YH, Zhong ZY, Jiang JX, Su FB (2018) Silicon nanoparticles prepared from industrial wastes as high-performing anode materials for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Ion 325:141–147
Huang TY, Selvaraj B, Lin HY, Sheu HS, Song YF, Wang CC, Hwang BJ, Wu NL (2016) Exploring an interesting Si source from photovoltaic industry waste and engineering it as a Li-ion battery high-capacity anode. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:5769–5775
Lee SJ, Kim HJ, Hwang TH, Choi SH, Park SH, Deniz E, Jung DS, Choi JW (2017) Delicate structural control of Si-SiOx-C composite via high-speed spray pyrolysis for Li-ion battery anodes. Nano Lett 17:1870–1876
Weng W, Lin HJ, Chen XL, Ren J, Zhang ZT, Qiu LB, Guan GZ, Peng HS (2014) Flexible and stable lithium ion batteries based on three-dimensional aligned carbon nanotube/silicon hybrid electrodes. J Mater Chem A 2:9306–9312
Hassan FM, Chabot V, Elsayed AR, Xiao X, Chen Z (2014) Engineered Si electrode nanoarchitecture: a scalable postfabrication treatment for the production of nextgeneration Li-ion batteries. Nano Lett 14:277–283
Han X, Chen HX, Liu JJ, Liu HH, Wang P, Huang K, Li C, Chen SY, Yang Y (2015) A peanut shell inspired scalable synthesis of three-dimensional carbon coated porous silicon particles as an anode for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 156:11–19
Mohiddon MA, Krishna MG (2013) Crystallite size and film–substrate interface mediated structural evolution of silicon thin films. J Phys Chem Solids 74:1249–1253
Zhang Liya, Zhang Li, Zhang Juan, Hao Weiwei, Zheng Honghe (2015) Robust polymeric coating enables the stable operation of silicon micro-plate anodes recovered from photovoltaic industry waste for high-performance Li-ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 3:15432–15443
Zhang L, Rajagopalan R, Guo HP, Hu XL, Dou SX, Liu HK (2016) A green and facile way to prepare granadilla-like silicon-based anode materials for Li-ion batteries. Adv Funct Mater 26:440–446
Kim HJ, Kim JS, Song SW (2019) Uniform distribution of siloxane-grafted SiOx nanoparticles in micron hard-carbon matrix for high-rate composite anode in Li-ion batteries. J Solid State Chem 270:479–486
Li B, Li SX, Jin Y, Zai JT, Chen M, Nazakat A, Zhan P, Huang Y, Qian XF (2018) Porous Si@C ball-in-ball hollow spheres for lithium-ion capacitors with improved energy and power densities. J Mater Chem A 6:21098–21103
Cai Y, Huang Y, Jia W, Wang X, Guo Y, Jia D, Sun Z, Pang W, Guo Z (2016) Super high-rate, long cycle life of europium-modified, carbon-coated, hierarchical mesoporous lithium-titanate anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Mater Chem A 4:9949–9957
Wu G, Ding ZP, Mu DB, Wu BR, Bi JY, Zang L, Yang H, Wu HF, Wu F (2019b) Hierarchical void structured Si/PANi/C hybrid anode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 300:341–348
Tang H, Zhang J, Zhang YJ, Xiong QQ, Tong YY, Li Y, Wang XL, Gu CD, Tu JP (2015) Porous reduced graphene oxide sheet wrapped silicon composite fabricated by steam etching for lithium-ion battery application. J Power Sources 286:431–437
Choi S, Jung DS, Choi JW (2014) Scalable fracture-free SiOC glass coating for robust silicon nanoparticle anodes in lithium secondary batteries. Nano Lett 14:7120–7125
Park MS, Park E, Lee J, Jeong G, Kim KJ, Kim JH, Kim YJ, Kim H (2014) Hydrogen silsequioxane-derived Si/SiOx nanospheres for high-capacity lithium storage materials. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:9608–9613
Hwang J, Kim K, Jung WS, Choi H, Kim JH (2019) Facile and scalable synthesis of SiOx materials for Li-ion negative electrodes. J Power Sources 436:226883
Majeed MK, Ma GY, Cao YX, Mao HZ, Ma XJ, Ma WZ (2019) Metal-organic frameworks-derived mesoporous Si/SiOx@NC nanospheres as a long-lifespan anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Eur J 25:11991–11997
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 51672235 and 51902277), the National Ten Thousand Program (2017), Science and Technology Talents Training Project of Urumqi, and the Xinjiang Tianchi Doctoral Project (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, T., Gao, Y., Tang, Y. et al. Porous silicon from industrial waste engineered for superior stability lithium-ion battery anodes. J Nanopart Res 23, 209 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05280-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-021-05280-8